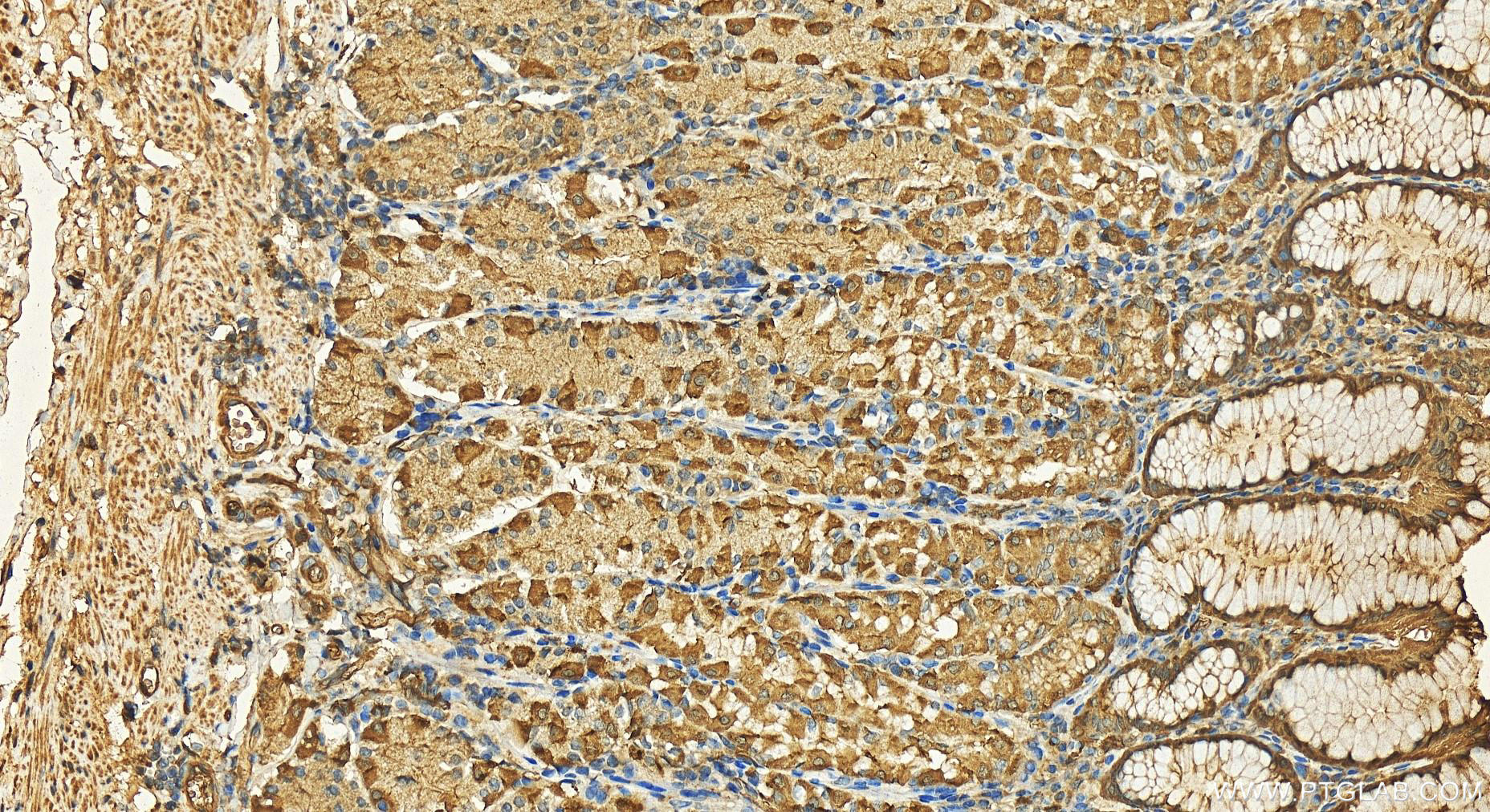
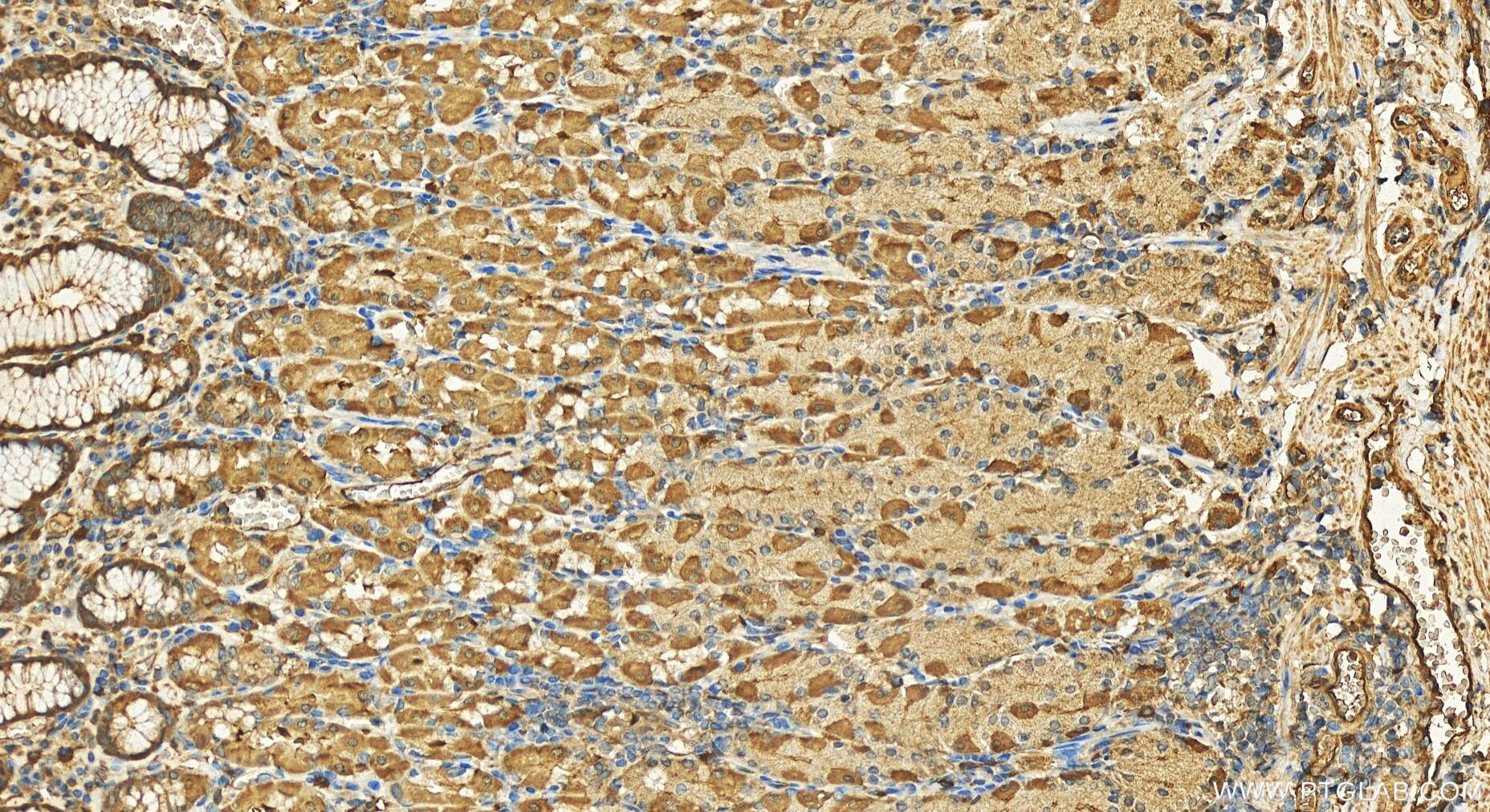
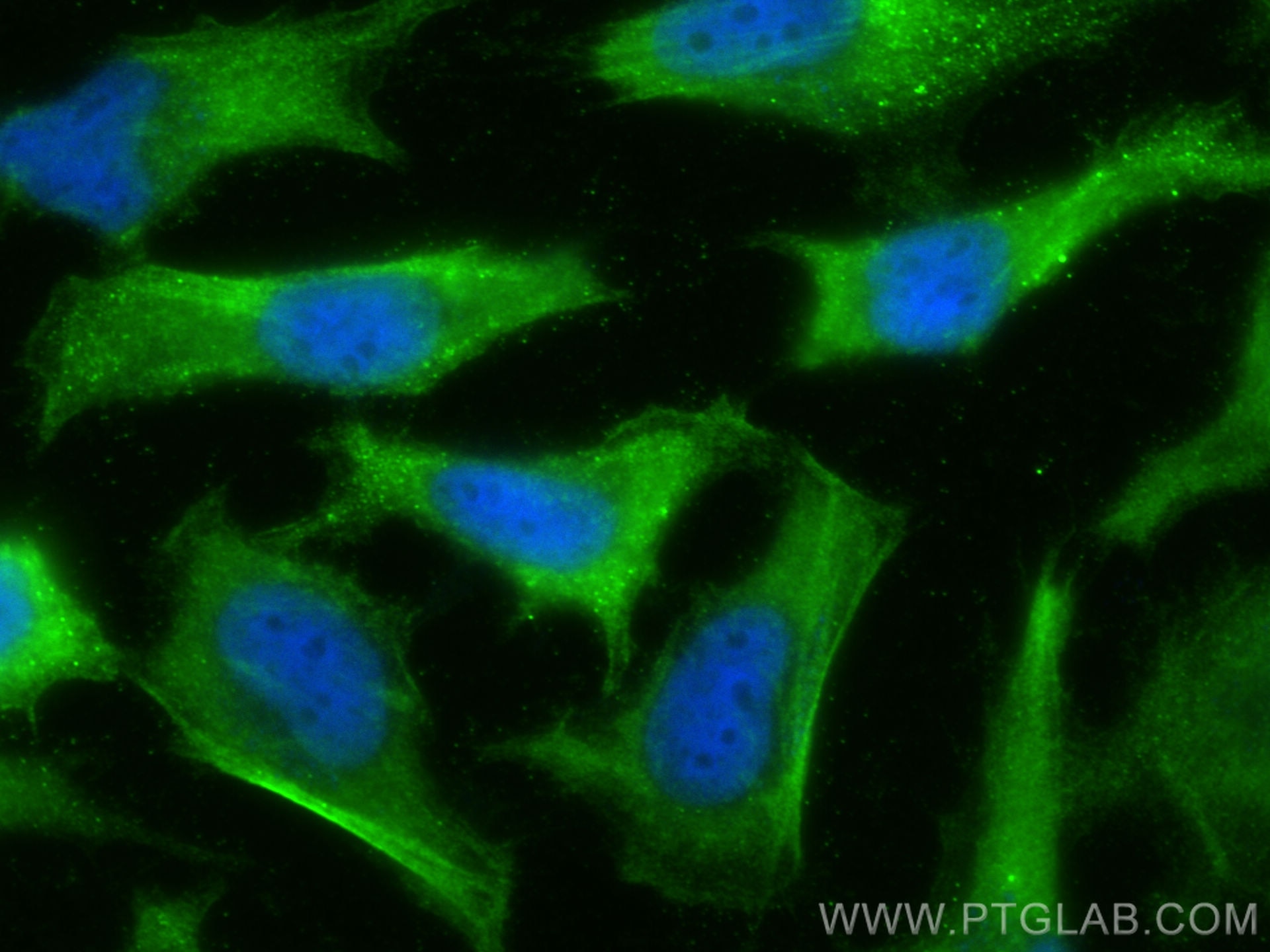
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
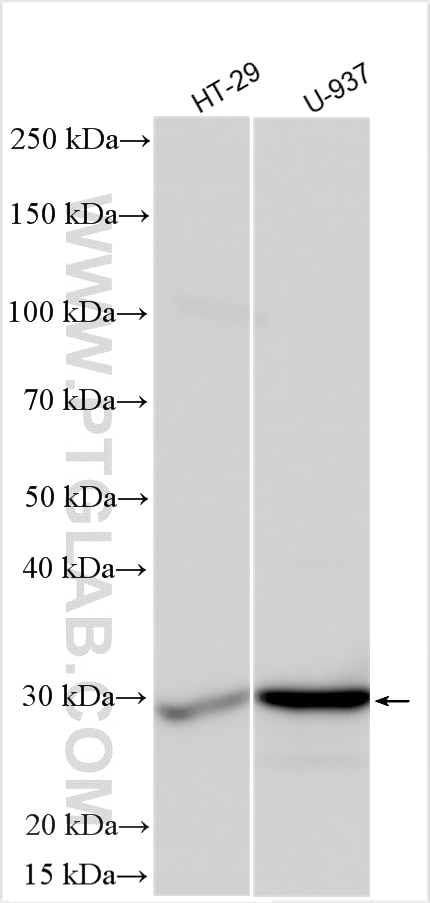
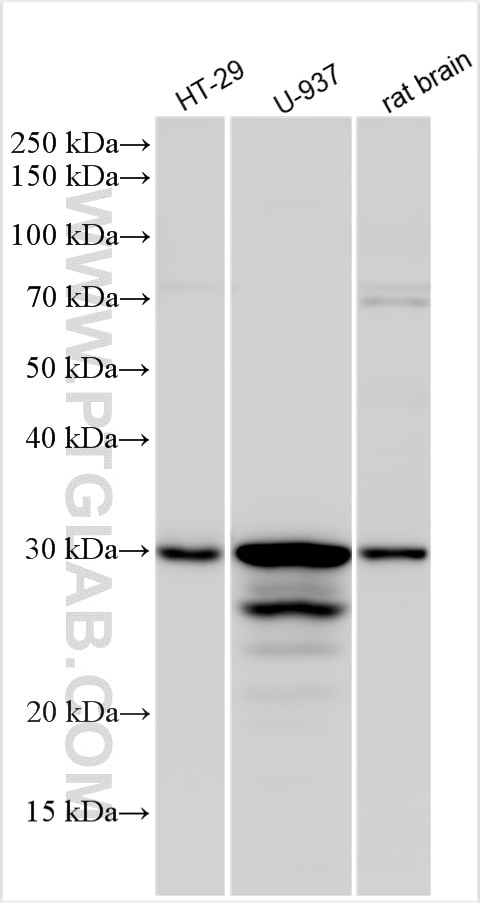
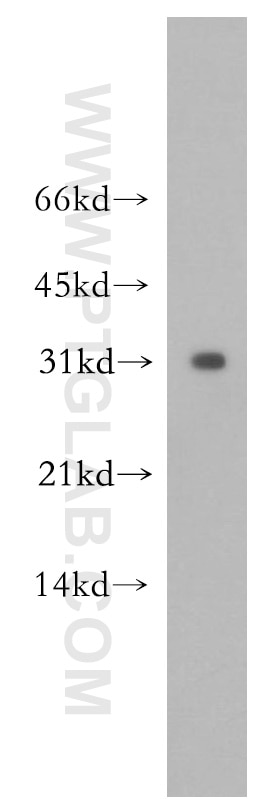
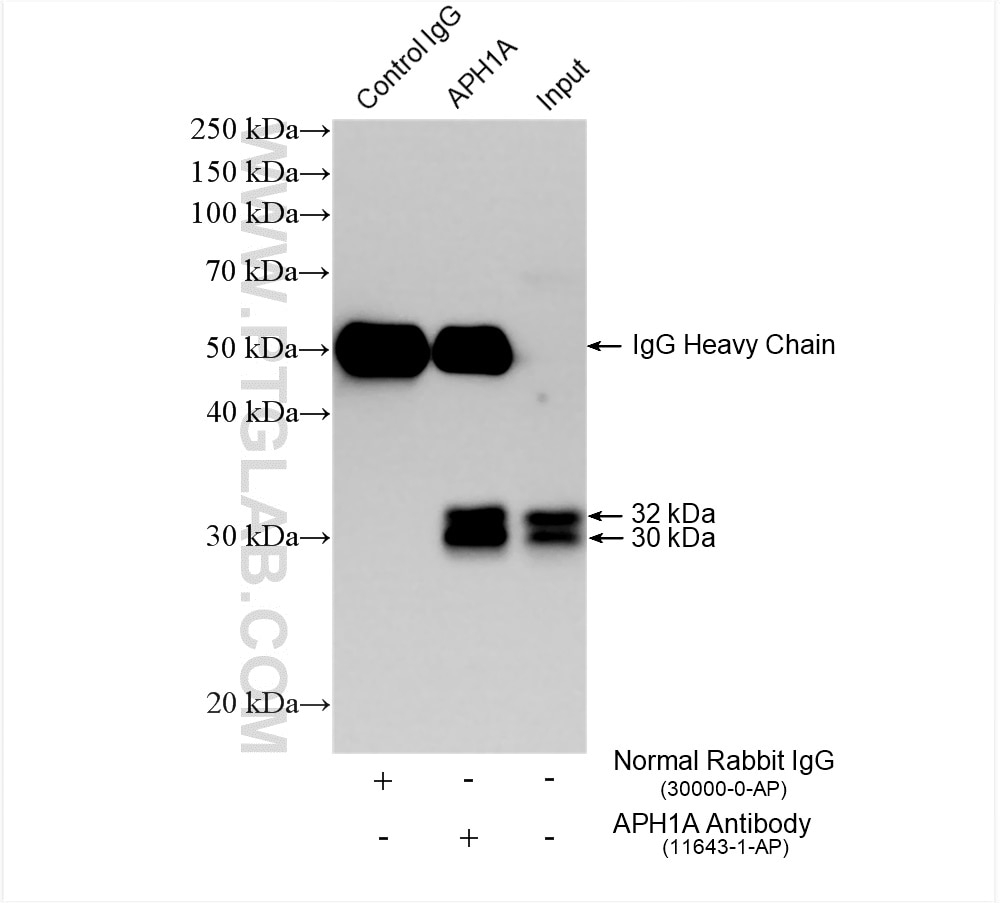
11643-1-PBS targets APH1A in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag2238 