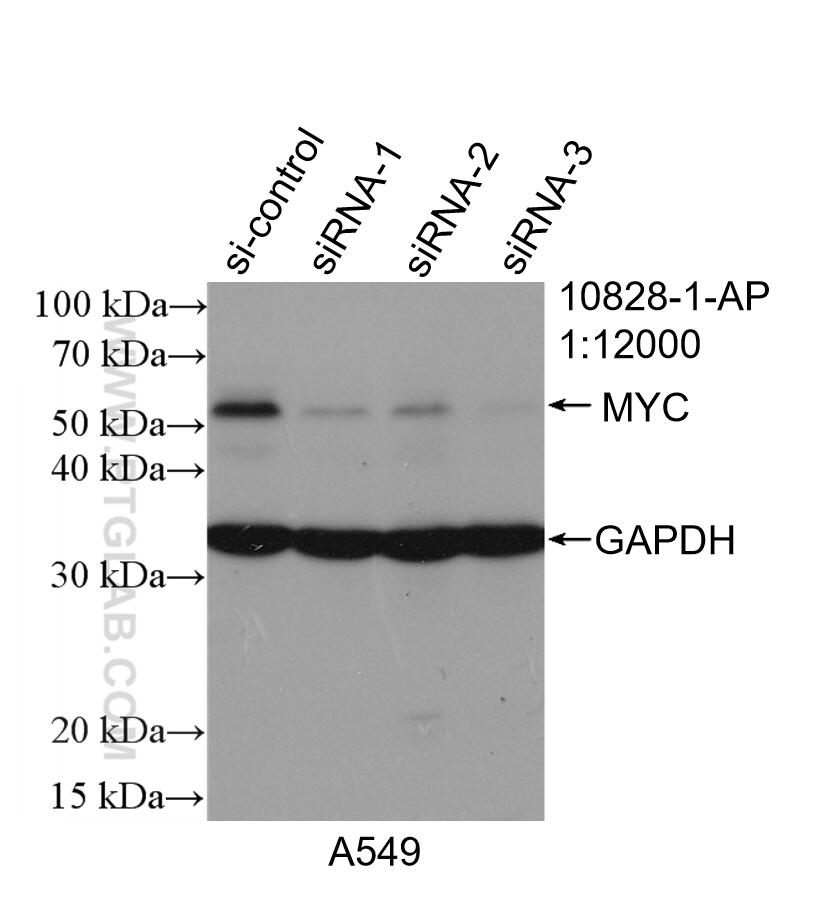
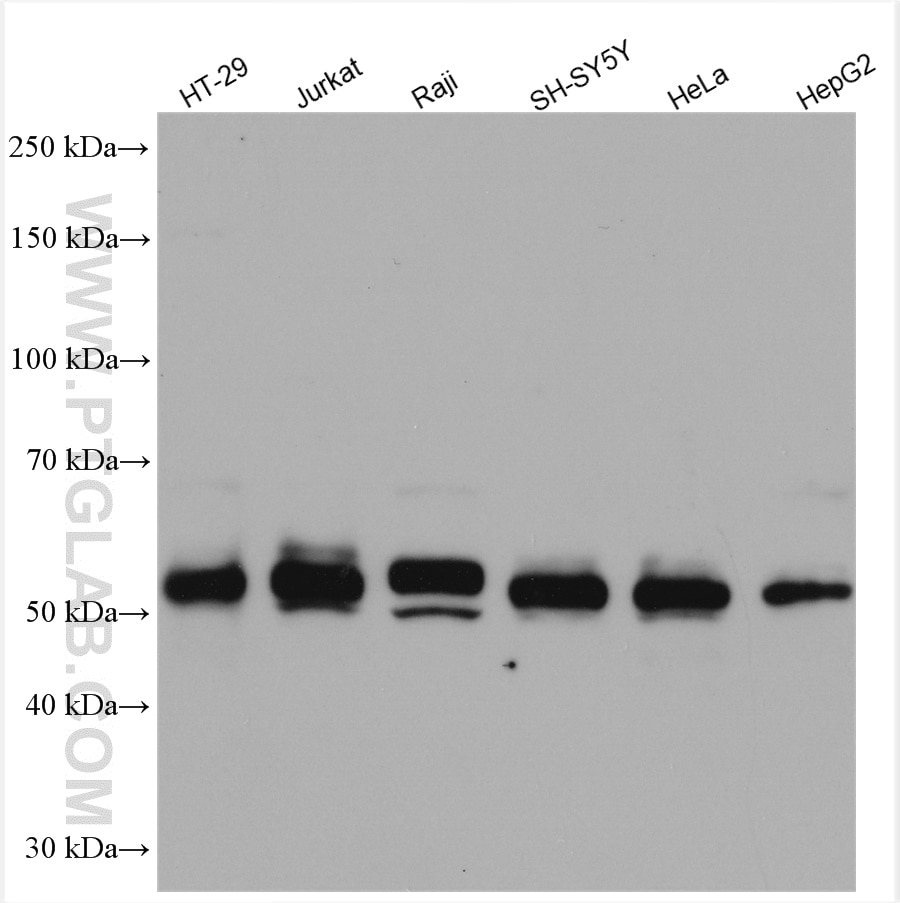
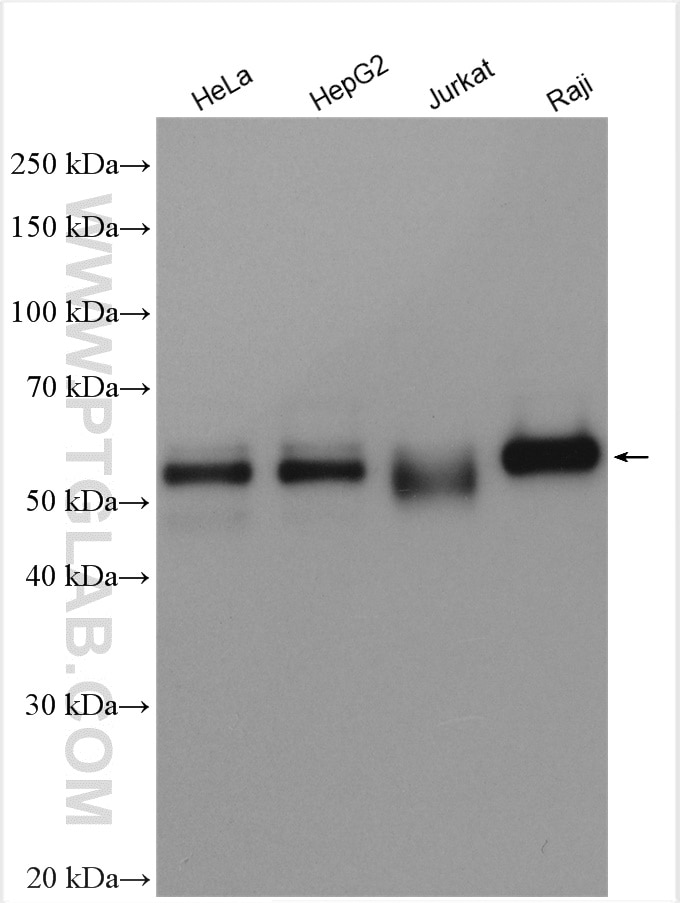
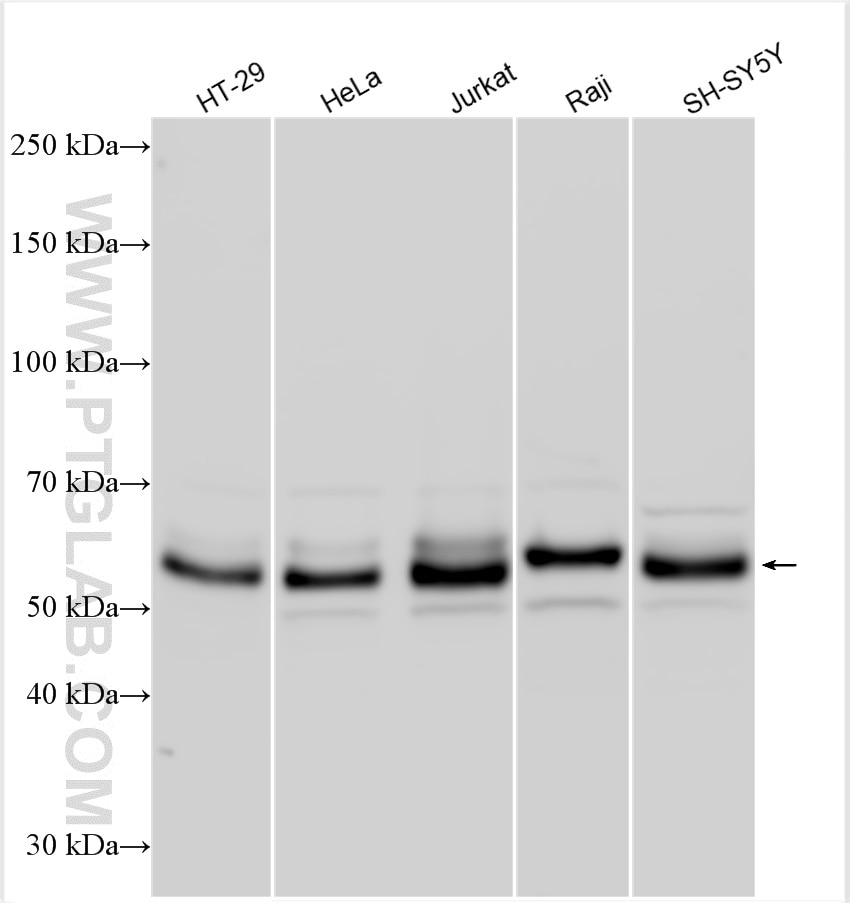
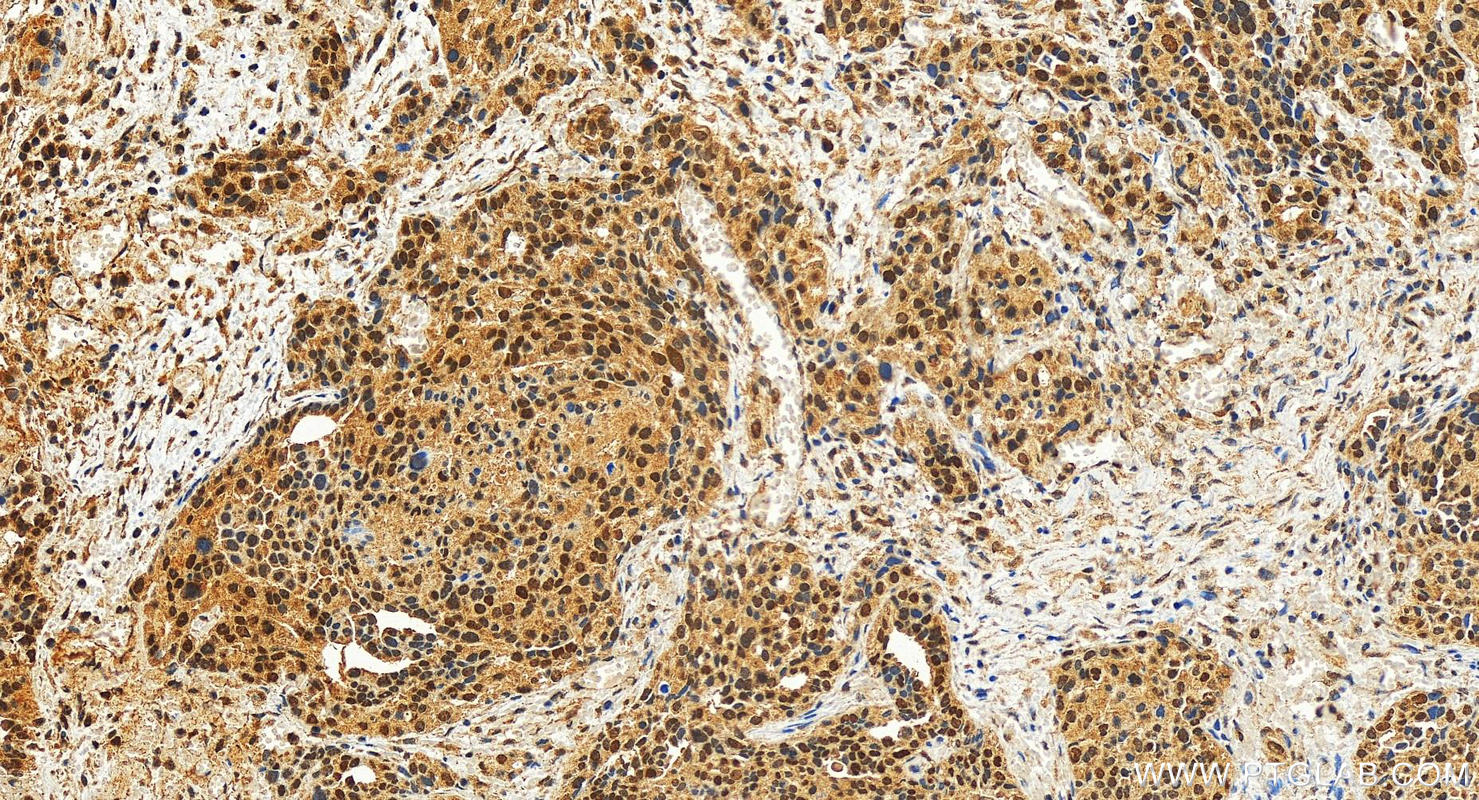
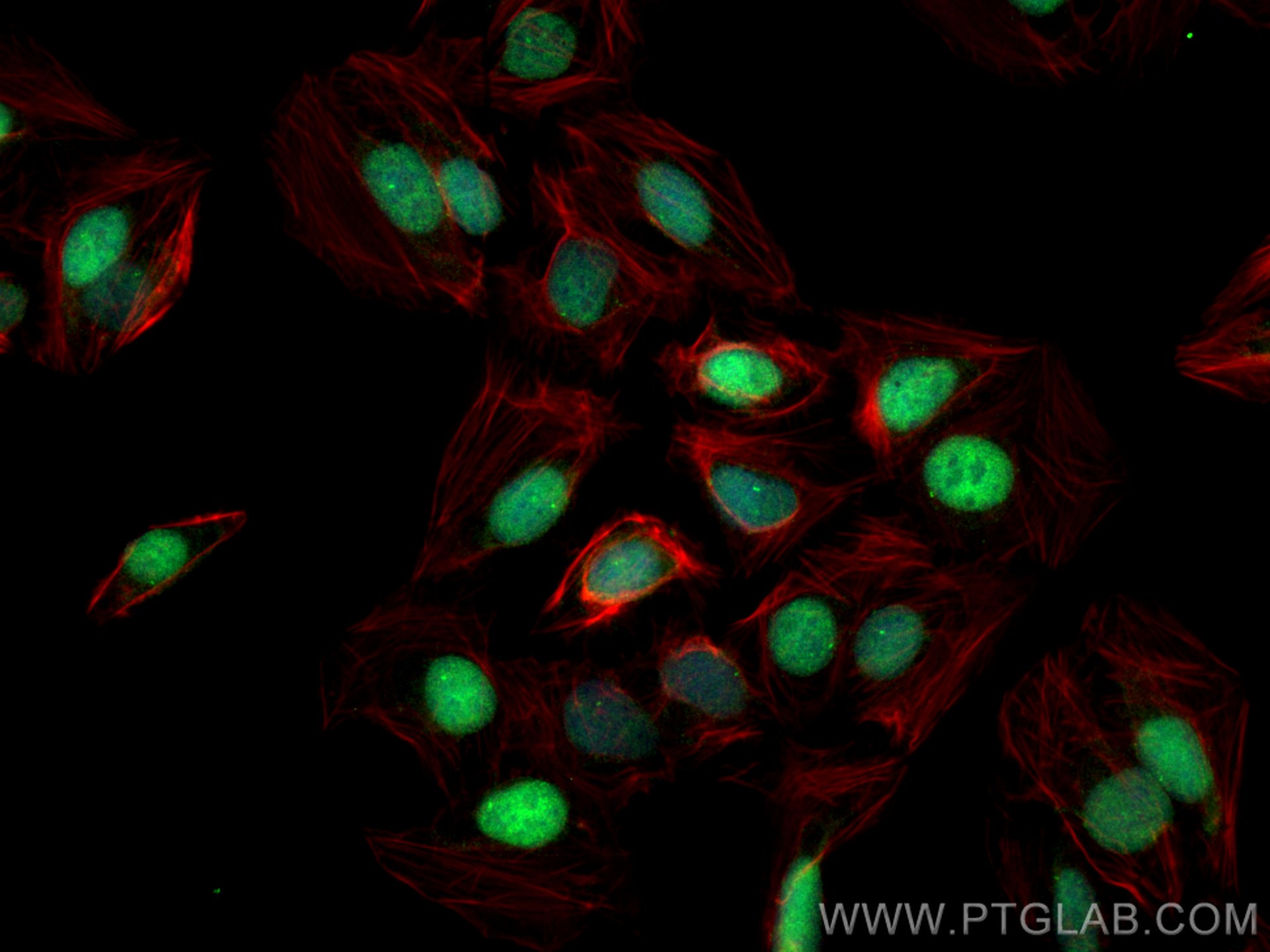
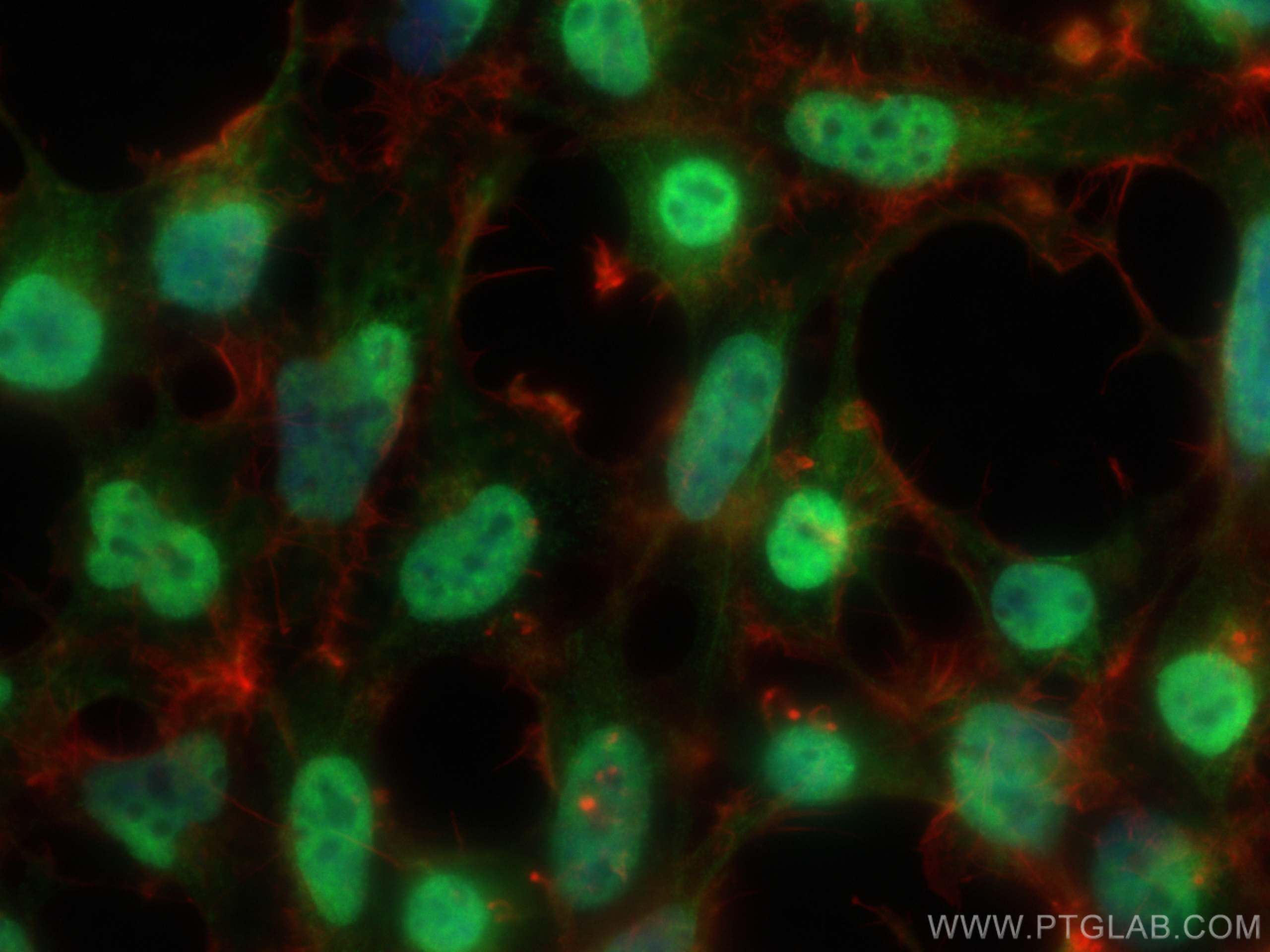
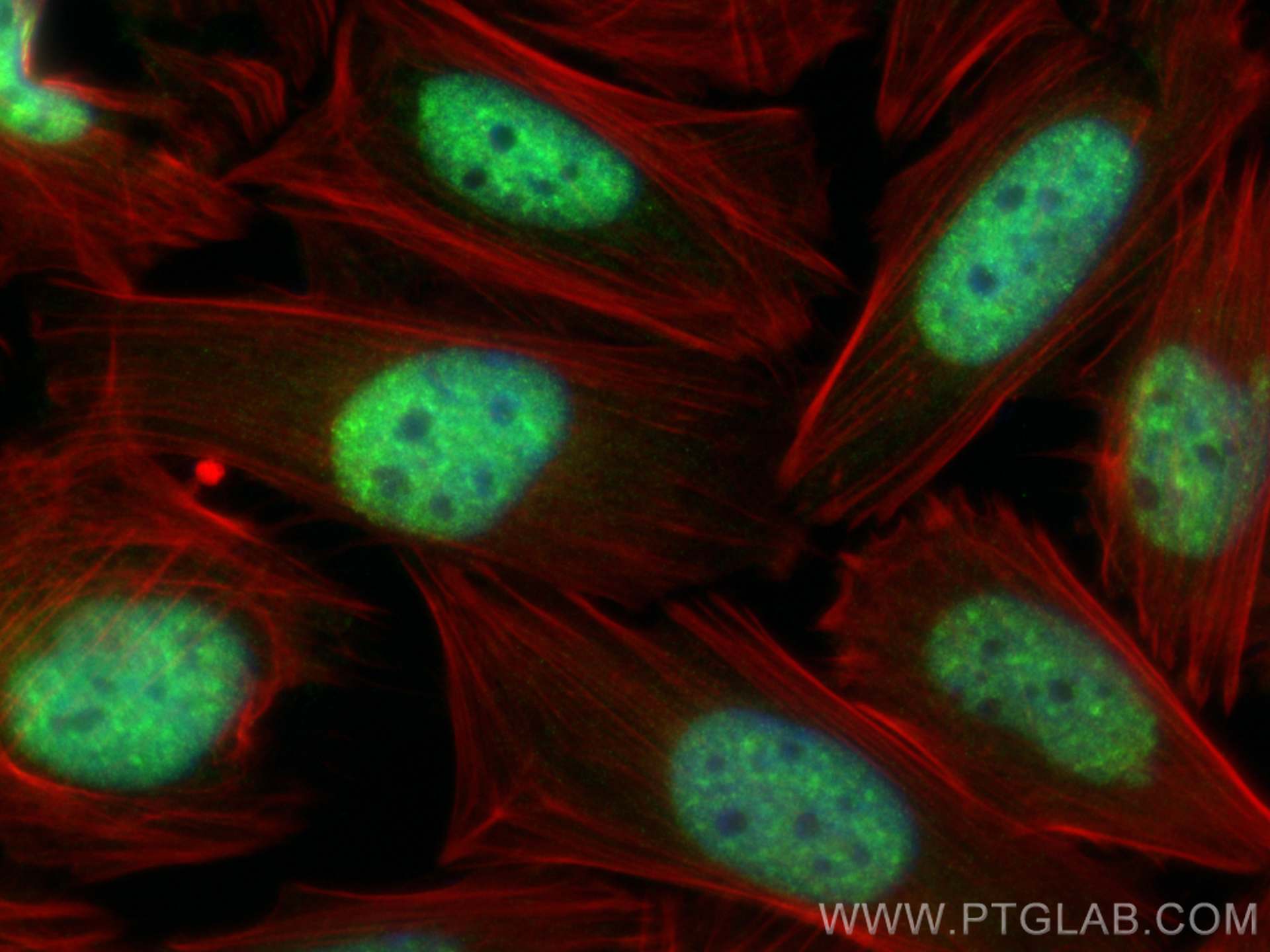
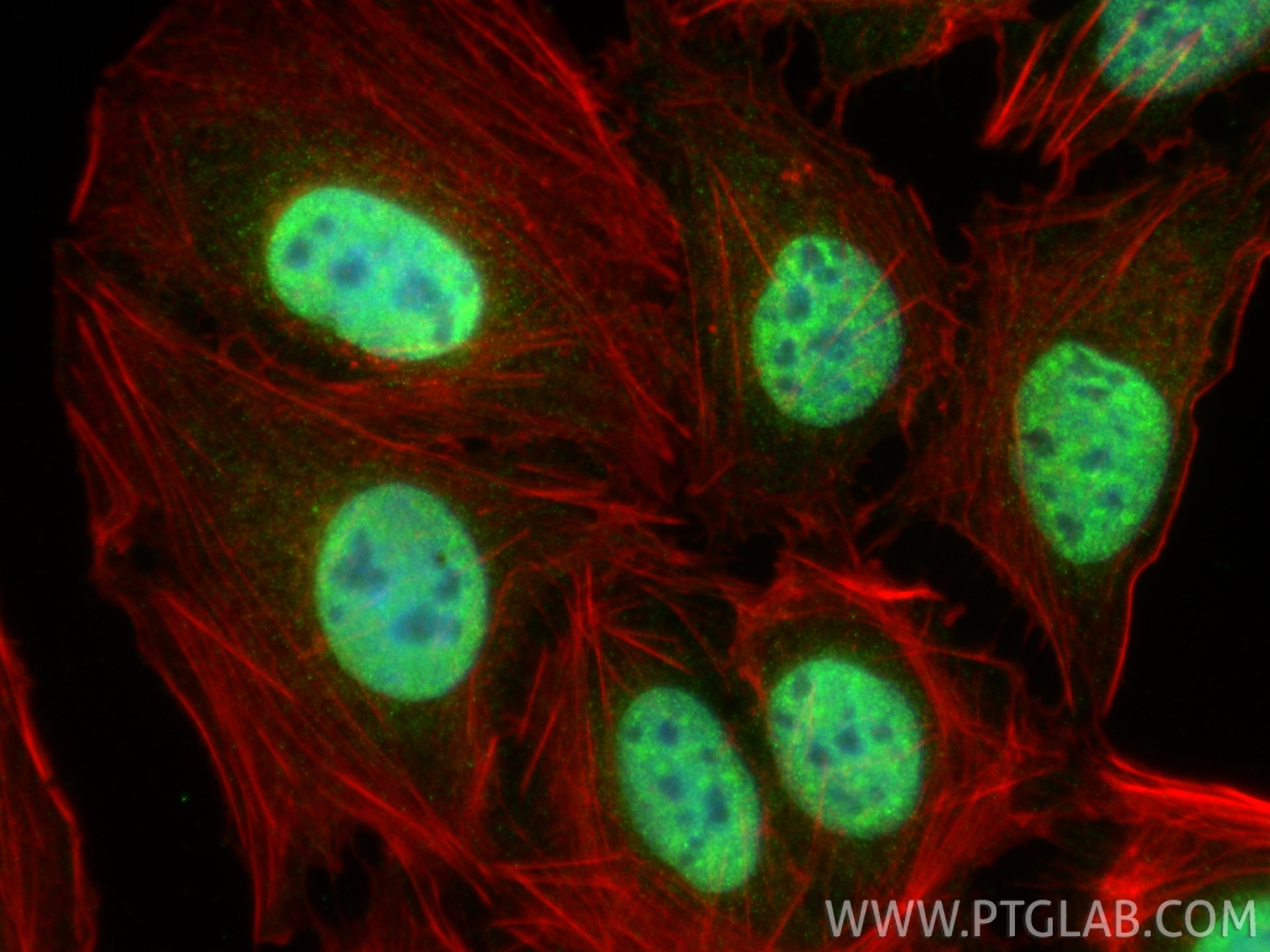
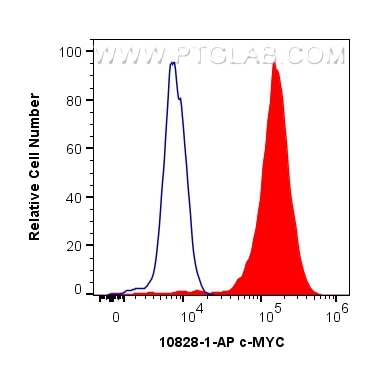
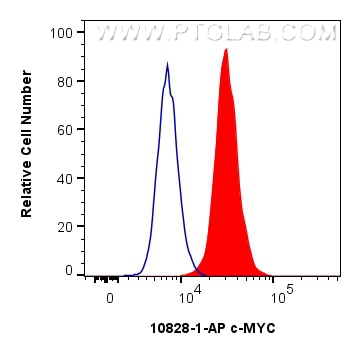
