WB Figures
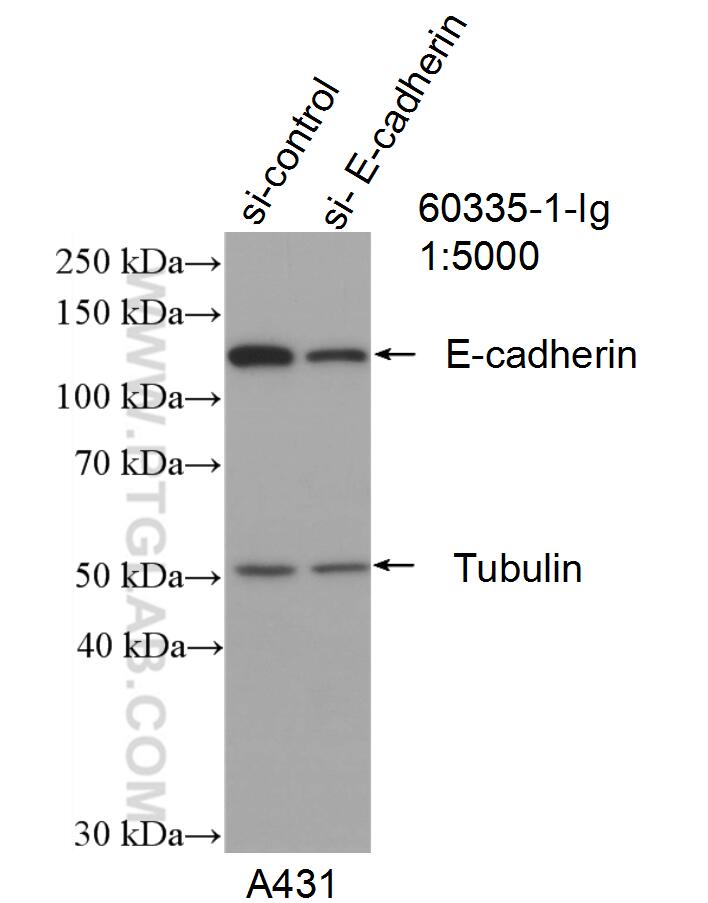
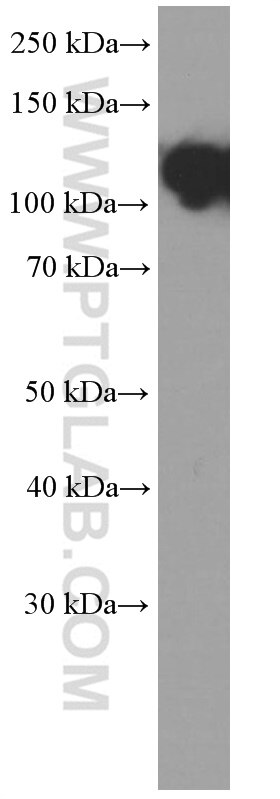
WB analysis of A431 using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
WB result of E-cadherin antibody (60335-1-Ig; 1:5000; incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours) with sh-Control and sh-E-cadherin transfected A431 cells. This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
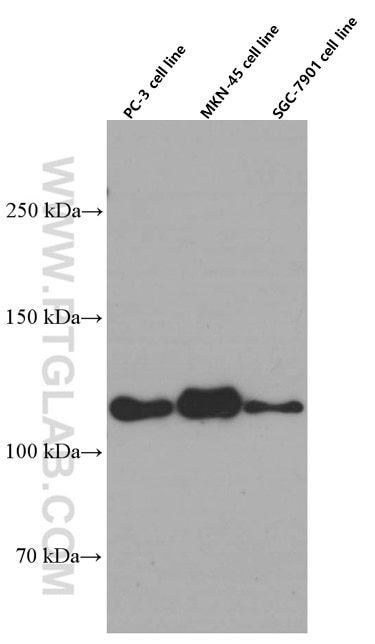
WB analysis of PC-3 using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
PC-3, MKN-45, SGC-7901 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin Antibody) at dilution of 1:4000 incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours. This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
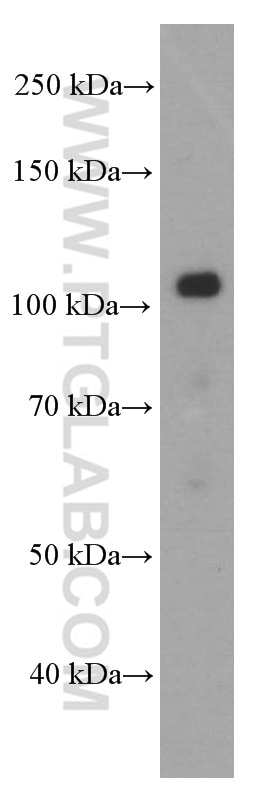