Product name: Recombinant human APH1A protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-265 aa of BC015568 Sequence: MGAAVFFGCTFVAFGPAFALFLITVAGDPLRVIILVAGAFFWLVSLLLASVVWFILVHVTDRSDARLQYGLLIFGAAVSVLLQEVFRFAYYKLLKKADEGLASLSEDGRSPISIRQMAYVSGLSFGIISGVFSVINILADALGPGVVGIHGDSPYYFLTSAFLTAAIILLHTFWGVVFFDACERRRYWALGLVVGSHLLTSGLTFLNPWYEASLLPIYAVTVSMGLWAFITAGGSLRSIQRSLLCRRQEDSRVMVYSALRIPPED 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | anterior pharynx defective 1 homolog A (C. elegans) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 265 aa, 29 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 27-32 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC015568 |
| Gene Symbol | APH1A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 51107 |
| RRID | AB_2242861 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q96BI3 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
APH1A is a component of the gamma secretase complex that cleaves integral membrane proteins such as Notch receptors and beta-amyloid precursor protein. The gamma secretase complex contains this gene product, or the paralogous anterior pharynx defective 1 homolog B (APH1B), along with the presenilin, nicastrin, and presenilin enhancer-2 proteins. The precise function of this seven-transmembrane-domain protein is unknown though it is suspected of facilitating the association of nicastrin and presenilin in the gamma secretase complex as well as interacting with substrates of the gamma secretase complex prior to their proteolytic processing. Polymorphisms in a promoter region of this gene have been associated with an increased risk for developing sporadic Alzheimer's disease