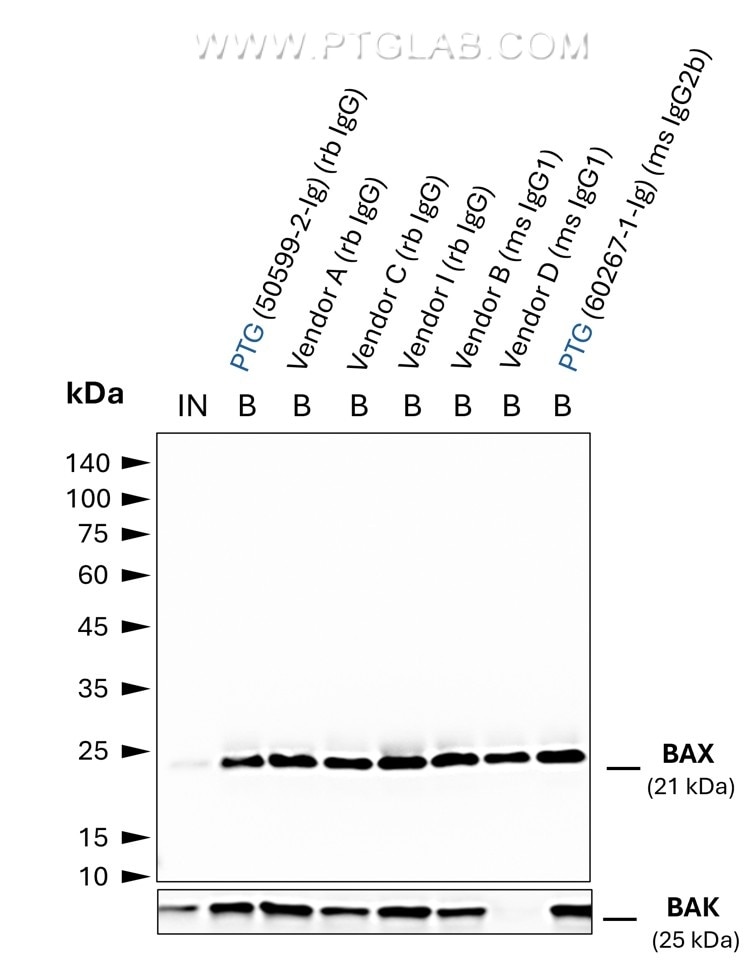
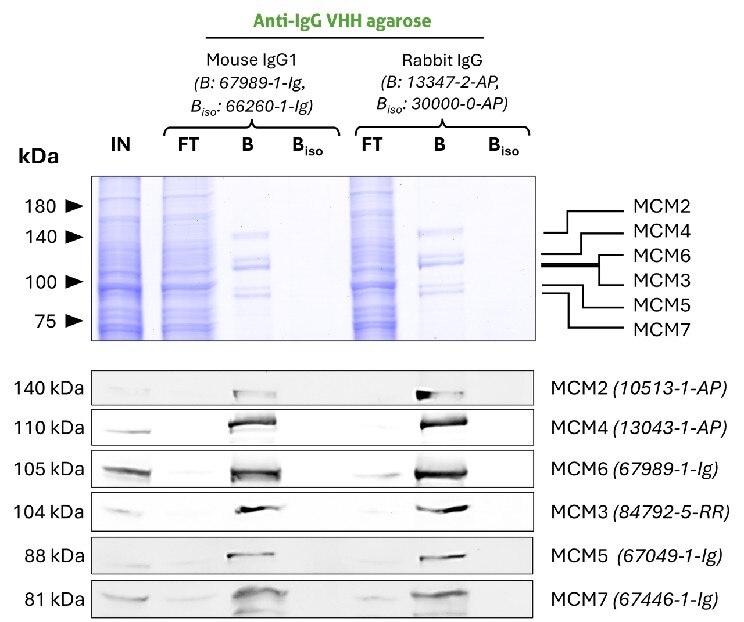
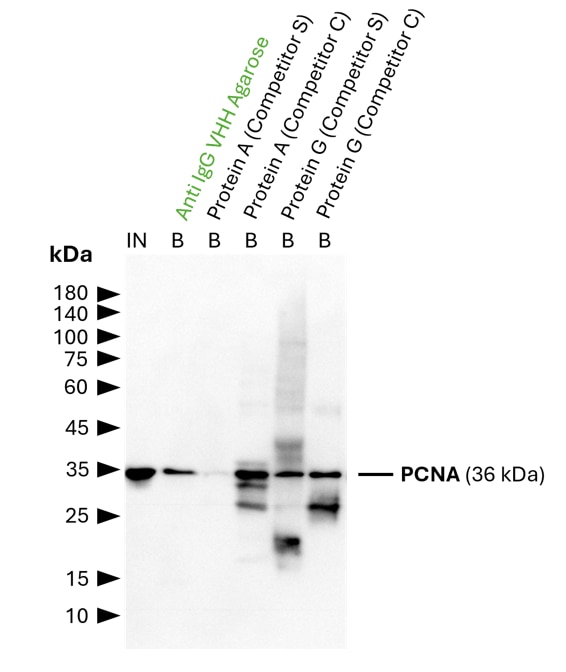
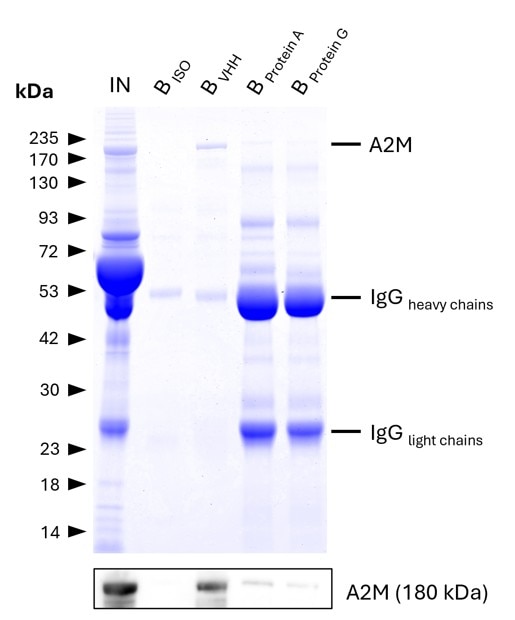
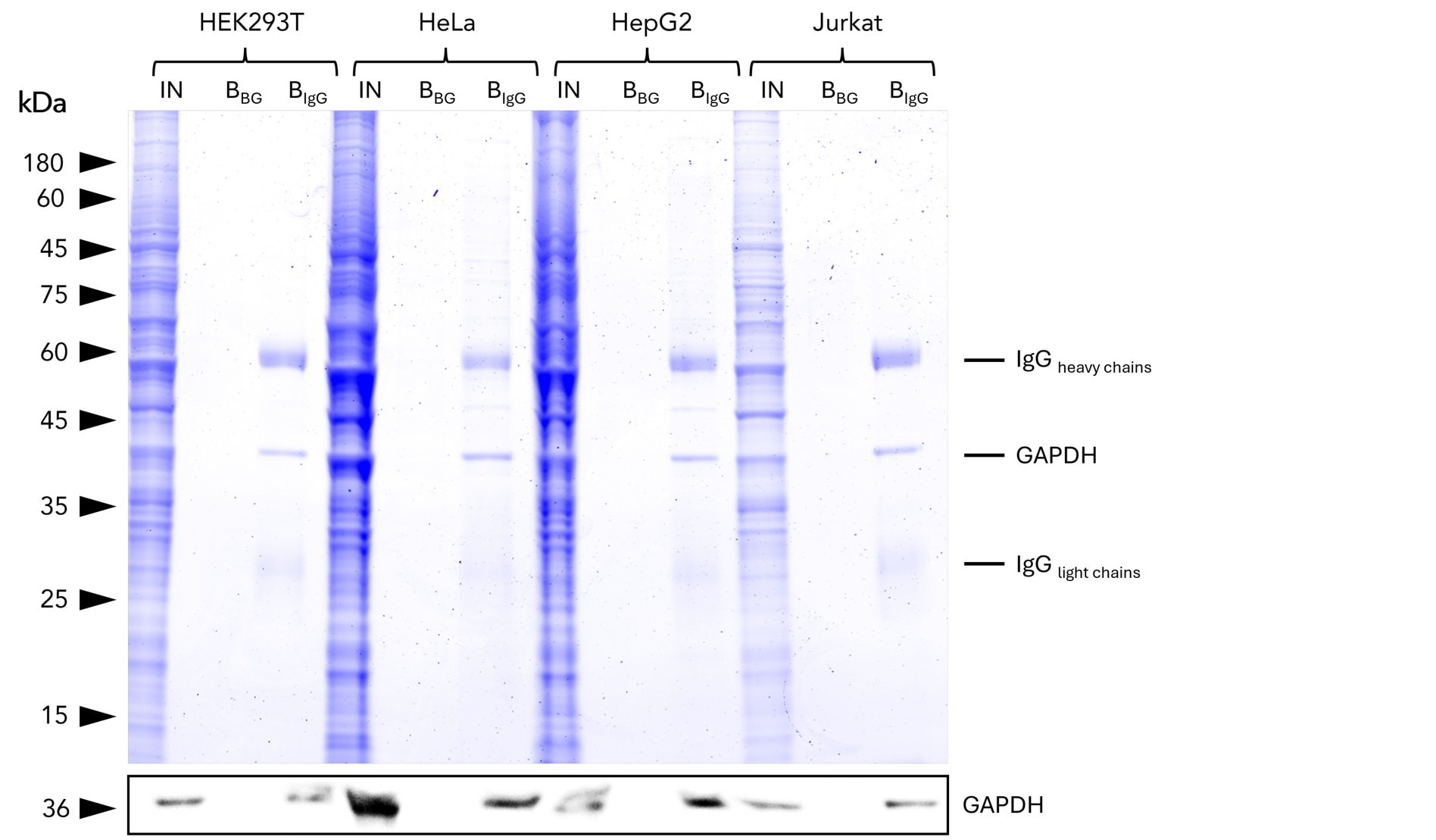
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
anti-Rabbit / anti-Mouse IgG IP Beads is an affinity resin for IP of all subtypes of Rabbit and Mouse IgG. It consists of rabbit and mouse IgG specific VHHs (Nanobodies) coupled to Agarose beads.
| Description | Ready to use VHH coupled Agarose Beads for Immunoprecipitation of all subtypes of Rabbit and Mouse IgG. • Fast, reliable and efficient one-step Immunoprecipitation • Ready-to-use • Stable in harsh buffer conditions • Suitable for downstream mass spec analysis • Specific to all Rabbit and all Mouse IgG subtypes • Low background |
| Applications | IP, Co-IP |
| Conjugate | Agarose beads |
| Bead Size | 90 µm (cross-linked 4% agarose beads) |
| Binding capacity | >60 μg of rabbit or mouse IgG per 25 μL bead slurry |
| Elution buffer | SDS Sample Buffer |
| Type | Nanobody |
| Class | Recombinant - Animal free production |
| Host | Alpaca |
| Immunogen | Rabbit IgG / Mouse IgG |
| RRID | AB_3697100 |
| Storage Buffer | 20% Ethanol |
| Storage Condition | +4°C / do not freeze! |
| Shipping | Ambient Temp |
| Size | 1 ml; 2 ml; 5 ml |