WB analysis of pig brain using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
pig brain tissue were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin Antibody) at dilution of 1:1000 incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours. This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
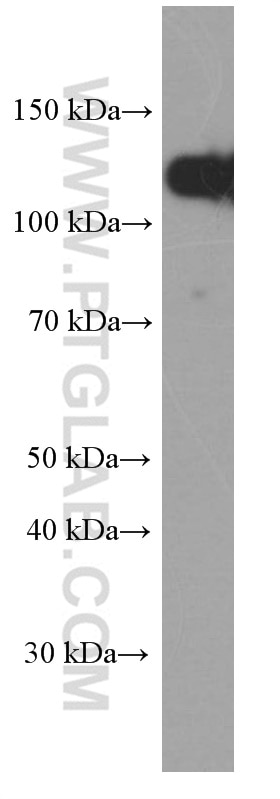
WB analysis of A431 using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
A431 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin Antibody) at dilution of 1:8000 incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours. This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
WB analysis of MCF-7 using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
MCF-7 cells were subjected to SDS PAGE followed by western blot with 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin Antibody) at dilution of 1:8000 incubated at room temperature for 1.5 hours. This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IHC Figures
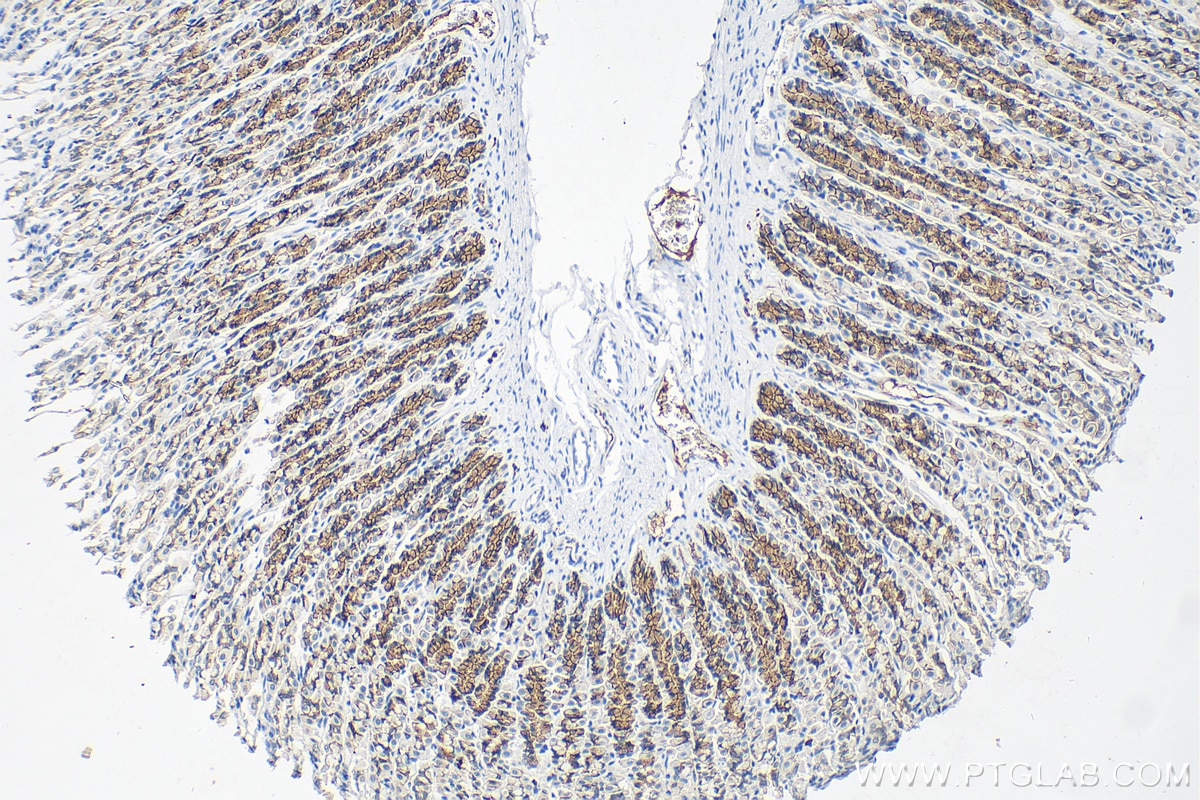
IHC staining of rat stomach using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat stomach tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:2000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IHC staining of rat stomach using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat stomach tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:2000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
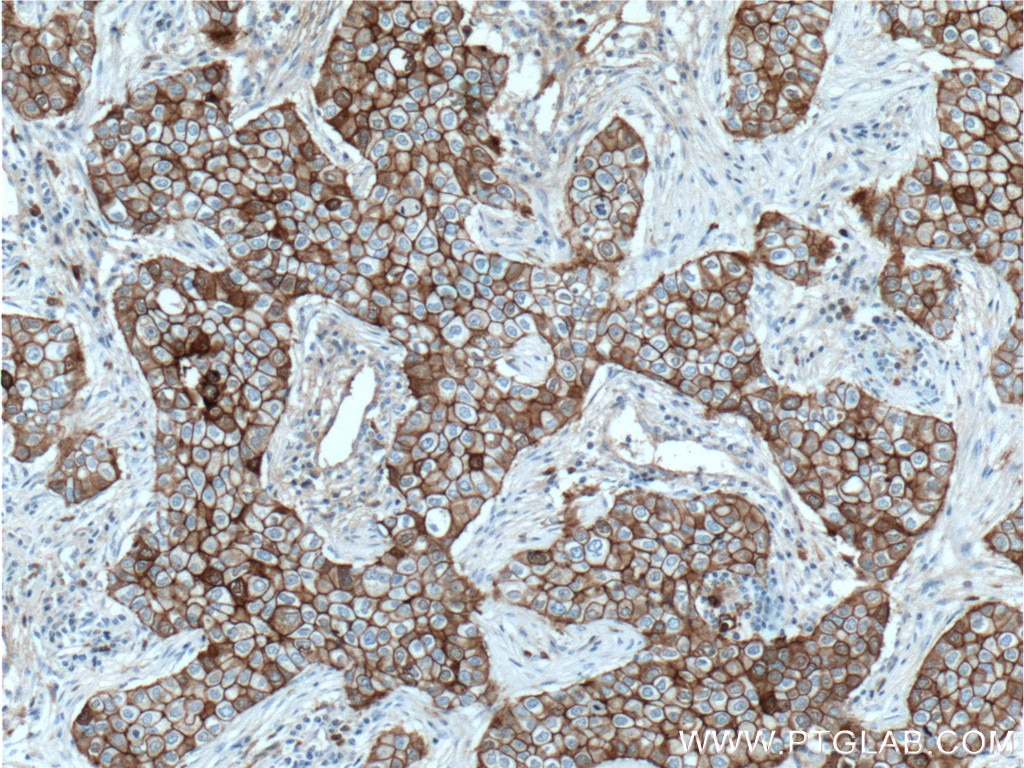
IHC staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:2000 (under 10x lens. Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IHC staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:2000 (under 40x lens. Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
