Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
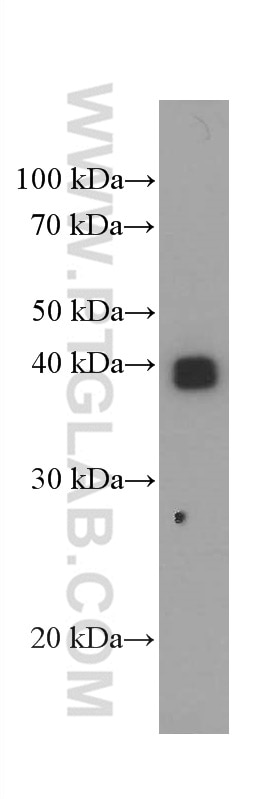
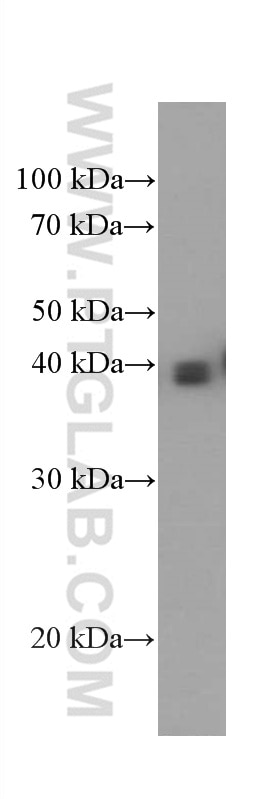
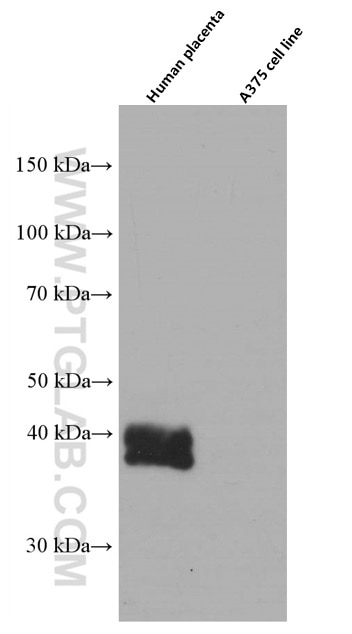
| Positive WB detected in | human placenta tissue |
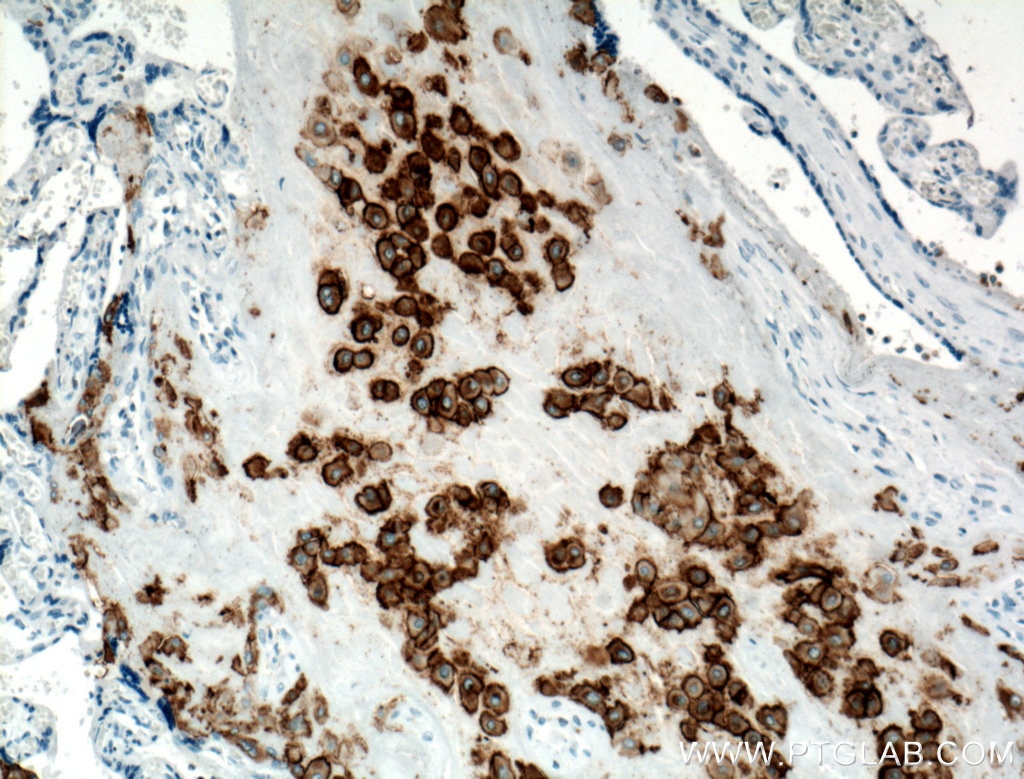
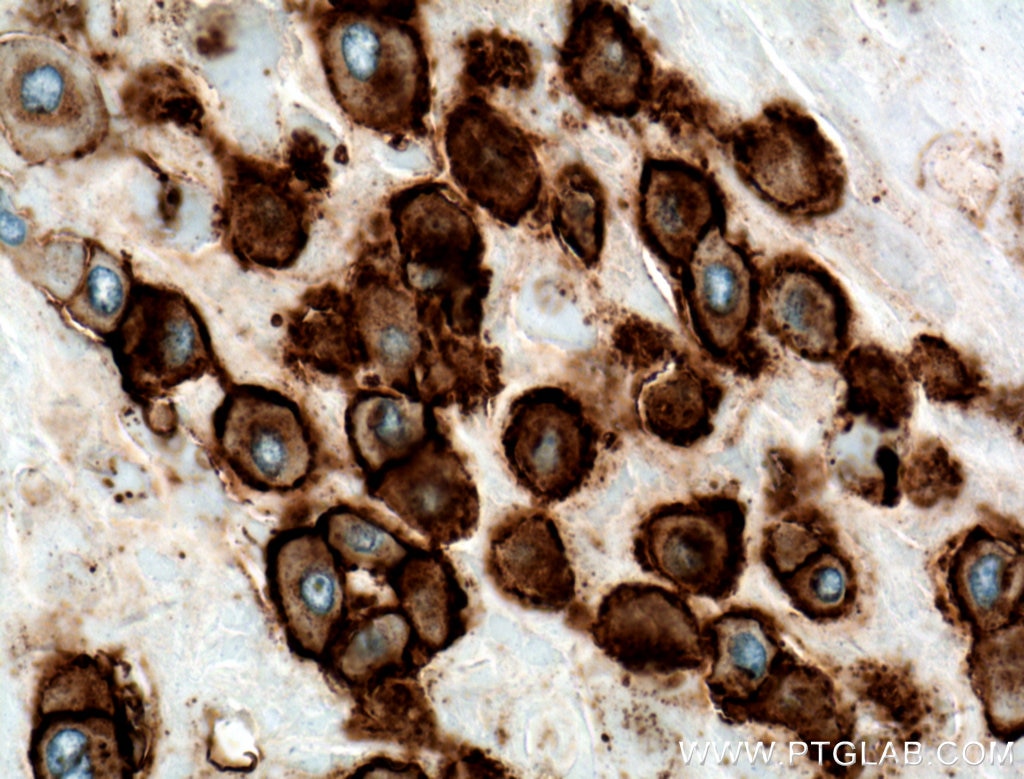
| Positive IHC detected in | human placenta tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:20000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IHC | See 14 publications below |
| IF | See 21 publications below |
Product Information
66447-1-Ig targets HLA-G in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag10839 Product name: Recombinant human HLA-G protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 26-308 aa of BC021708 Sequence: SHSMRYFSAAVSRPSRGEPRFIAMGYVDDTQFVRFDSDSACPRMEPRAPWVEREGPEYWEEETRNTKAHAQTDRMNLQTLRGYYNQSEASSHTLQWMIGCDLGSDGRLLRGYEQYAYDGKDYLALNEDLRSWTAADTAAQISKRKCEAANVAEQRRAYLEGTCVEWLHRYLENGKEMLQRADPPKTHVTHHPVFDYEATLRCWALGFYPAEIILTWQRDGEDQTQDVELVETKPAGDGTFQKWAAVVVPSGEEQRYTCHVQHEGLPEPLMLRWKQSSLPTIPI 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | major histocompatibility complex, class I, G |
| Calculated molecular weight | 338 aa, 38 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 33-45 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC021708 |
| Gene Symbol | HLA-G |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3135 |
| RRID | AB_2881816 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P17693 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens, also referred to as human leukocyte antigens (HLA), are encoded by genes located on the short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3). HLA-G is a non-classical MHC class I molecule with multiple immunoregulatory