Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
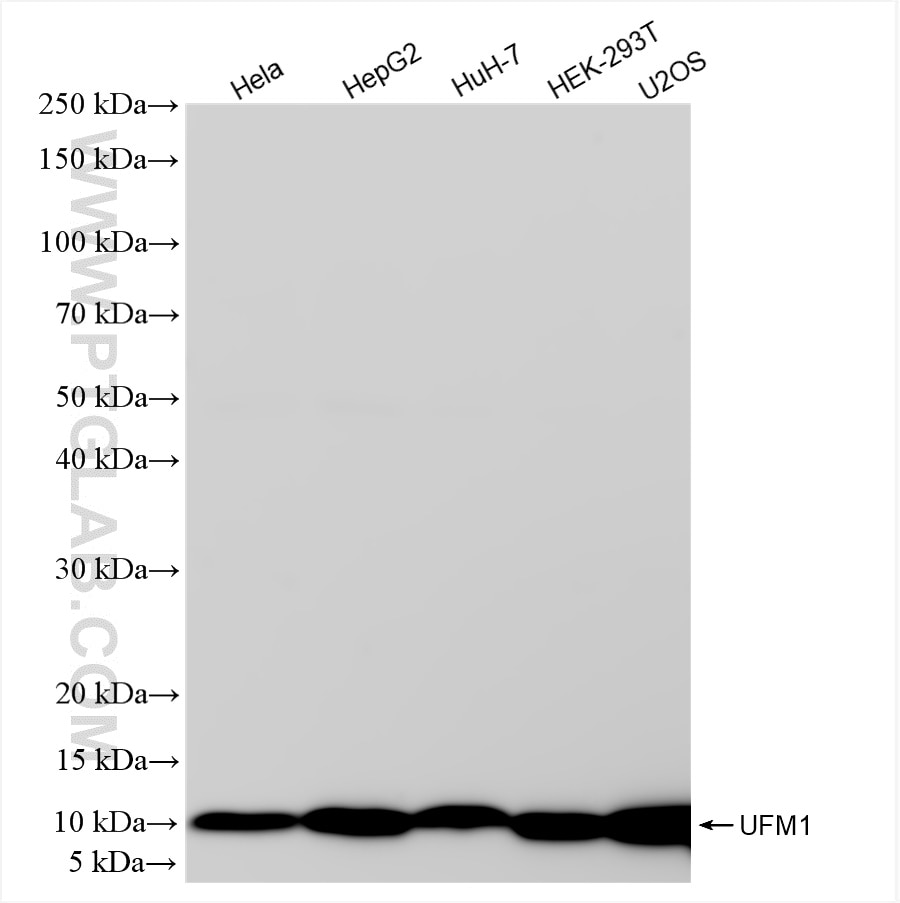
85068-5-PBS targets UFM1 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag8667 Product name: Recombinant human UFM1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-85 aa of BC005193 Sequence: MSKVSFKITLTSDPRLPYKVLSVPESTPFTAVLKFAAEEFKVPAATSAIITNDGIGINPAQTAGNVFLKHGSELRIIPRDRVGSC 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 85 aa, 9 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 9-12 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC005193 |
| Gene Symbol | UFM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 51569 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P61960 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
UFM1 (Ubiquitin-fold modifier 1) is a ubiquitin-like protein covalently conjugated with intracellular proteins through UFMylation (modification by UFM1), a process similar to ubiquitylation (PMID: 38141606). UFM1 is conjugated to its target proteins by E1-like activating enzyme UBE1DC1 and E2-like conjugating enzyme UFC1 in a manner analogous to ubiquitylation (PMID: 28234446; 33066455). At the molecular level, UFMylation is an important mediator of the protein function. Dysregulation of the UFM1 system, e.g., the knockout of UFMylation components, disturbs proteome homeostasis and triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress. Such changes are linked to developmental disorders, tumorigenesis, tissue injury, inflammation, and several hereditary neurological syndromes (PMID: 36932998).