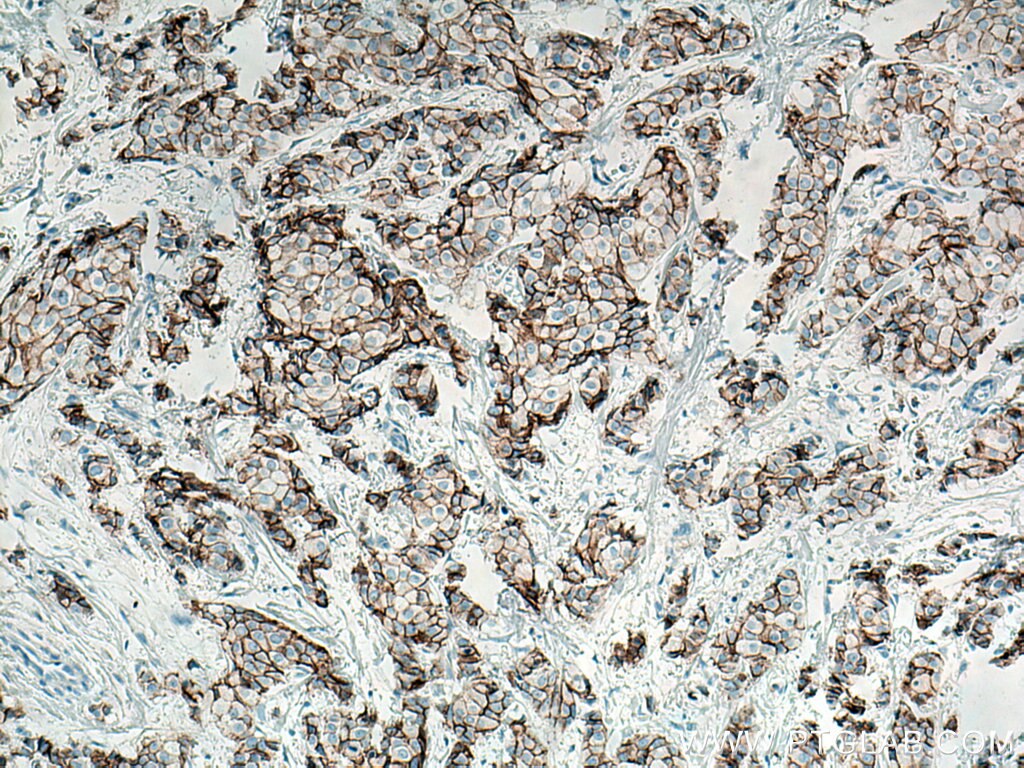
IHC staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:8000 (under 10x lens. Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IHC staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:10000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IHC staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:10000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
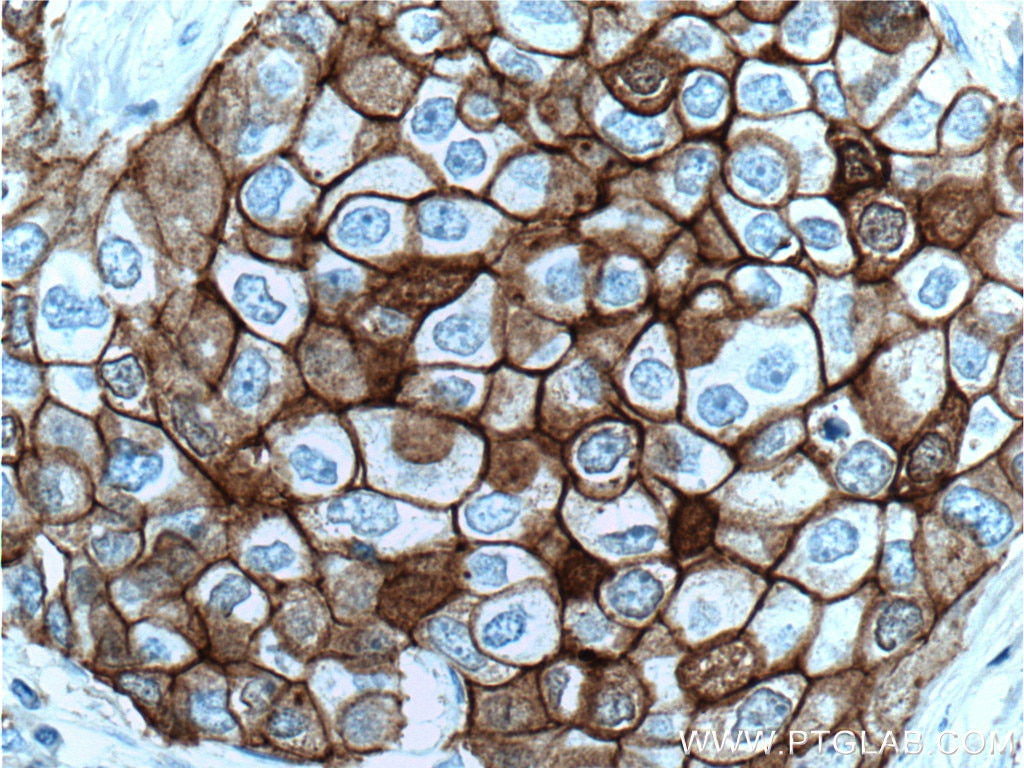
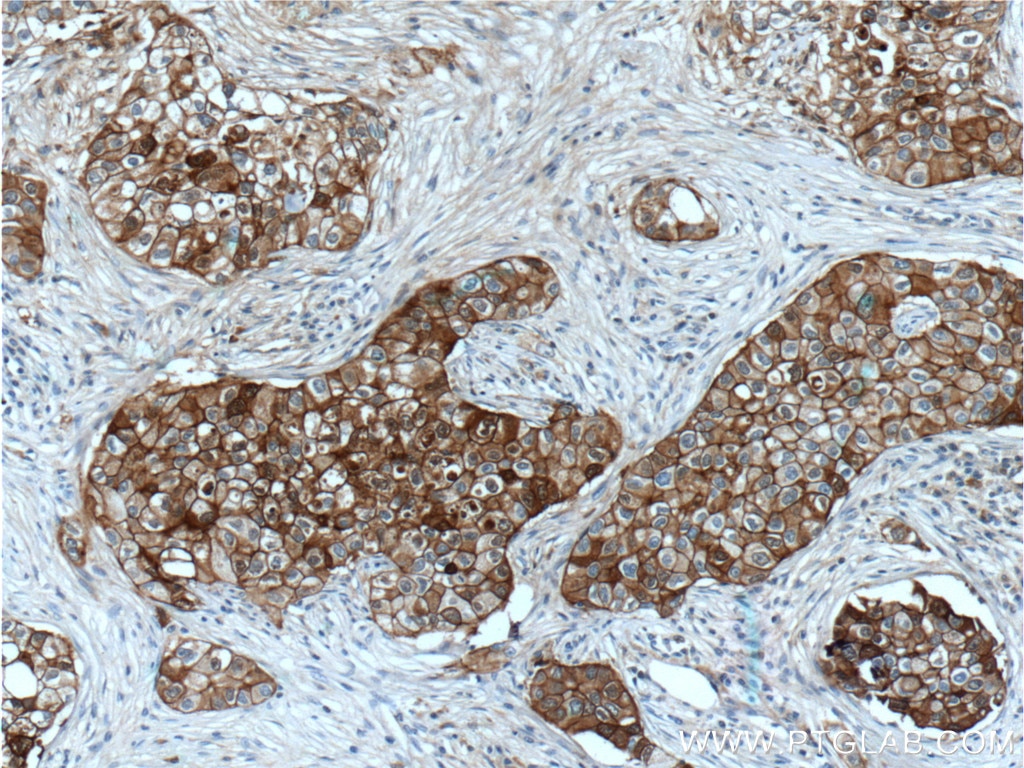
IHC staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin Antibody) at dilution of 1:300 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
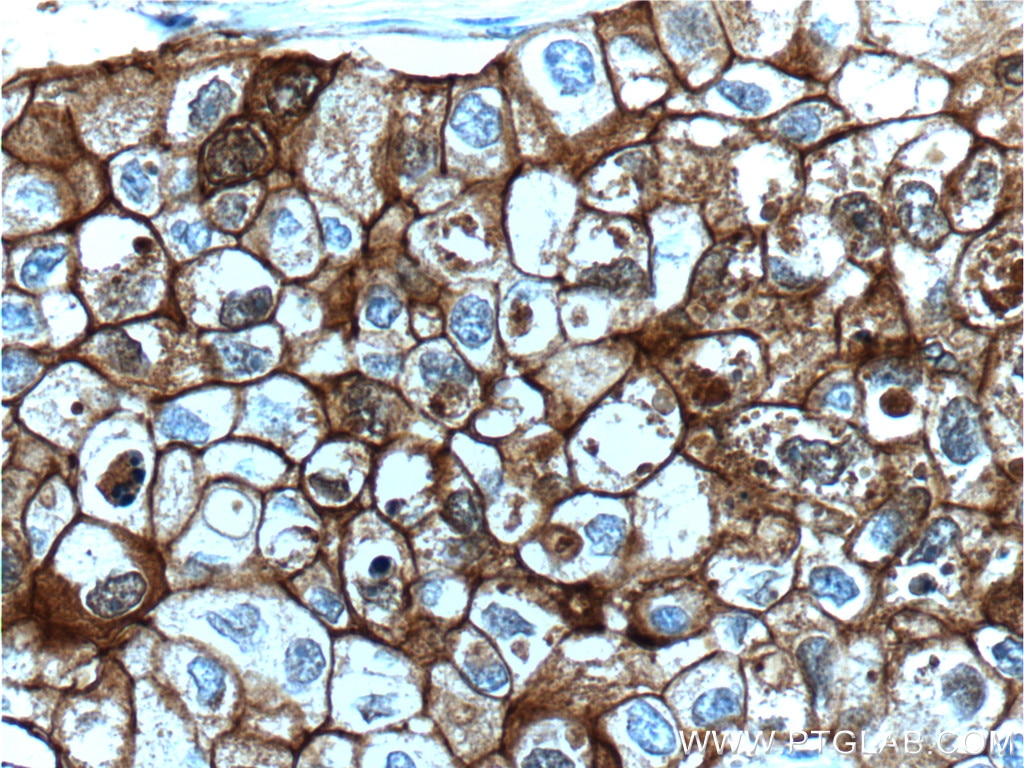
