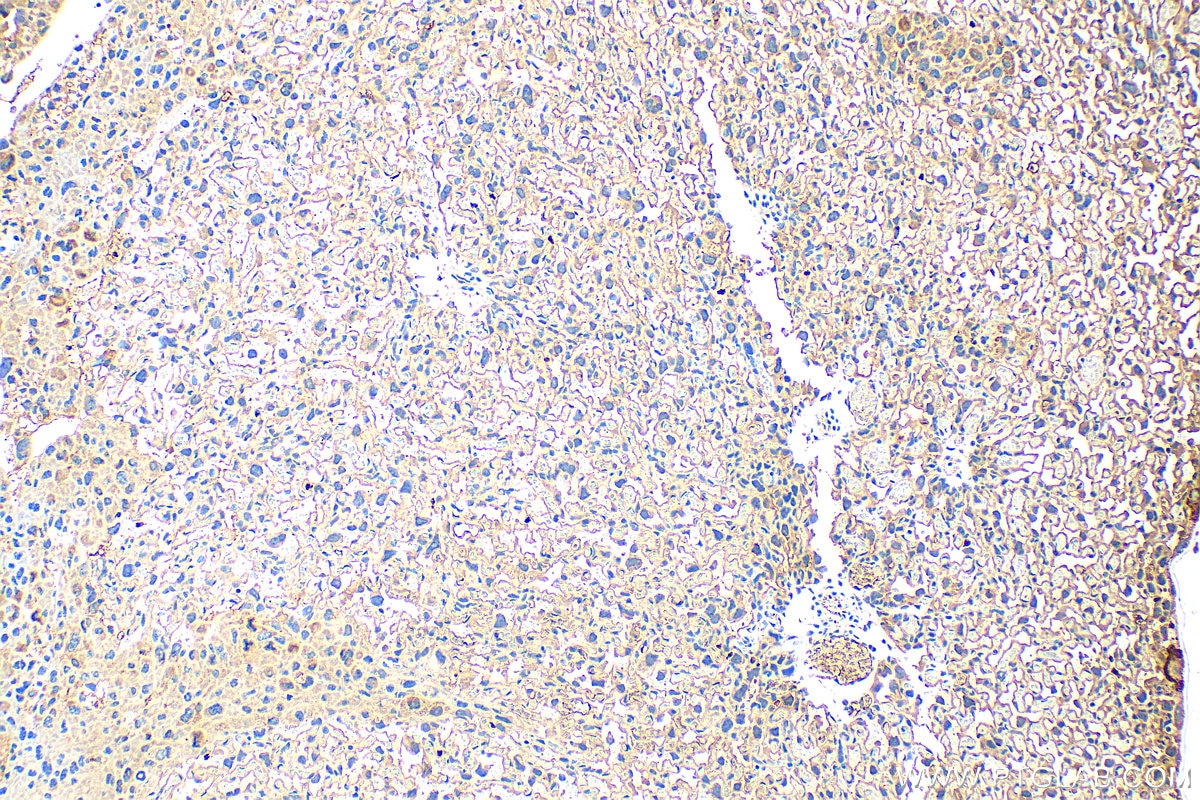
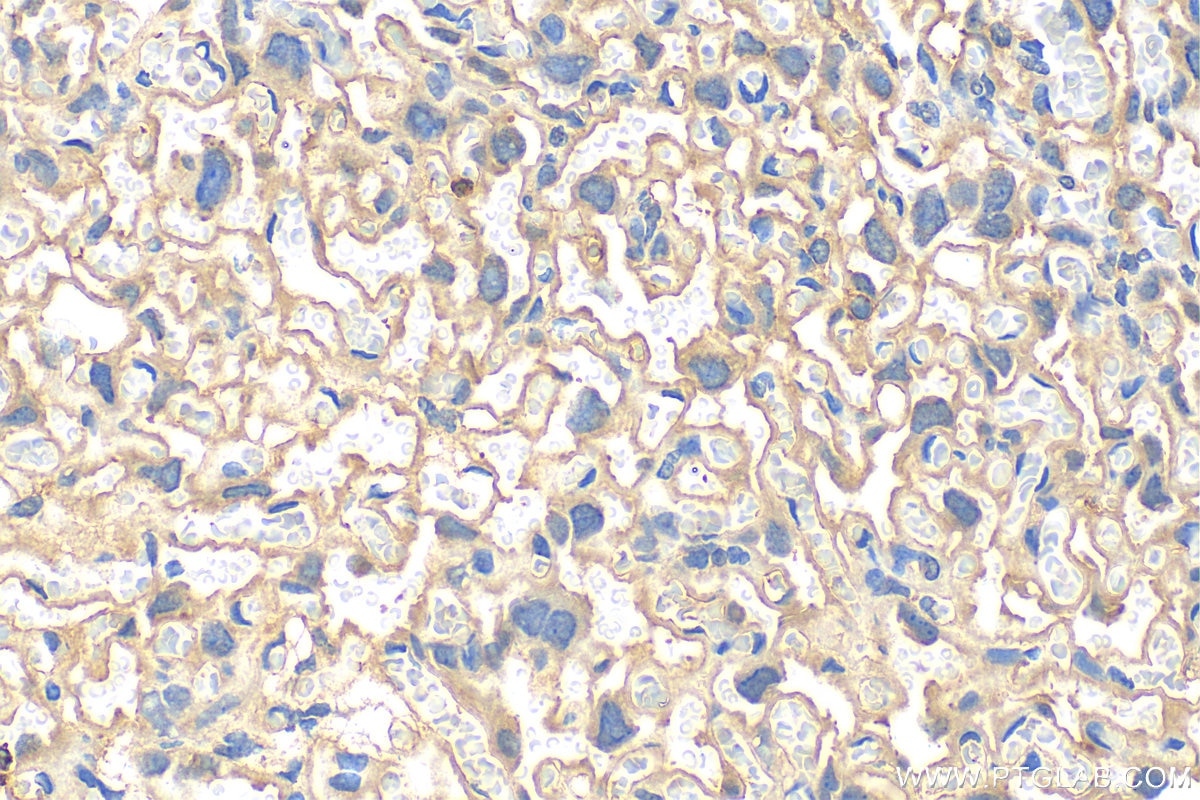
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
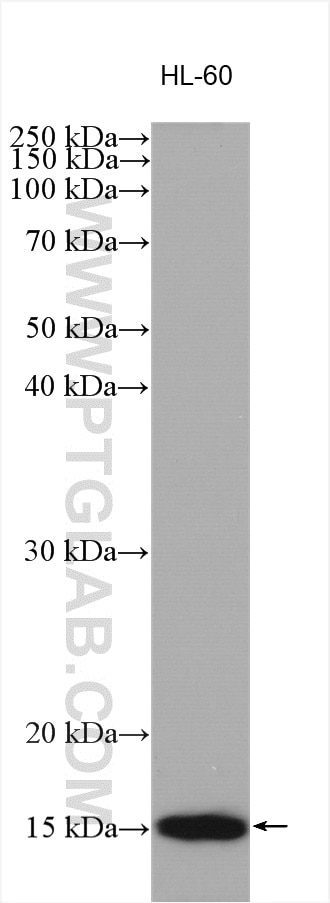
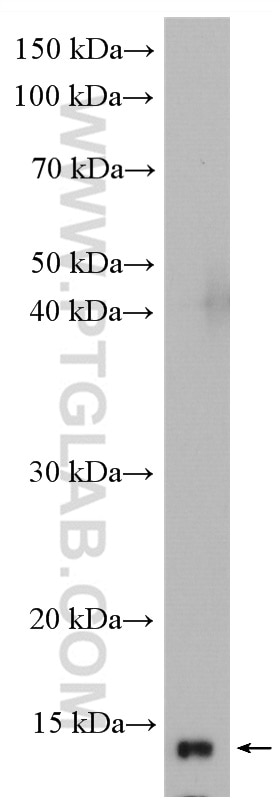
| Positive WB detected in | HL-60 cells, PC-12 cells, THP-1 cells |
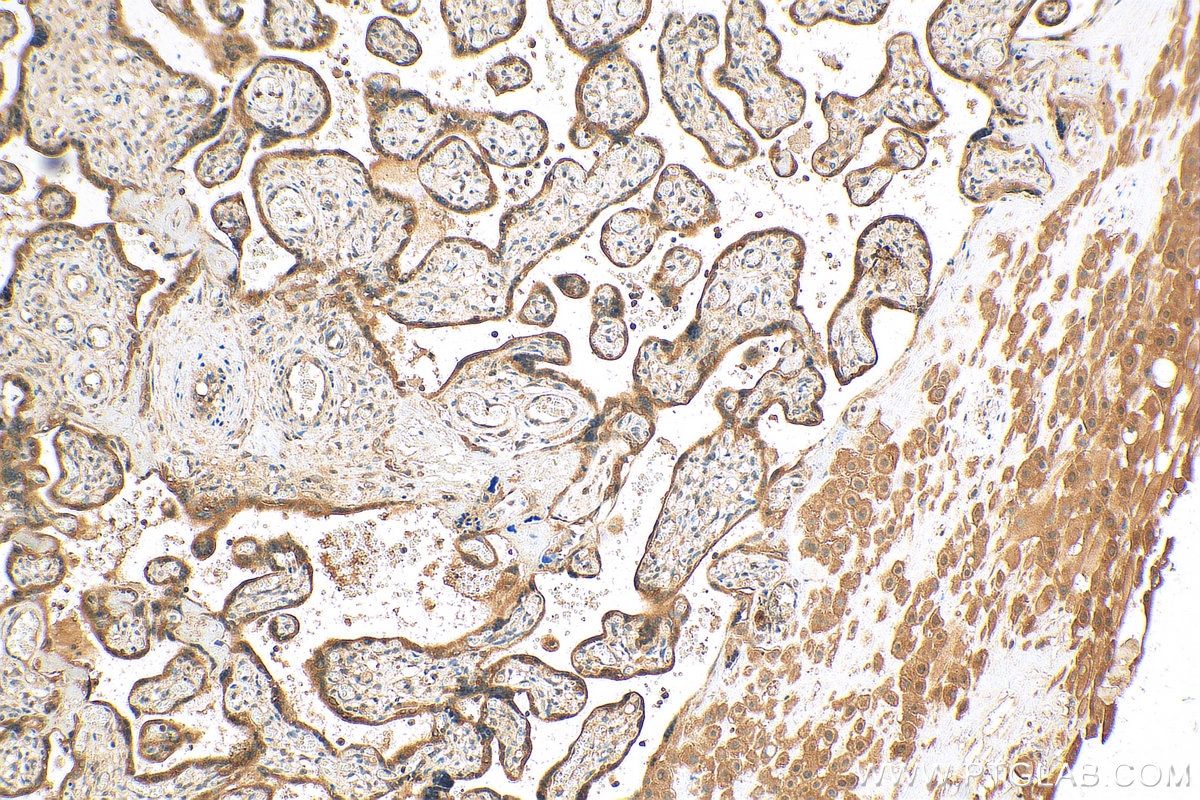
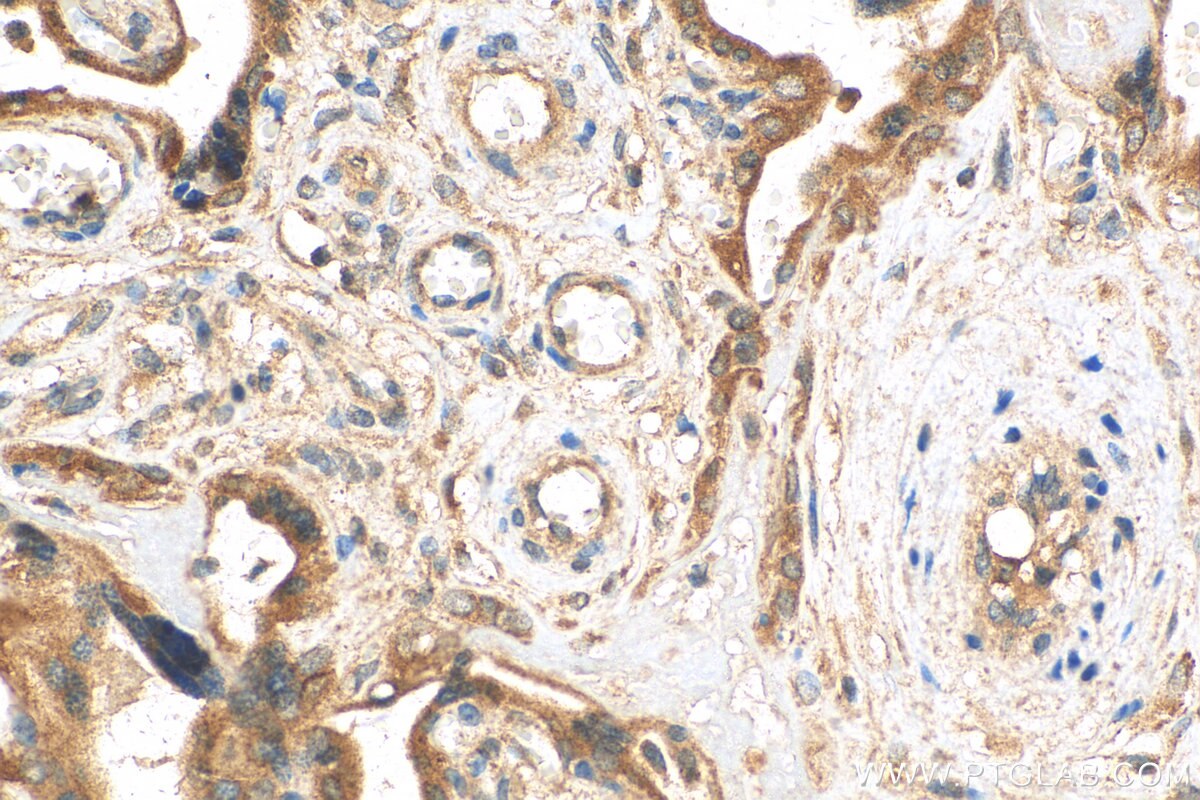
| Positive IHC detected in | human placenta tissue, mouse placenta tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 19 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
| CoIP | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
15546-1-AP targets VAMP8 in WB, IHC, IF, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag7903 Product name: Recombinant human VAMP8 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-81 aa of BC001634 Sequence: