Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
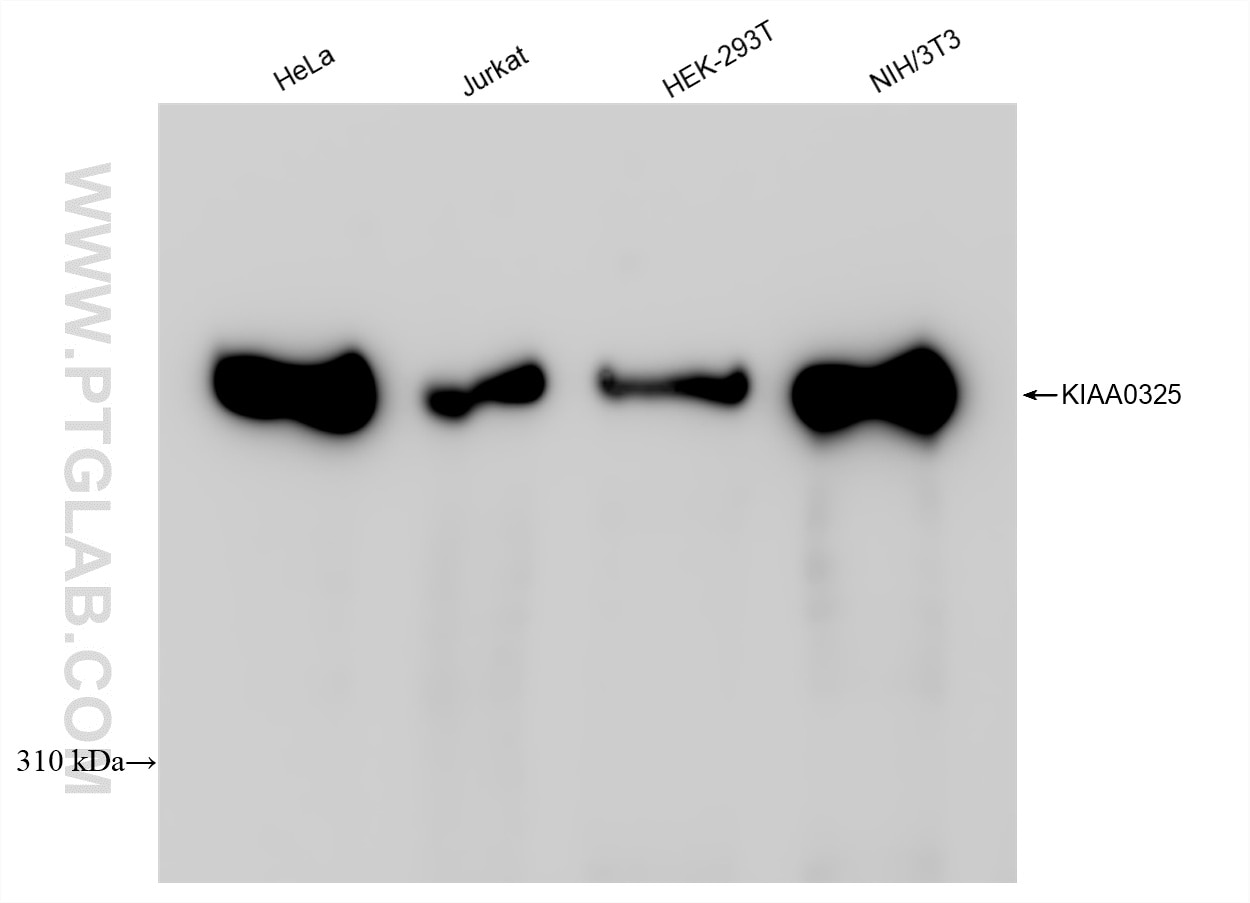
85397-4-PBS targets DYNC1H1 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag2999 Product name: Recombinant human KIAA0325 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 590-989 aa of BC021297 Sequence: MAQSIYGGRVDNEFDQRLLNTFLERLFTTRSFDSEFKLACKVDGHKDIQMPDGIRREEFVQWVELLPDTQTPSWLGLPNNAERVLLTTQGVDMISKMLKMQMLEDEDDLAYAETEKKTRTDSTSDGRPAWMRTLHTTASNWLHLIPQTLSHLKRTVENIKDPLFRFFEREVKMGAKLLQDVRQDLADVVQVCEGKKKQTNYLRTLINELVKGILPRSWSHYTVPAGMTVIQWVSDFSERIKQLQNISLAAASGGAKELKNIHVCLGGLFVPEAYITATRQYVAQANSWSLEELCLEVNVTTSQGATLDACSFGVTGLKLQGATCNNNKLSLSNAISTALPLTQLRWVKQTNTEKKASVVTLPVYLNFTRADLIFTVDFEIATKEDPRSFYERGVAVLCTE 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | dynein, cytoplasmic 1, heavy chain 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 4646 aa, 532 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 532 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC021297 |
| Gene Symbol | DYNC1H1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1778 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14204 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Dyneins are a group of microtubule-activated ATPases that convert chemical energy into mechanical energy. It can be divided into 2 large subgroups, namely, the axonemal and cytoplasmic dyneins. The conventional cytoplasmic dynein comprises 2 heavy chain polypeptides and several intermediate and light chains. DYNC1H1 is a cytoplasmic dynein and belongs to the dynein heavy chain family. It acts as a motor for the intracellular retrograde motility of vesicles and organelles along microtubules. DYNC1H1 has been implicated in the degeneration of dopaminergic neuron axons and motor neurons in PD patients.