Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
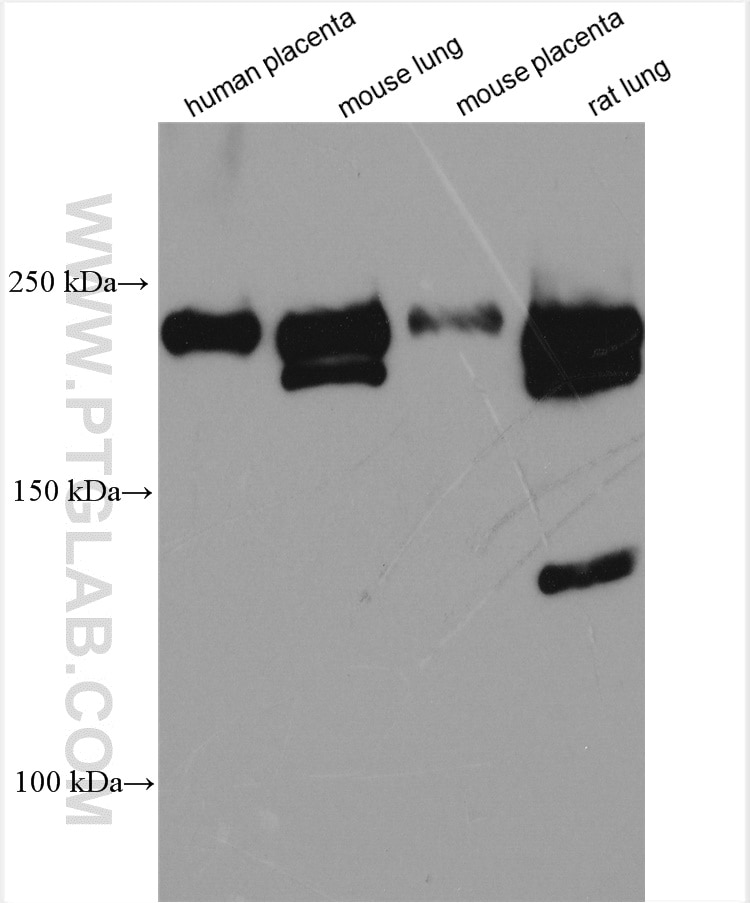
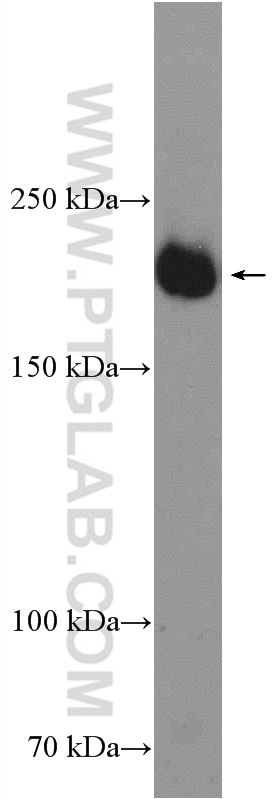
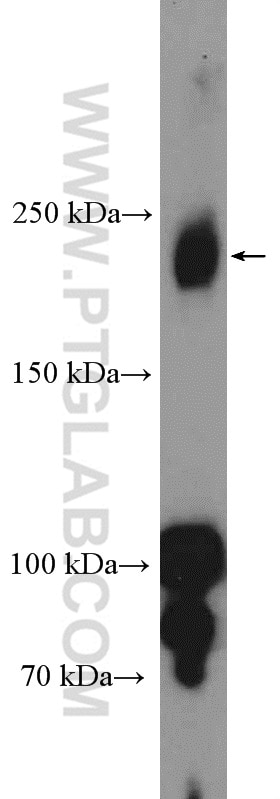
| Positive WB detected in | human placenta tissue, mouse heart tissue, mouse lung tissue, mouse placenta tissue, rat lung tissue |
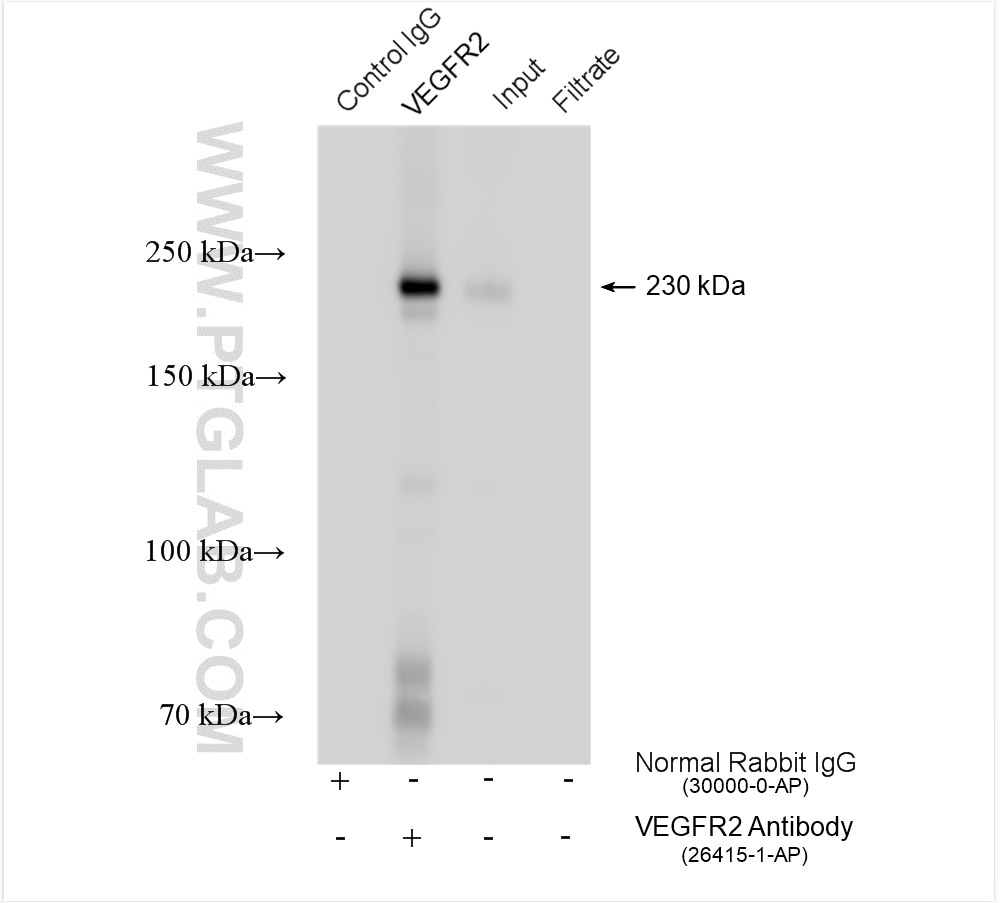
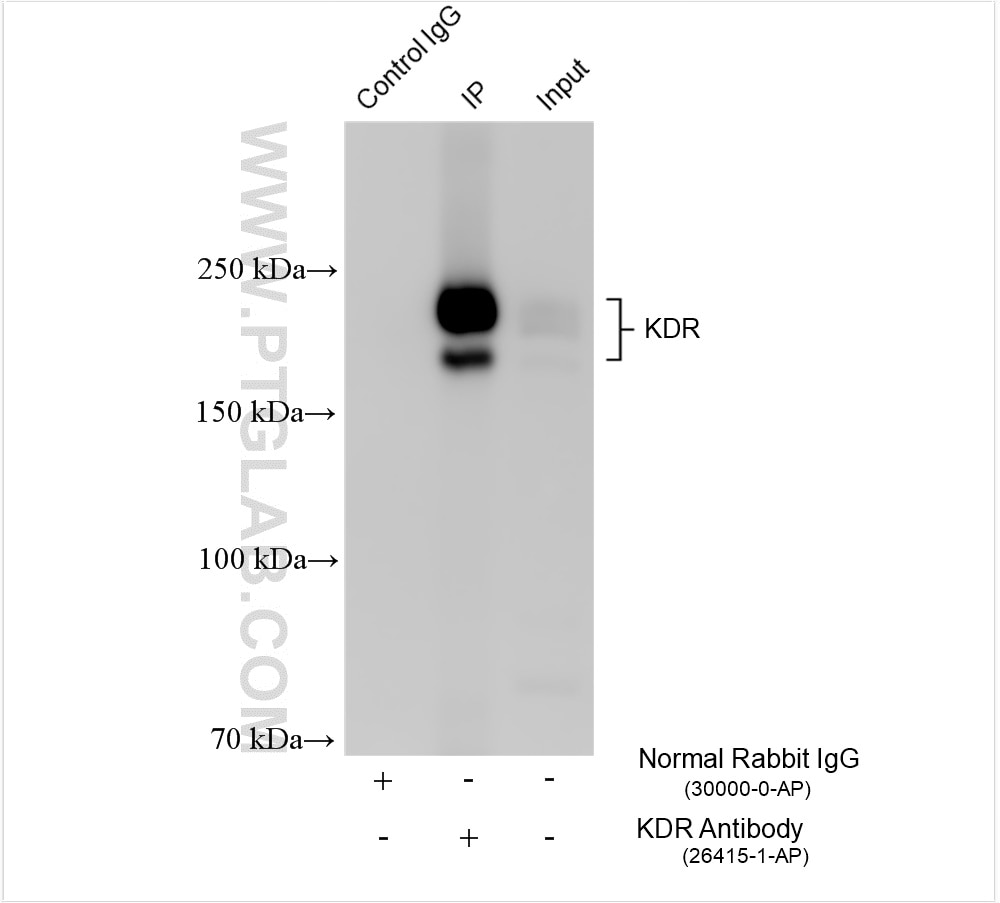
| Positive IP detected in | human placenta tissue, rat skeletal muscle tissue |
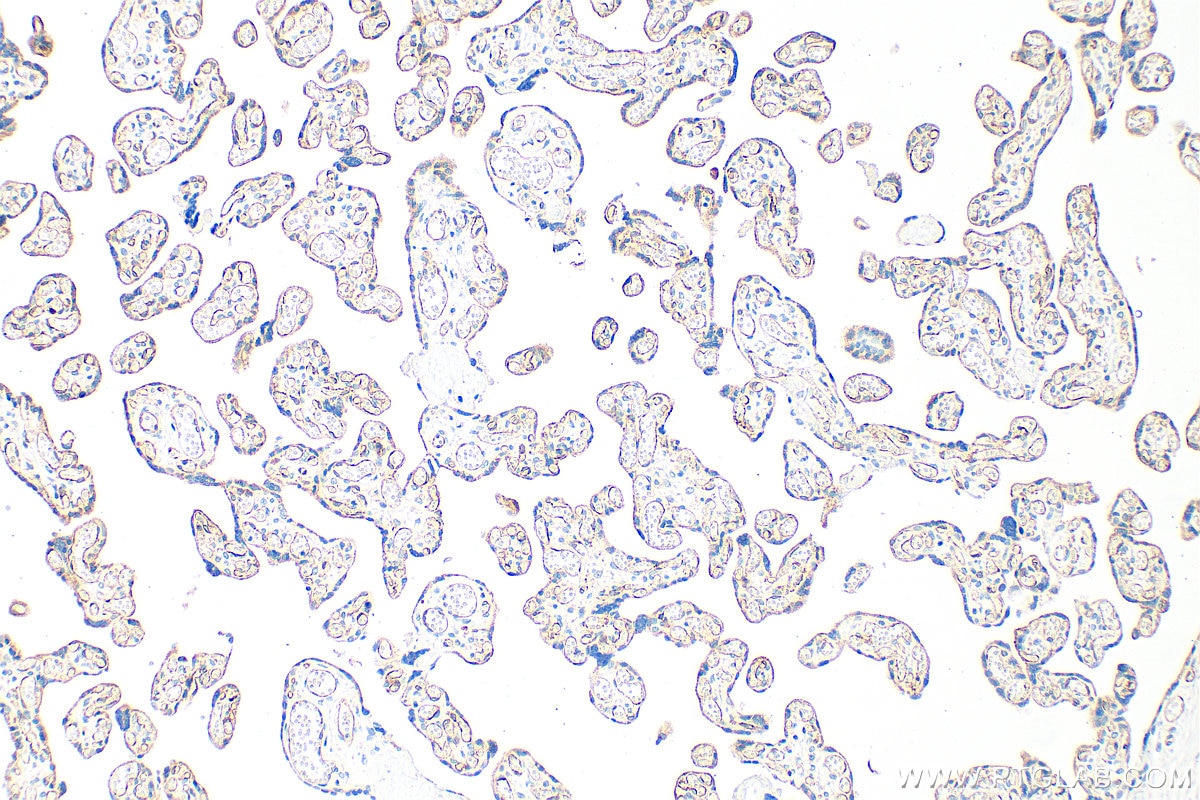
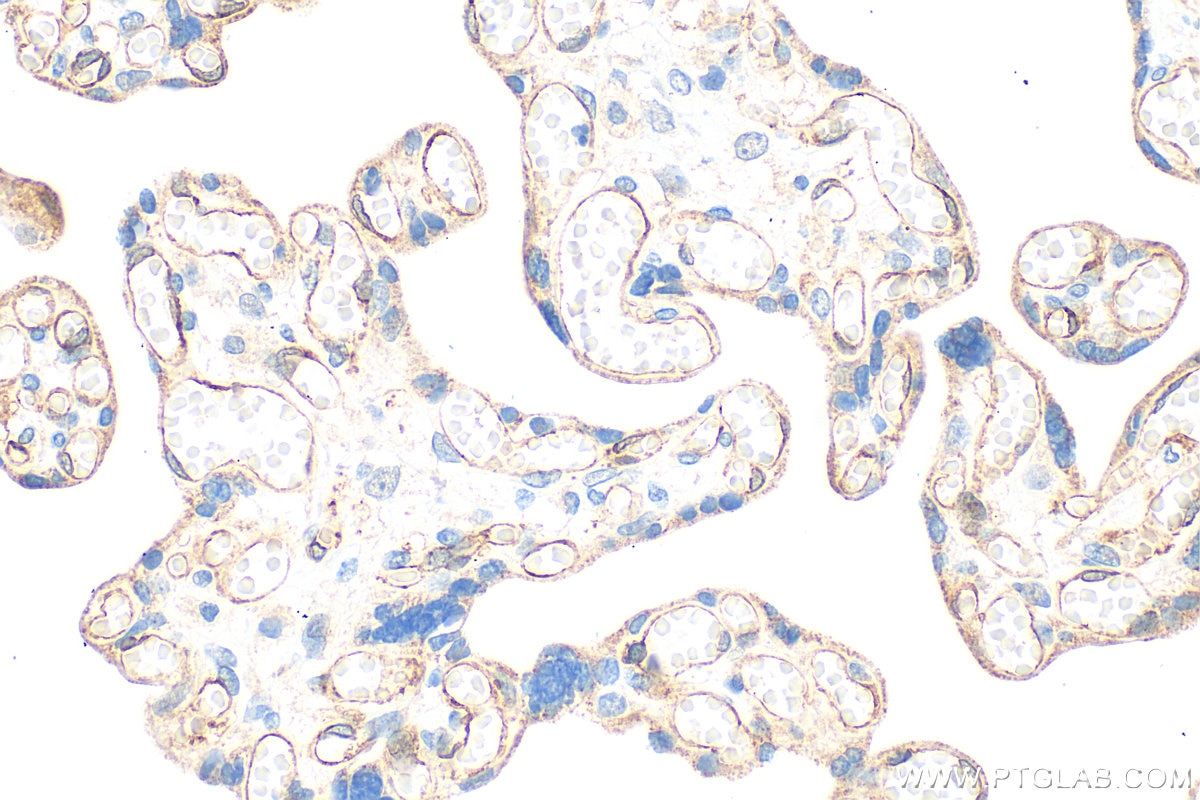
| Positive IHC detected in | human placenta tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
