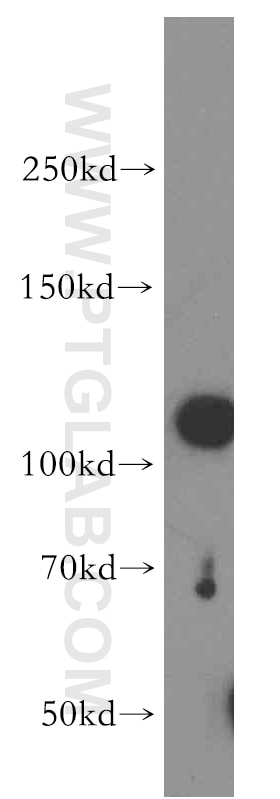
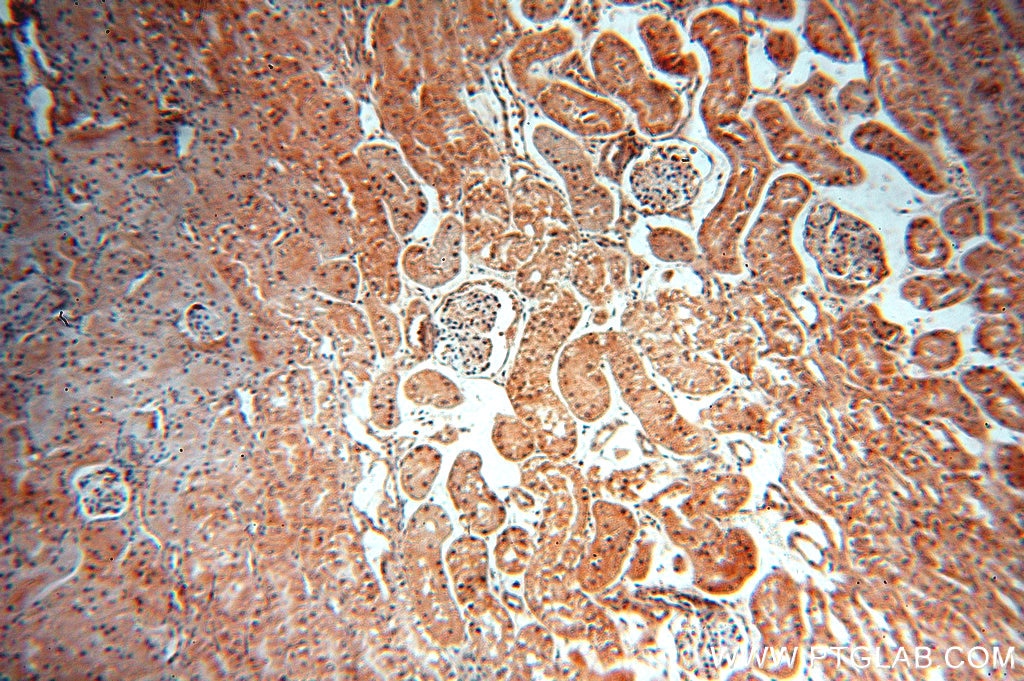
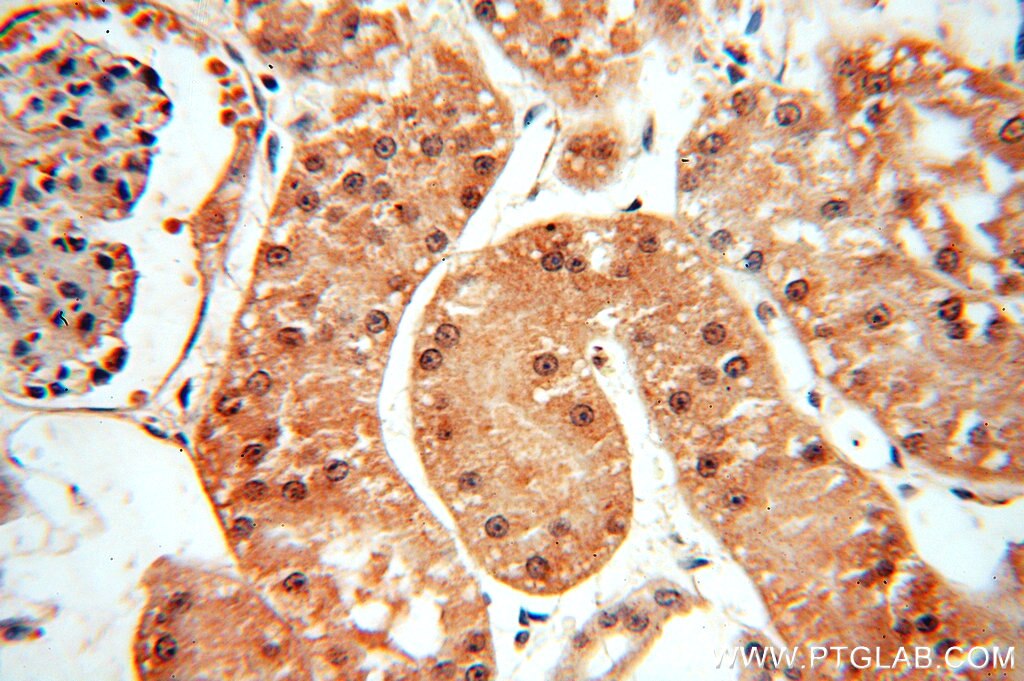
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
12915-1-AP targets CRM1 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag3488 Product name: Recombinant human XPO1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-302 aa of BC032847 Sequence: MPAIMTMLADHAARQLLDFSQKLDINLLDNVVNCLYHGEGAQQRMAQEVLTHLKEHPDAWTRVDTILEFSQNMNTKYYGLQILENVIKTRWKILPRNQCEGIKKYVVGLIIKTSSDPTCVEKEKVYIGKLNMILVQILKQEWPKHWPTFISDIVGASRTSESLCQNNMVILKLLSEEVFDFSSGQITQVKSKHLKDSMCNEFSQIFQLCQFVMENSQNAPLVHATLETLLRFLNWIPLGYIFETKLISTLIYKFLNVPMFRNVSLKCLTEIAGVSVSQYEEQFVTLFTLTMMQLKQMLPLNT 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | exportin 1 (CRM1 homolog, yeast) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 1071 aa, 123 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 100-110 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC032847 |
| Gene Symbol | CRM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7514 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O14980 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
CRM1 (chromosome region maintenance 1, also known as exportin-1 or XPO1), a member of the karyopherin β family of transport receptors, is an important nuclear export receptor recognizing proteins bearing a leucine-rich nuclear export signal (PMID: 9323133). CRM1 is the major receptor for the export of proteins out of the nucleus and is also required for transport of many RNAs (PMID: 17317185). In addition to nuclear export, CRM1 also plays a role in centrosome duplication and spindle assembly (PMID: 22773955). Elevated CRM1 expression has been reported in several cancers, which implicates CRM1 as a potential anti-cancer drug target (PMID: 22677130; 21683812 ).