IHC staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human breast cancer tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin Antibody) at dilution of 1:300 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
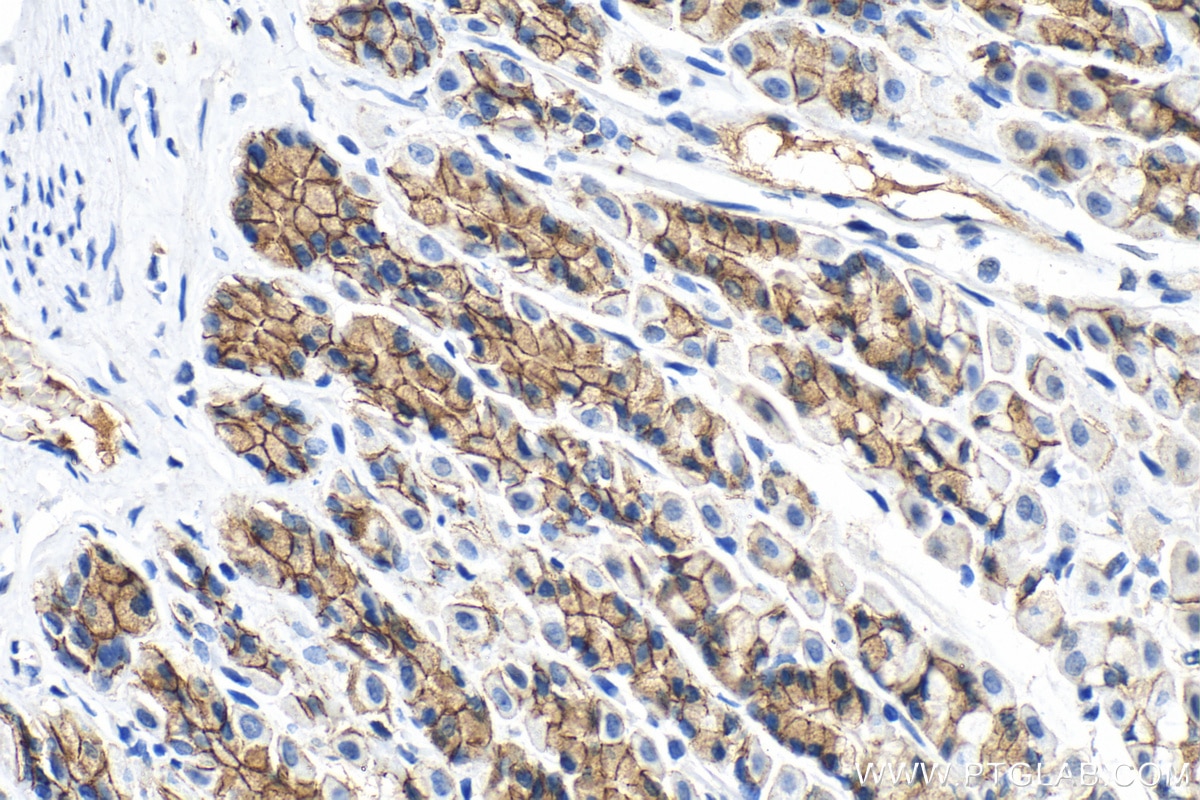
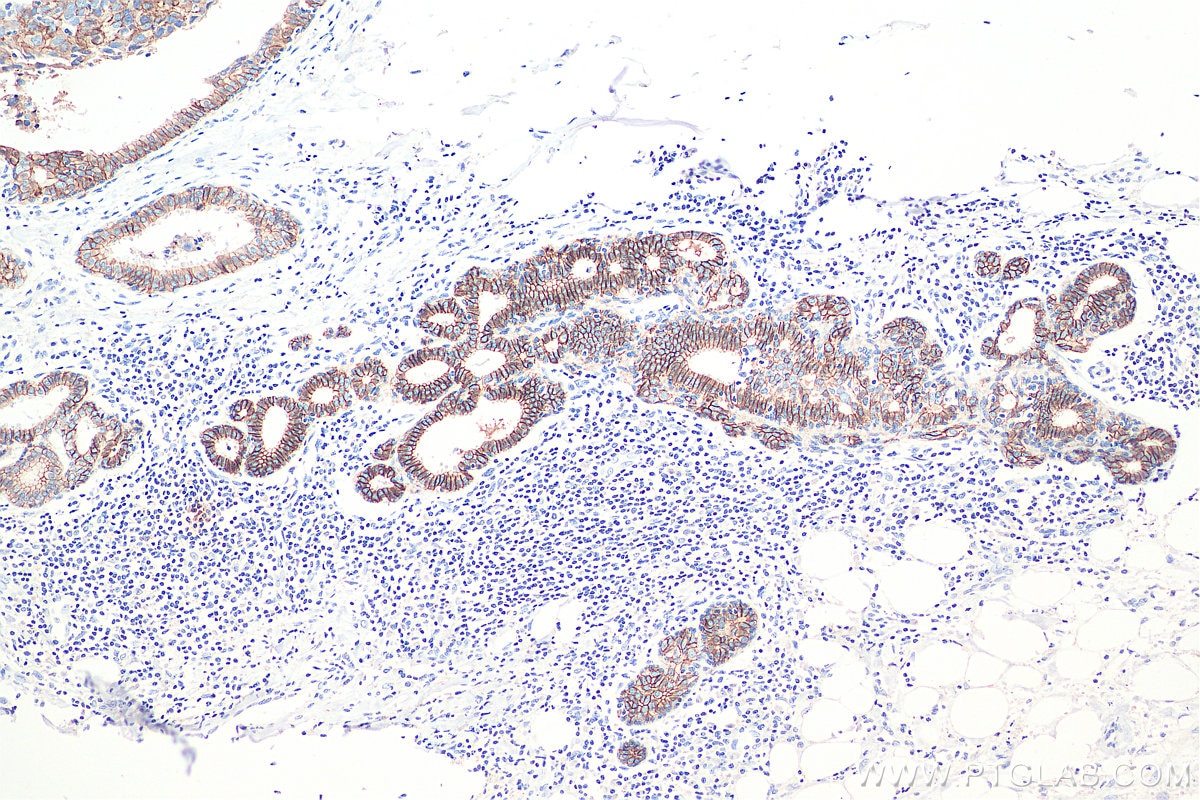
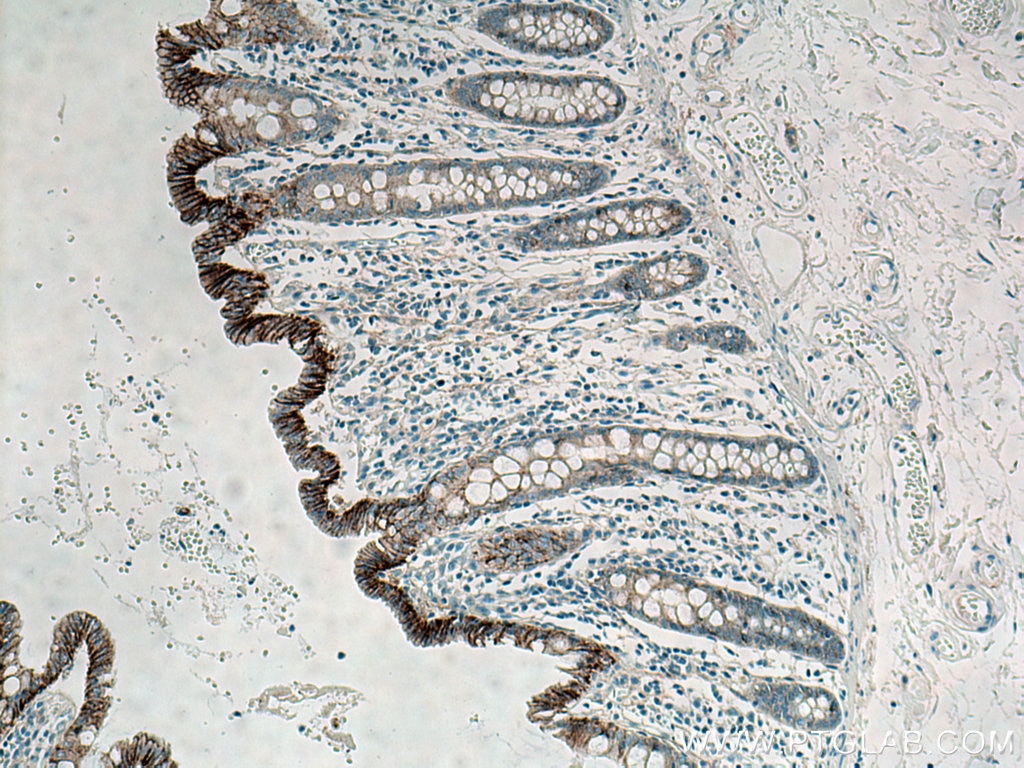
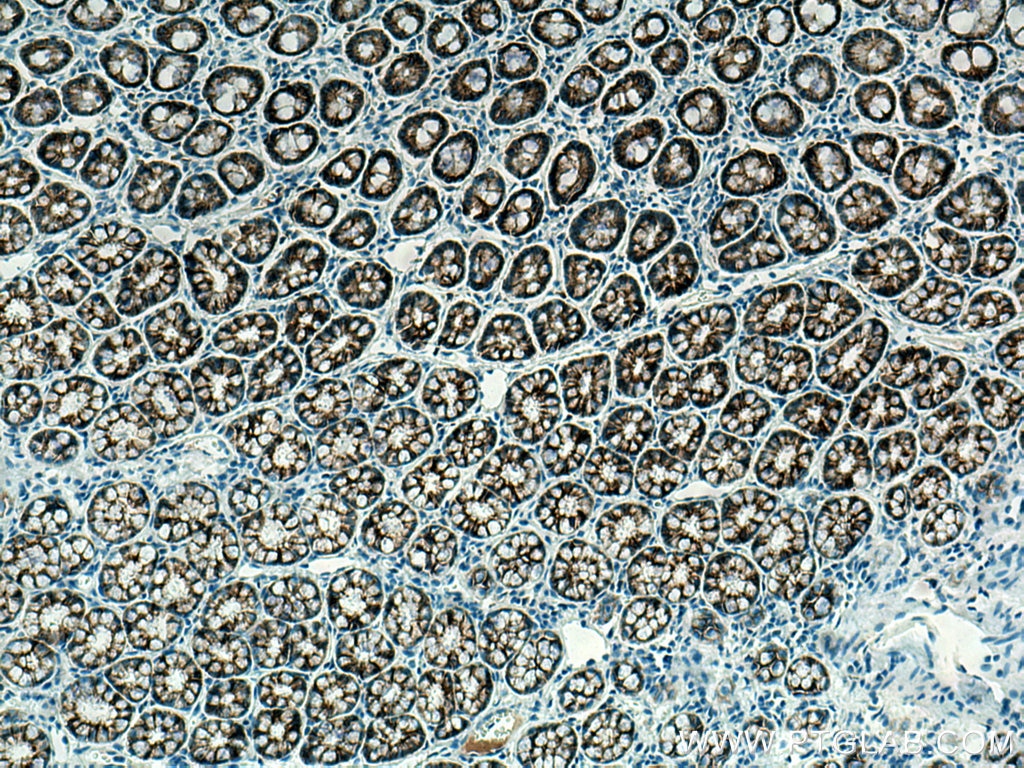
IHC staining of human colon using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:4000 (under 10x lens. Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
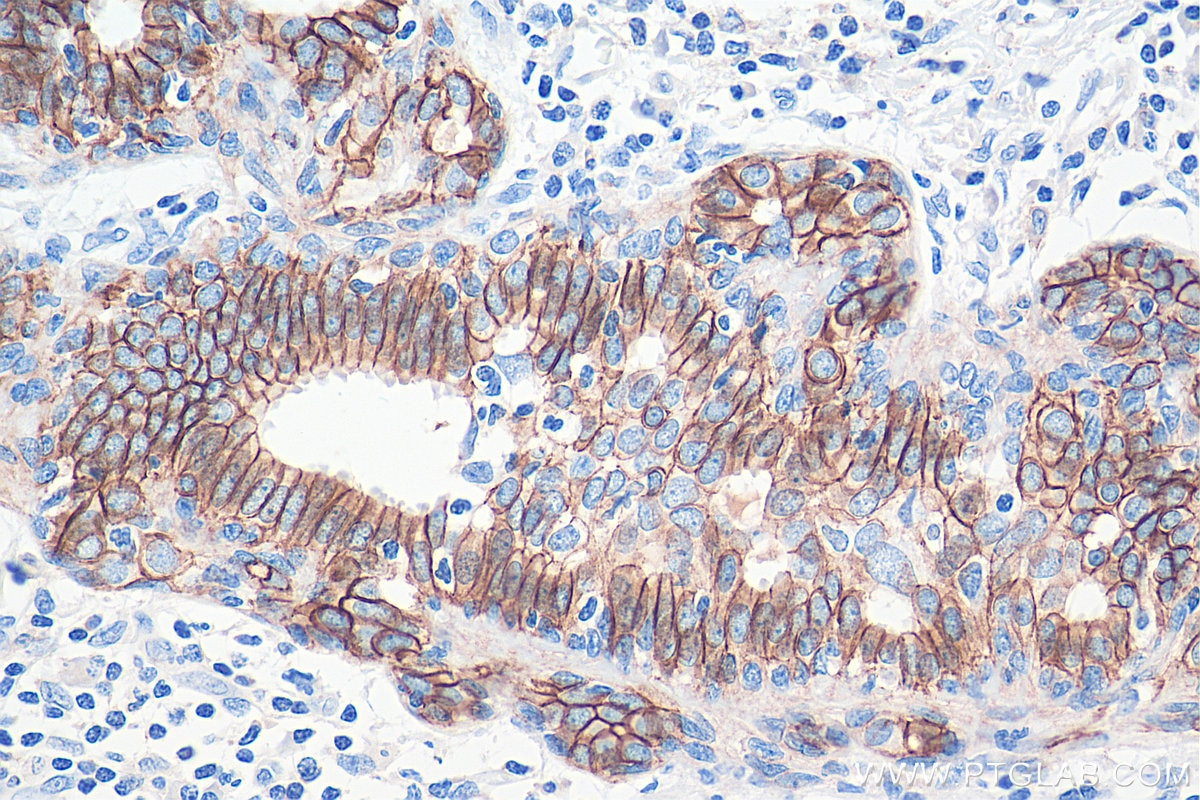
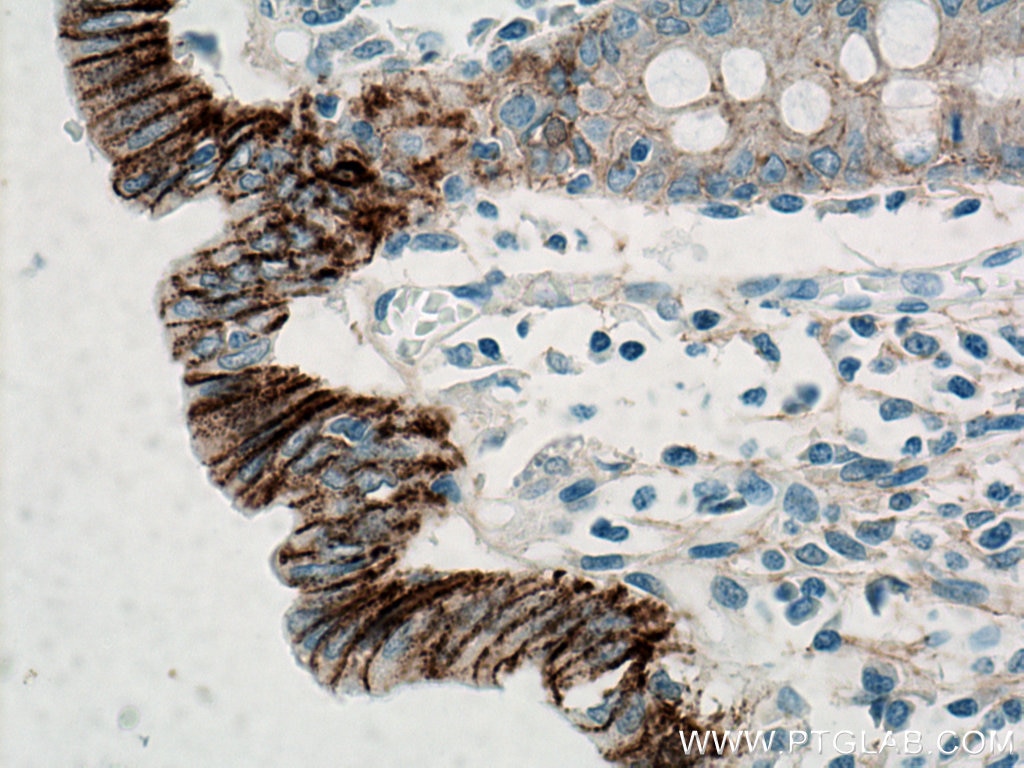
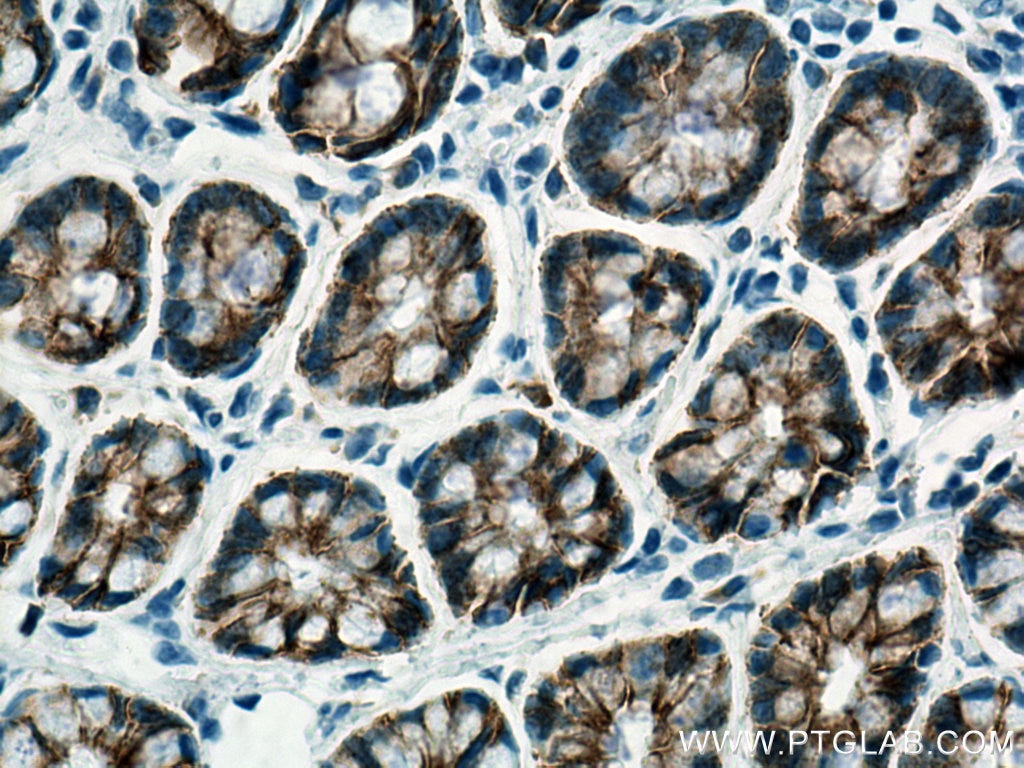
IHC staining of human colon using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded human colon tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:4000 (under 40x lens. Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IHC staining of rat colon using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat colon tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:2000 (under 10x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IHC staining of rat colon using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded rat colon tissue slide using 60335-1-Ig (E-cadherin antibody) at dilution of 1:2000 (under 40x lens). Heat mediated antigen retrieval with Tris-EDTA buffer (pH 9.0). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IF-P Figures
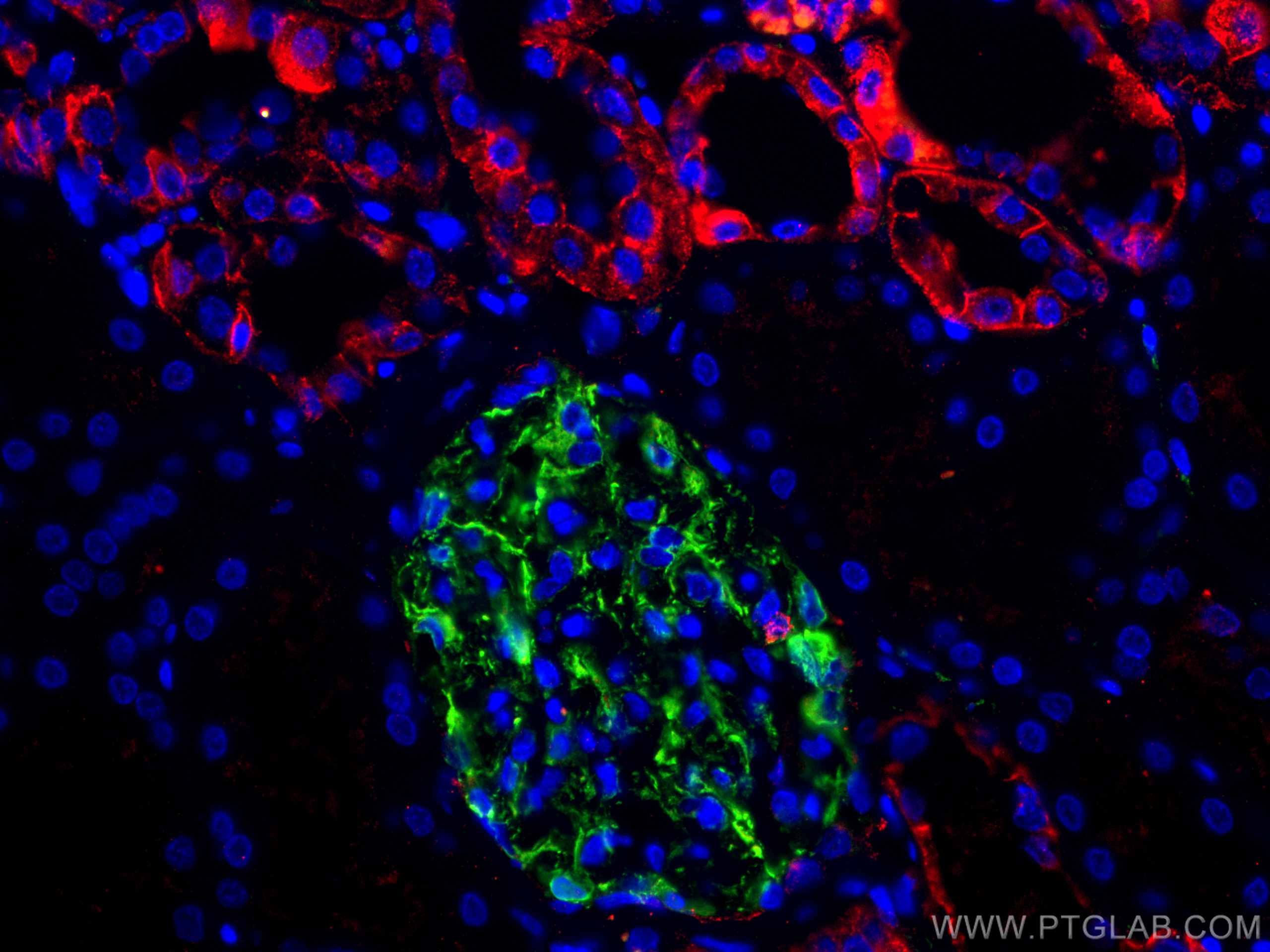
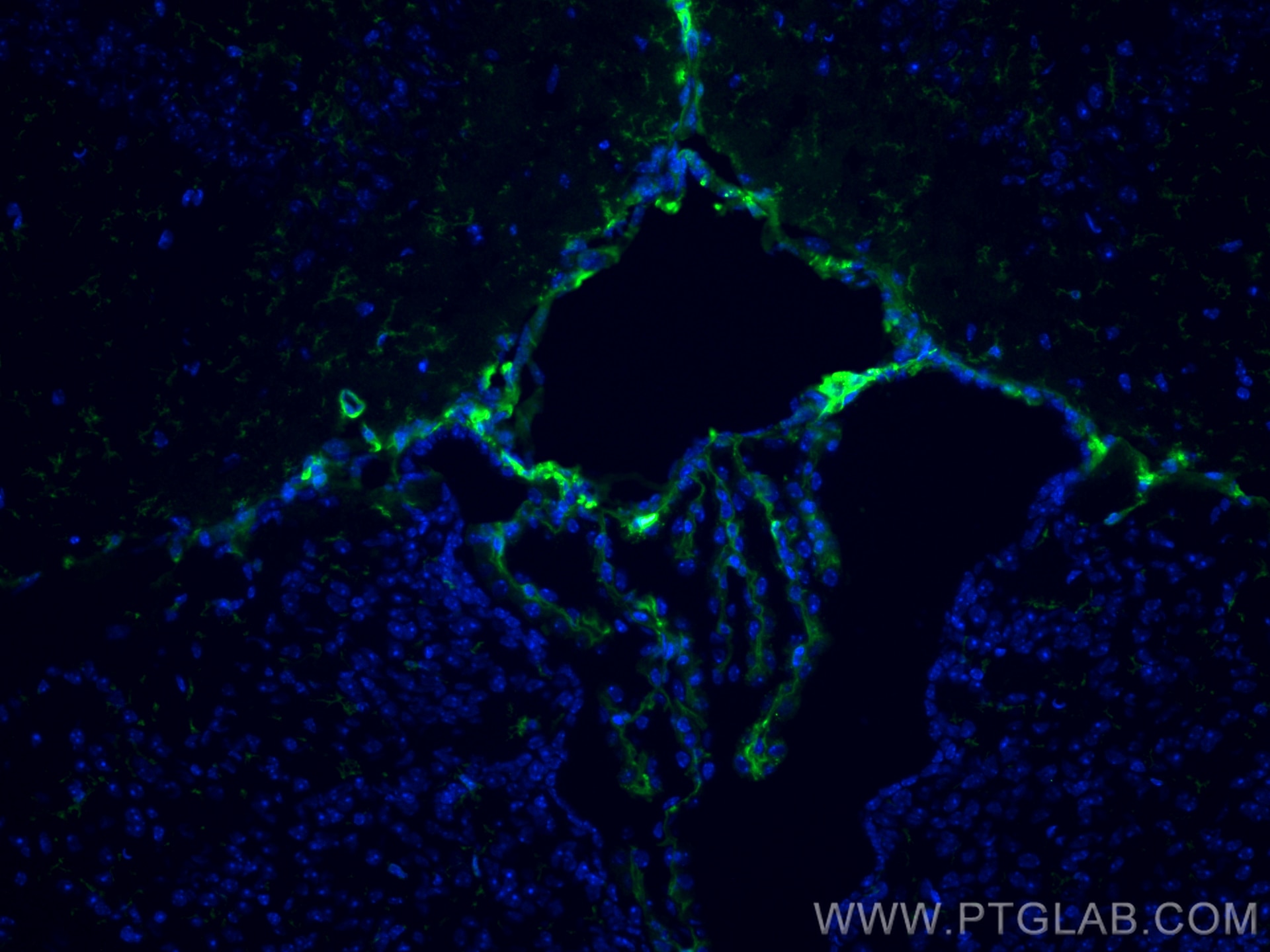
IF Staining of human kidney using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed human kidney tissue using E-cadherin antibody (60335-1-Ig, Clone: 