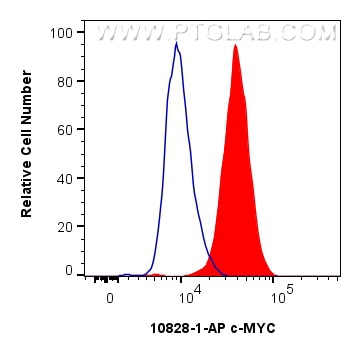
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
10828-1-PBS targets c-MYC in WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag1263 Product name: Recombinant human MYC protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 16-454 aa of BC000141 Sequence: MPLNVSFTNRNYDLDYDSVQPYFYCDEEENFYQQQQQSELQPPAPSEDIWKKFELLPTPPLSPSRRSGLCSPSYVAVTPFSLRGDNDGGGGSFSTADQLEMVTELLGGDMVNQSFICDPDDETFIKNIIIQDCMWSGFSAAAKLVSEKLASYQAARKDSGSPNPARGHSVCSTSSLYLQDLSAAASECIDPSVVFPYPLNDSSSPKSCASQDSSAFSPSSDSLLSSTESSPQGSPEPLVLHEETPPTTSSDSEEEQEDEEEIDVVSVEKRQAPGKRSESGSPSAGGHSKPPHSPLVLKRCHVSTHQHNYAAPPSTRKDYPAAKRVKLDSVRVLRQISNNRKCTSPRSSDTEENVKRRTHNVLERQRRNELKRSFFALRDQIPELENNEKAPKVVILKKATAYILSVQAEEQKLISEEDLLRKRREQLKHKLEQLRNSCA 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | v-myc myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog (avian) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 49 kDa |
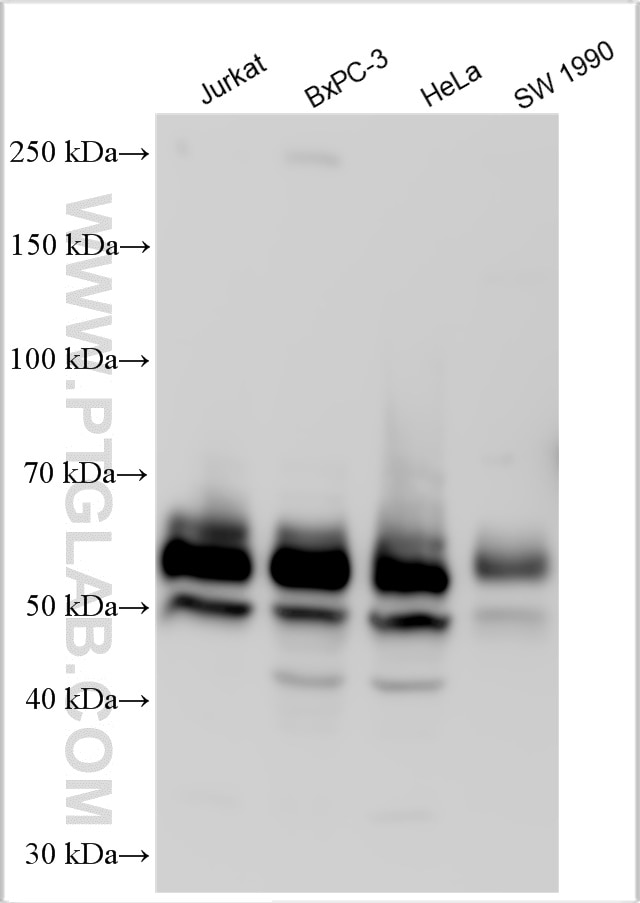
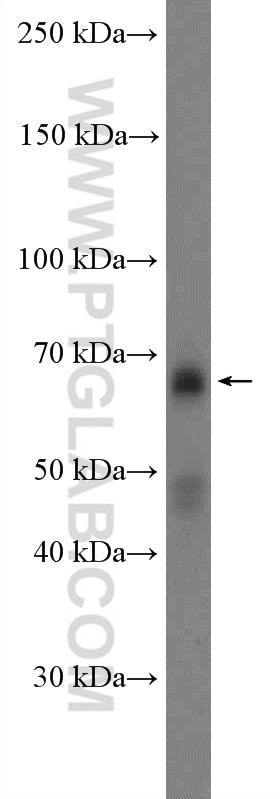
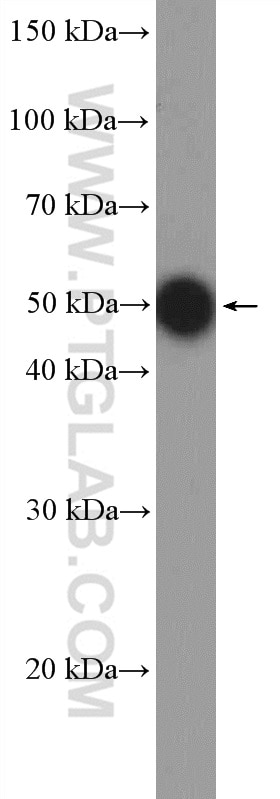
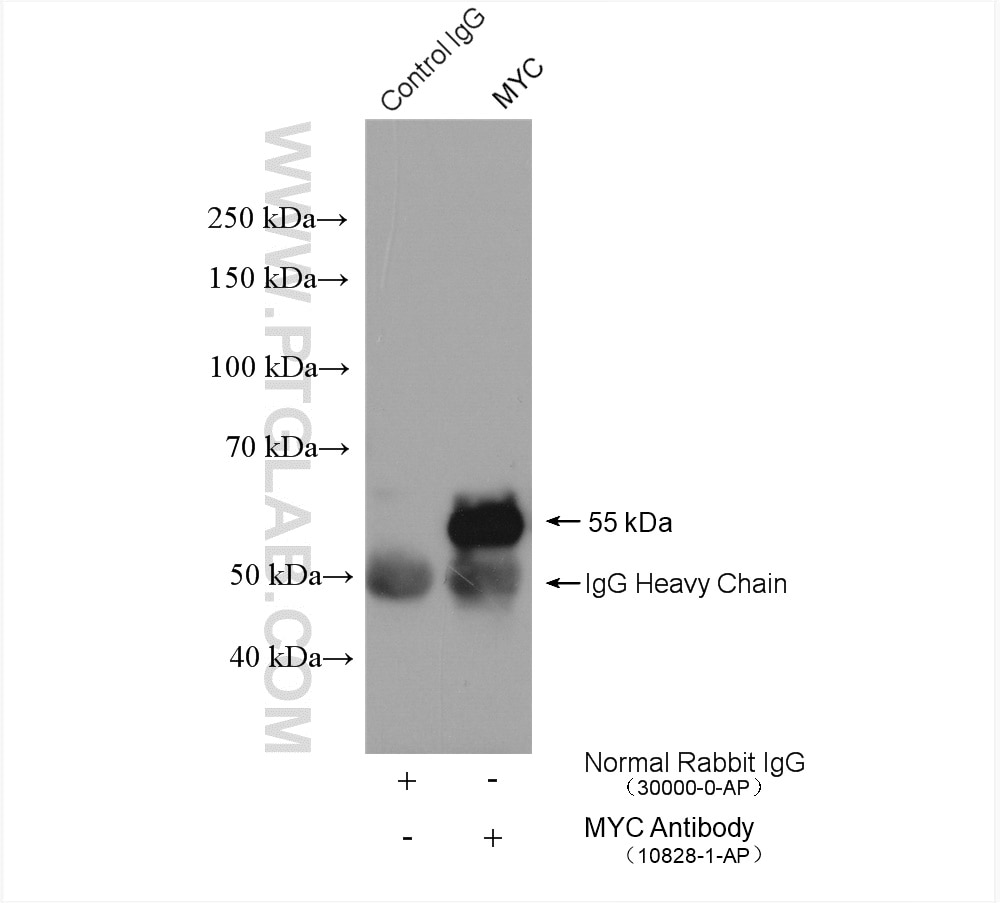
| Observed molecular weight | 62-65 kDa, 50 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC000141 |
| Gene Symbol | MYC |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4609 |