properties. HLA-G exhibits a restricted pattern of expression that includes placental extravillous trophoblasts at the maternal-fetal interface, where it abolishes maternal immune cell activity against fetus and establishes immune tolerance. Aberrant expression of HLA-G has been found in a variety of human neoplastic diseases. It plays an important role in the escape of tumor cells from immunosurveillance.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for HLA-G antibody 66447-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for HLA-G antibody 66447-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Aging Cell Advanced Maternal Age-associated SIRT1 Deficiency Compromises Trophoblast Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through an Increase in Vimentin Acetylation. | ||
Oxid Med Cell Longev Deletion of ACLY Disrupts Histone Acetylation and IL-10 Secretion in Trophoblasts, Which Inhibits M2 Polarization of Macrophages: A Possible Role in Recurrent Spontaneous Abortion. | ||
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids miR21 modulates the Hippo signaling pathway via interference with PP2A Bβ to inhibit trophoblast invasion and cause preeclampsia | ||
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res Suppression of GATA3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and simultaneous cellular senescence in human extravillous trophoblasts | ||
FASEB J Cyclin G2 upregulation impairs migration, invasion, and network formation through RNF123/Dvl2/JNK signaling in the trophoblast cell line HTR8/SVneo, a possible role in preeclampsia. | ||
Cell Signal Hypermethylation and low expression of FOXM1 predisposes women to unexplained recurrent miscarriage by impairing trophoblast stem cell proliferation |