6B11F11 ) at dilution of 1:300 and CoraLite®594-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L), Podocalyxin antibody(18150-1-AP, green). DNA was stained by DAPI (blue). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
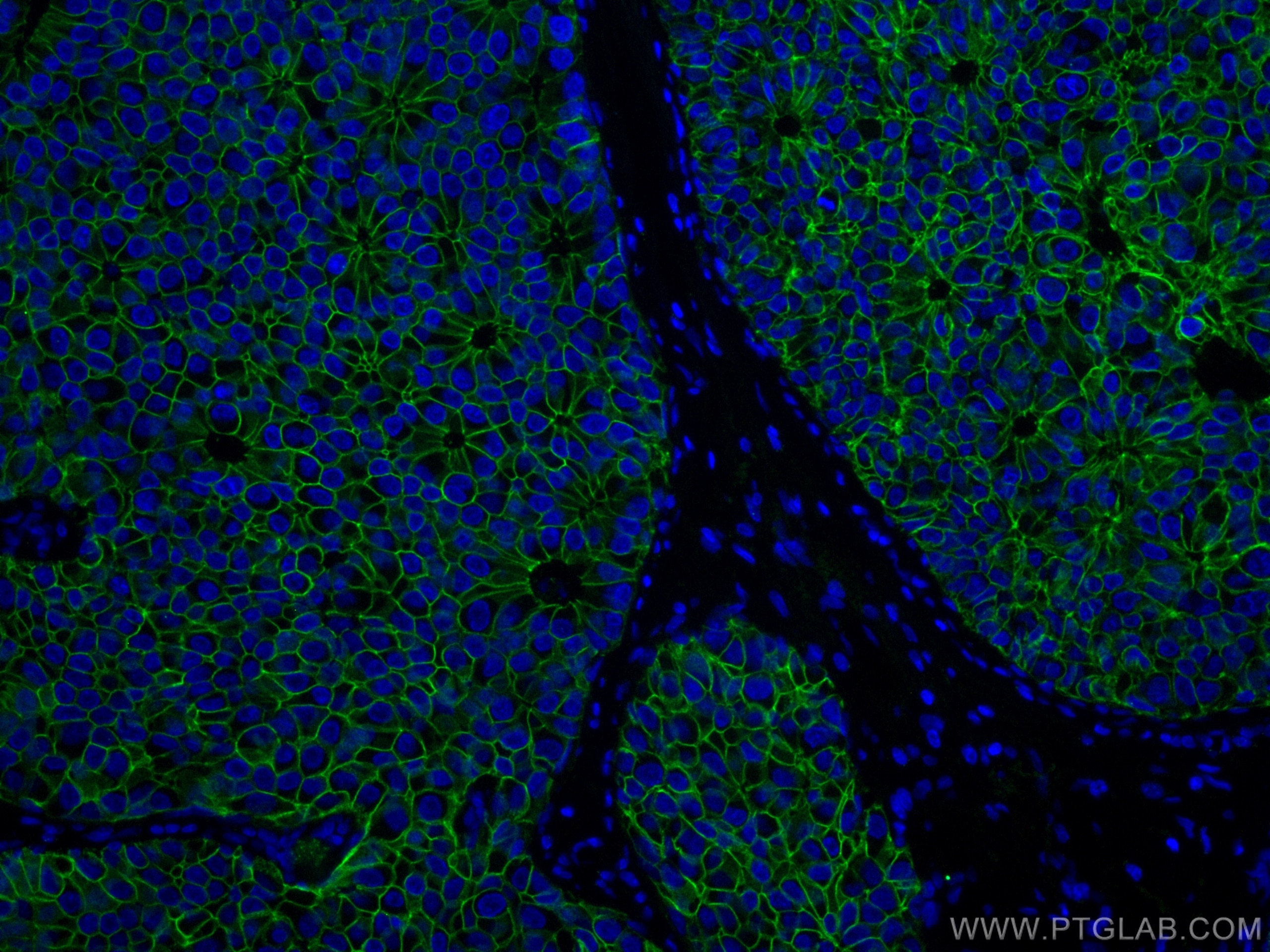
IF Staining of human breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed human breast cancer tissue using E-cadherin antibody (60335-1-Ig, Clone: 6B11F11 ) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
IF/ICC Figures
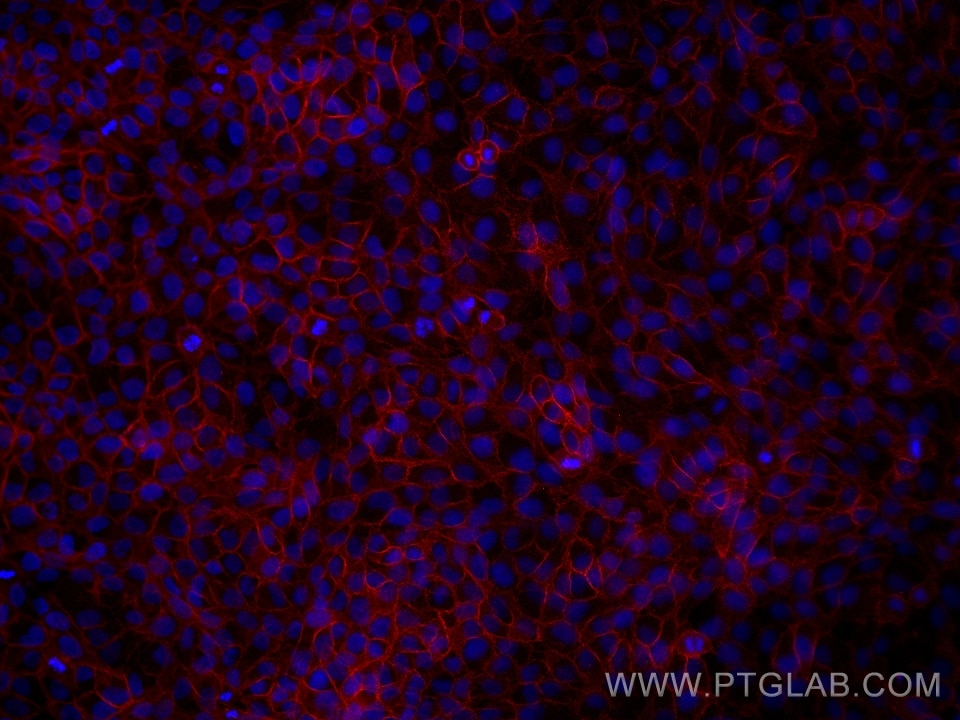
IF Staining of HaCaT using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed HaCaT cells using E-cadherin antibody (60335-1-Ig, Clone: 6B11F11 ) at dilution of 1:2000 and Multi-rAb CoraLite® Plus 594-Goat Anti-Mouse Recombinant Secondary Antibody (H+L) (Cat.NO. RGAM004 ). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