| RRID | AB_2148585 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01106 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Function
c-Myc (also known as Myc), together with l-Myc and n-Myc, belongs to the Myc family of transcription factors. c-Myc has a basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper domain and through heterodimerization can bind and regulate the transcriptional activity of genes, either by repression or activation. It is a key player in the regulation of cell growth and cell cycle progression and acts as a proto-oncogene.
Tissue specificity
c-Myc is ubiquitously expressed in almost all cell types and its expression positively correlates with tissue proliferative capacity. c-Myc is also expressed during embryogenesis and is upregulated in many cancer types.
Involvement in disease
· Upregulated in many cancer types, especially in aggressive, poorly differentiated tumors.
· Mutations in the MYC gene and breakpoint translocations within the MYC gene cause Burkitt lymphoma.
Isoforms
There are 3 different isoforms of c-Myc: c-Myc1, c-Myc2, and c-MycS (PMID: 16260605). They differ in molecular size, can be preferentially expressed during cell growth, and are reported to be functionally distinct. The 50kDa band recognized by antibody is the native form of MYC, while the other bands, between 60-70kDa, are the phosphorylated form of MYC (PMID: 12189186).
Post-translational modifications
c-Myc is subject to various post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, acetylation, and ubiquitinylation (PMID: 16987807), which regulate its activity.
Cellular localization
c-Myc localizes to the nucleus but can also be present in the cytoplasm of certain cancer types.