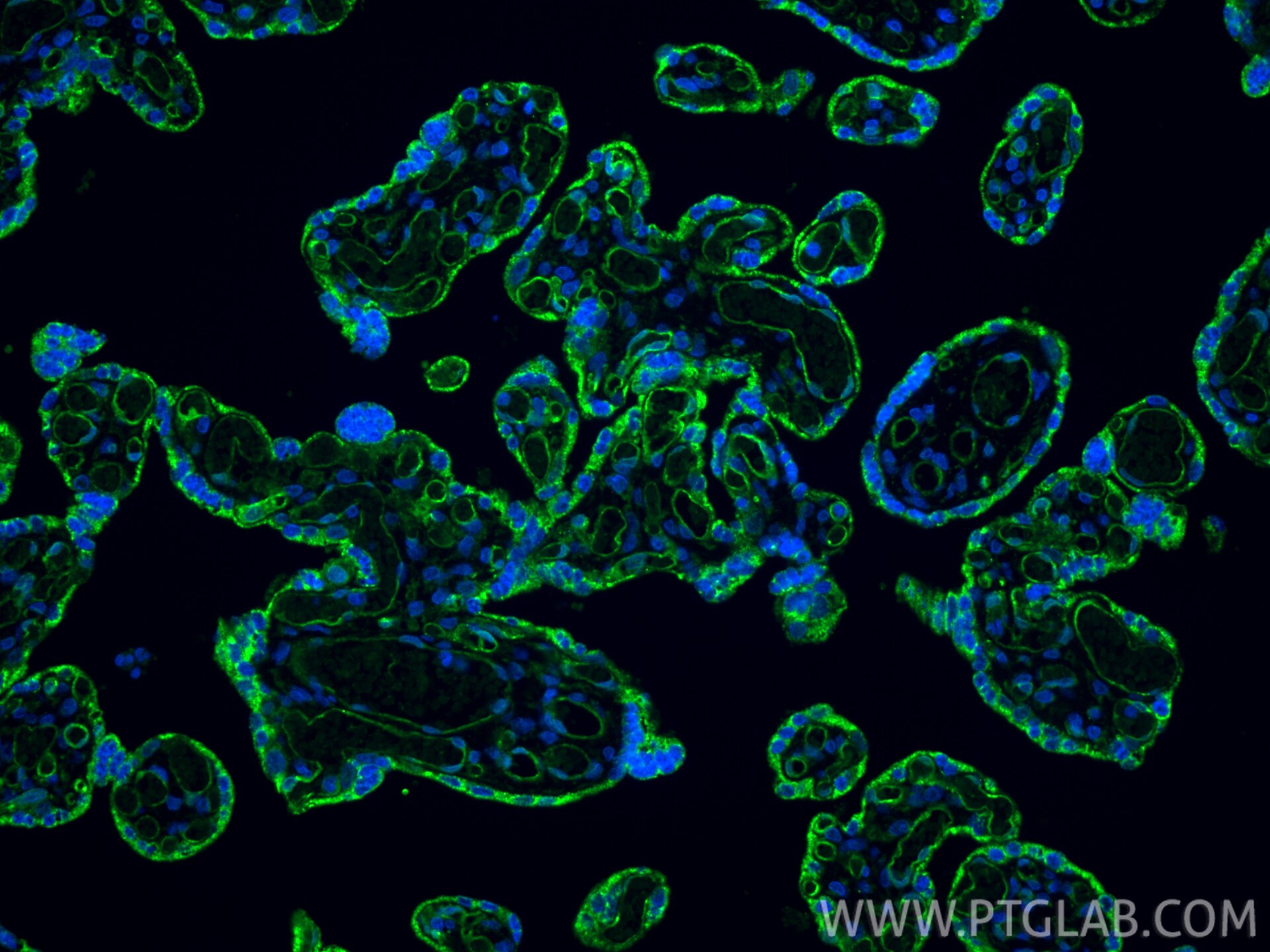
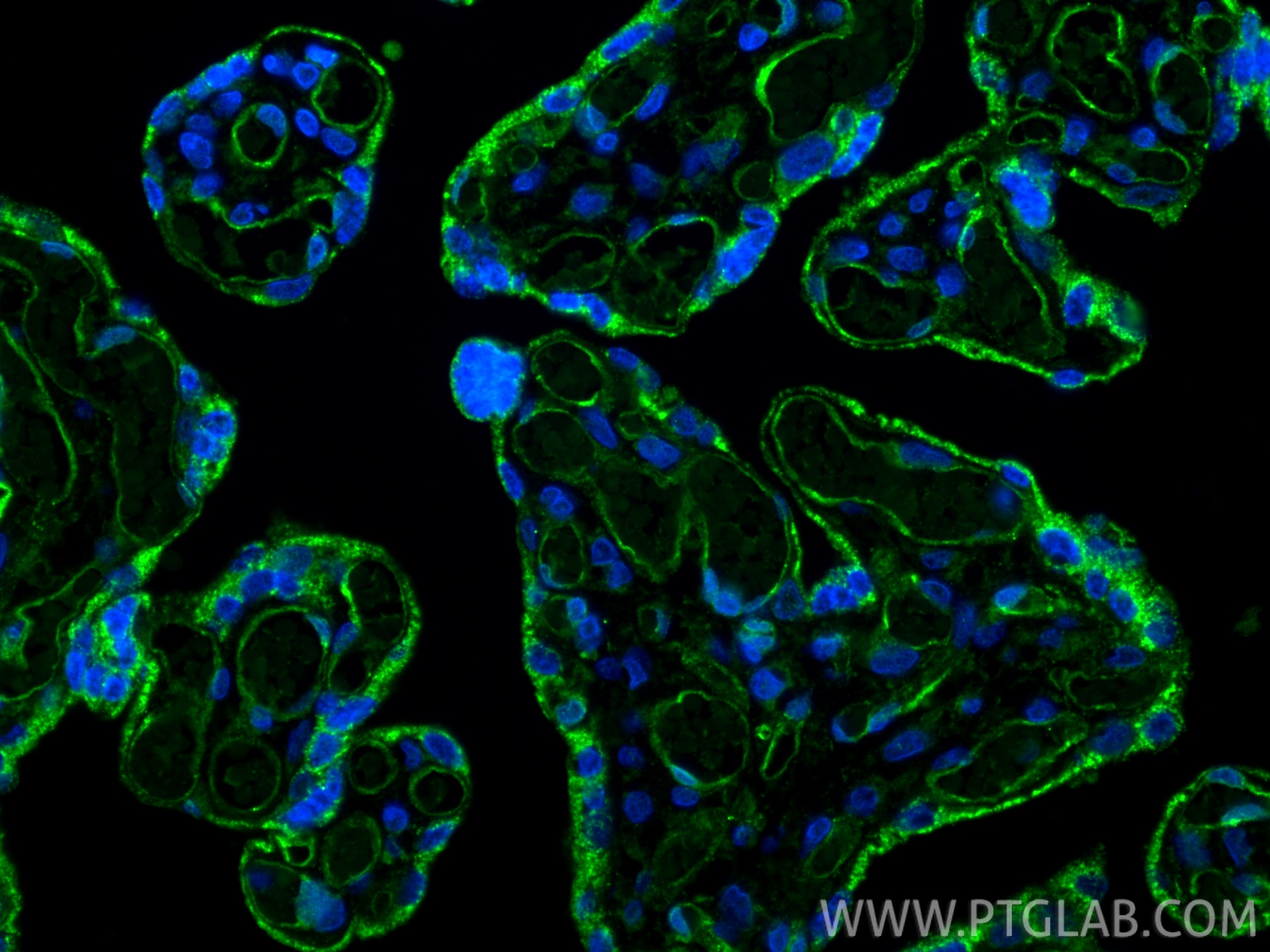
| Positive IF-P detected in | human placenta tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:8000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 102 publications below |
| IHC | See 19 publications below |
| IF | See 37 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
26415-1-AP targets VEGFR2/KDR in WB, IHC, IF-P, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, canine, sheep |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag24589 Product name: Recombinant human KDR protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1158-1345 aa of BC131822 Sequence: EHLGNLLQANAQQDGKDYIVLPISETLSMEEDSGLSLPTSPVSCMEEEEVCDPKFHYDNTAGISQYLQNSKRKSRPVSVKTFEDIPLEEPEVKVIPDDNQTDSGMVLASEELKTLEDRTKLSPSFGGMVPSKSRESVASEGSNQTSGYQSGYHSDDTDTTVYSSEEAELLKLIEIGVQTGSTAQILQP 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | kinase insert domain receptor (a type III receptor tyrosine kinase) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 1356 aa, 152 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 180-200 kDa, 230 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC131822 |
| Gene Symbol | KDR |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3791 |
| RRID | AB_2756527 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P35968 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
KDR, also named as VEGFR-2, FLK1 and CD309, is a receptor for VEGF or VEGFC. KDR which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, has a tyrosine-protein kinase activity. The VEGF-kinase ligand/receptor signaling system plays a key role in vascular development and regulation of vascular permeability. In case of HIV-1 infection, the interaction with extracellular viral Tat protein seems to enhance angiogenesis in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions. KDR functions as the main mediator of VEGF-induced endothelial proliferation, survival, migration, tubular morphogenesis and sprouting. Mutations of this gene are implicated in infantile capillary hemangiomas.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for VEGFR2/KDR antibody 26415-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for VEGFR2/KDR antibody 26415-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for VEGFR2/KDR antibody 26415-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for VEGFR2/KDR antibody 26415-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Bioact Mater A bioactive composite hydrogel dressing that promotes healing of both acute and chronic diabetic skin wounds | ||
Sci Bull (Beijing) Restoring sweat gland function in mice using regenerative sweat gland cells derived from chemically reprogrammed human epidermal keratinocytes | ||
J Exp Med Secretogranin III as a disease-associated ligand for antiangiogenic therapy of diabetic retinopathy. | ||
Aging Dis MSC-Derived Exosomes can Enhance the Angiogenesis of Human Brain MECs and Show Therapeutic Potential in a Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease. | ||
J Neuroinflammation Succinate-induced macrophage polarization and RBP4 secretion promote vascular sprouting in ocular neovascularization | ||
Bioact Mater Electrochemically derived nanographene oxide activates endothelial tip cells and promotes angiogenesis by binding endogenous lysophosphatidic acid. |