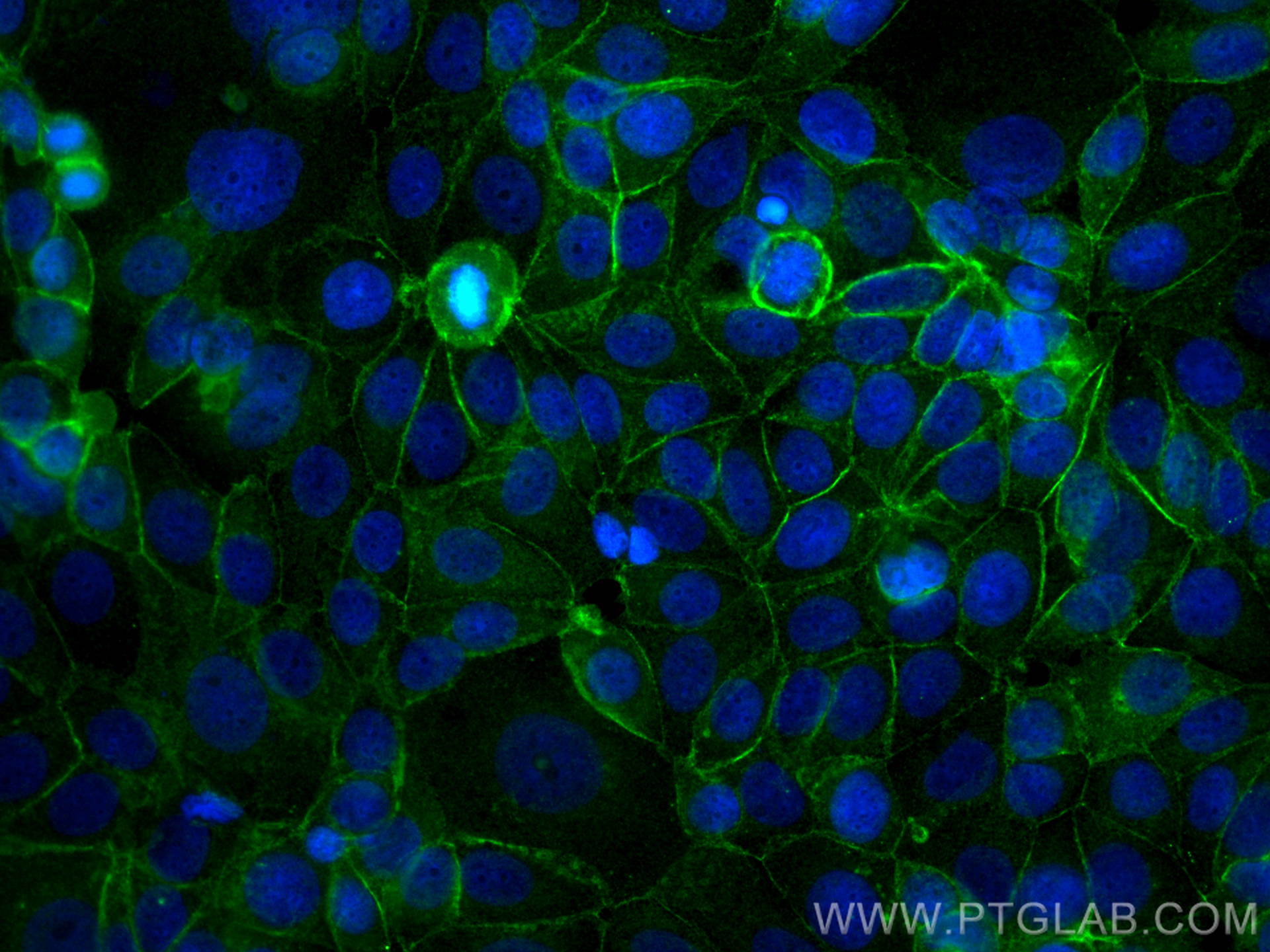
IF Staining of MCF-7 using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunofluorescent analysis of (-20°C Methanol) fixed MCF-7 cells using E-cadherin antibody (60335-1-Ig, Clone: 6B11F11 ) at dilution of 1:400 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.
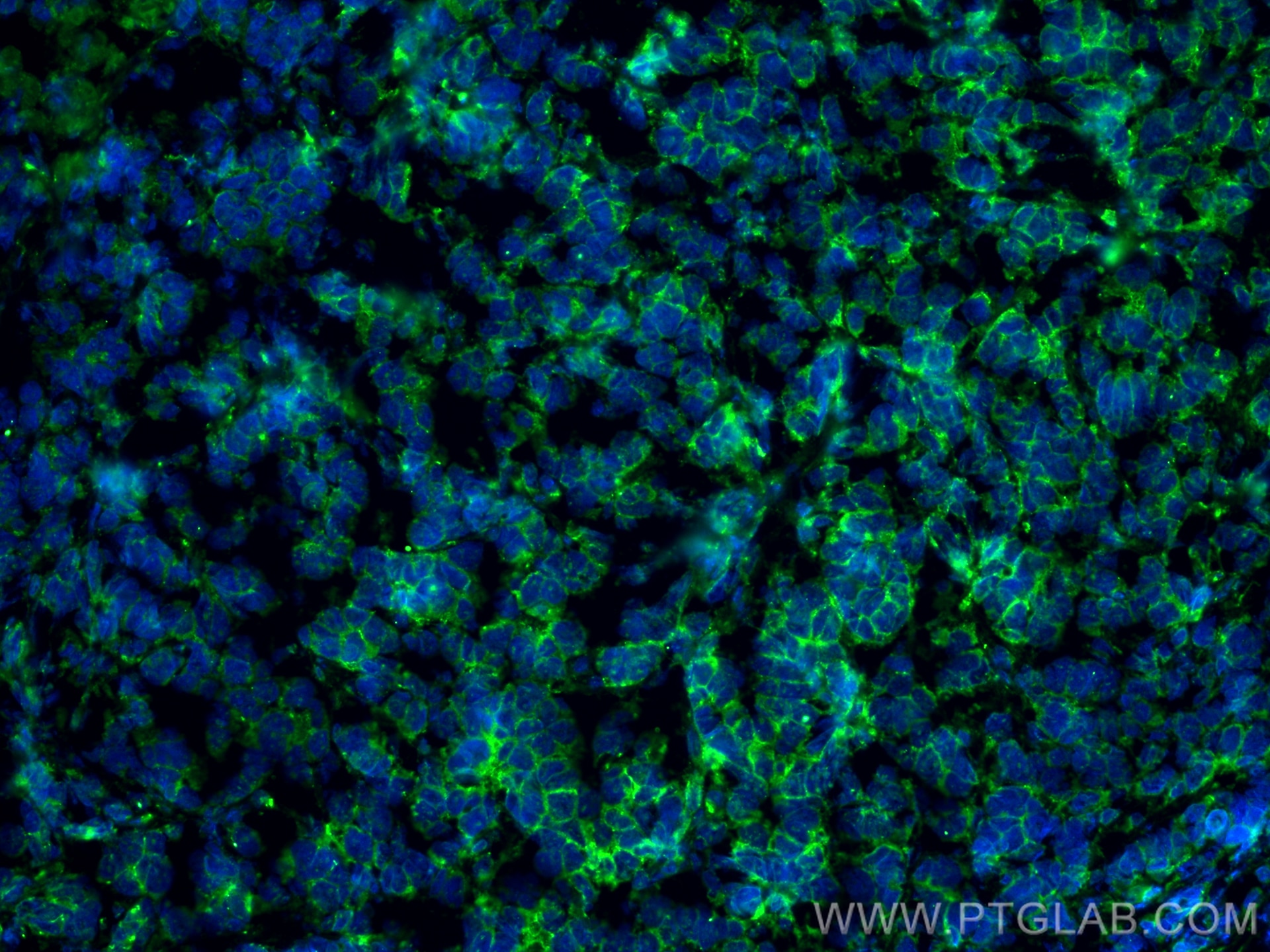
IF Staining of mouse breast cancer using 60335-1-Ig (same clone as 60335-1-PBS)
Immunofluorescent analysis of (4% PFA) fixed mouse breast cancer using E-cadherin antibody (60335-1-Ig, Clone: 6B11F11 ) at dilution of 1:800 and CoraLite®488-Conjugated Goat Anti-Mouse IgG(H+L) (SA00013-1). This data was developed using the same antibody clone with 60335-1-PBS in a different storage buffer formulation.