MEEASEGGGNDRVRNLQSEVEGVKNIMTQNVERILARGENLEHLRNKTEDLEATSEHFKTTSQKVARKFWWKNVKMIVLIC 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | vesicle-associated membrane protein 8 (endobrevin) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 11 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 15 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC001634 |
| Gene Symbol | VAMP8 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8673 |
| RRID | AB_2878150 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9BV40 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
VAMP8, also named endobrevin, is a member of the vesicle-associated membrane protein (VAMP)/synaptobrevin family and the SNARE (soluble NSF-attachment protein receptor) superfamily. Characterized by a common sequence called the SNARE motif, SNARE proteins are involved in membrane fusion and vesicular transport (PMID: 11252968). VAMP8 is involved in autophagy by directly controlling the fusion of autophagosomes with the lysosomal membrane. It is required for dense-granule secretion in platelets and plays a role in regulated enzyme secretion in pancreatic acinar cells. VAMP8 is also involved in the abscission of the midbody during cell division, which leads to completely separate daughter cells.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for VAMP8 antibody 15546-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for VAMP8 antibody 15546-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Extracell Vesicles Identification of the SNARE complex that mediates the fusion of multivesicular bodies with the plasma membrane in exosome secretion | ||
Autophagy SDC1-dependent TGM2 determines radiosensitivity in glioblastoma by coordinating EPG5-mediated fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes | ||
Cell Mol Life Sci IGF2BP1-HAX-1 positive feedback loop-mediated HAX-1 overexpression blocks autophagic flux and promotes chemoresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ||
Arch Toxicol Mystery of methamphetamine-induced autophagosome accumulation in hippocampal neurons: loss of syntaxin 17 in defects of dynein-dynactin driving and autophagosome-late endosome/lysosome fusion. | ||
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf Weakened interaction of ATG14 and the SNARE complex blocks autophagosome-lysosome fusion contributes to fluoride-induced developmental neurotoxicity. | ||
Stem Cell Res Ther Microtubule destabilization caused by silicate via HDAC6 activation contributes to autophagic dysfunction in bone mesenchymal stem cells. |