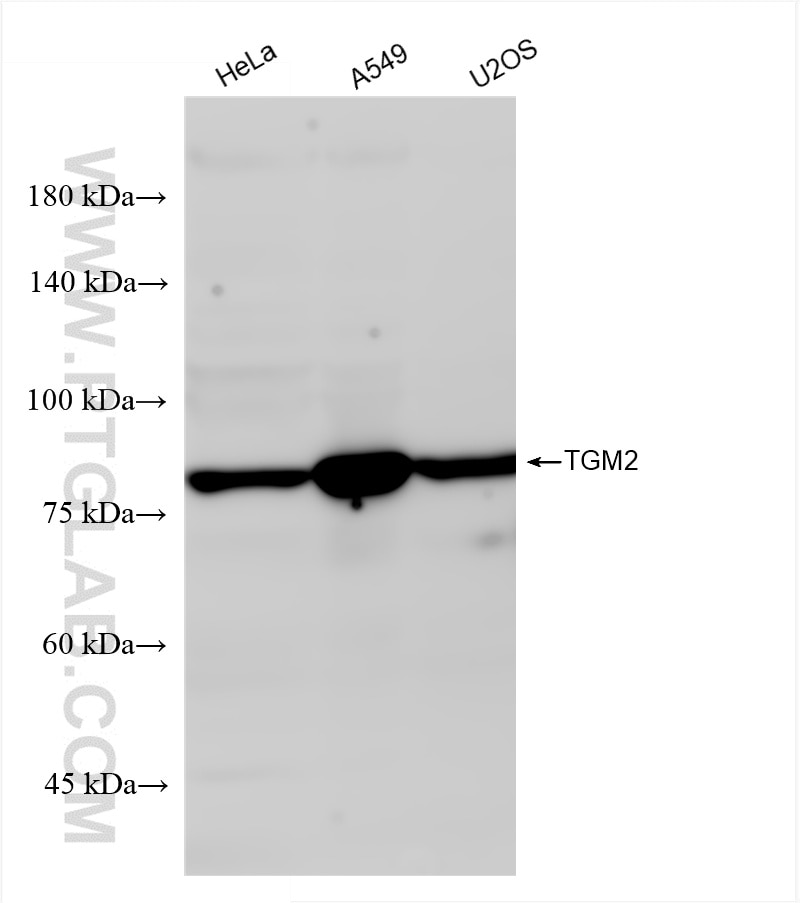
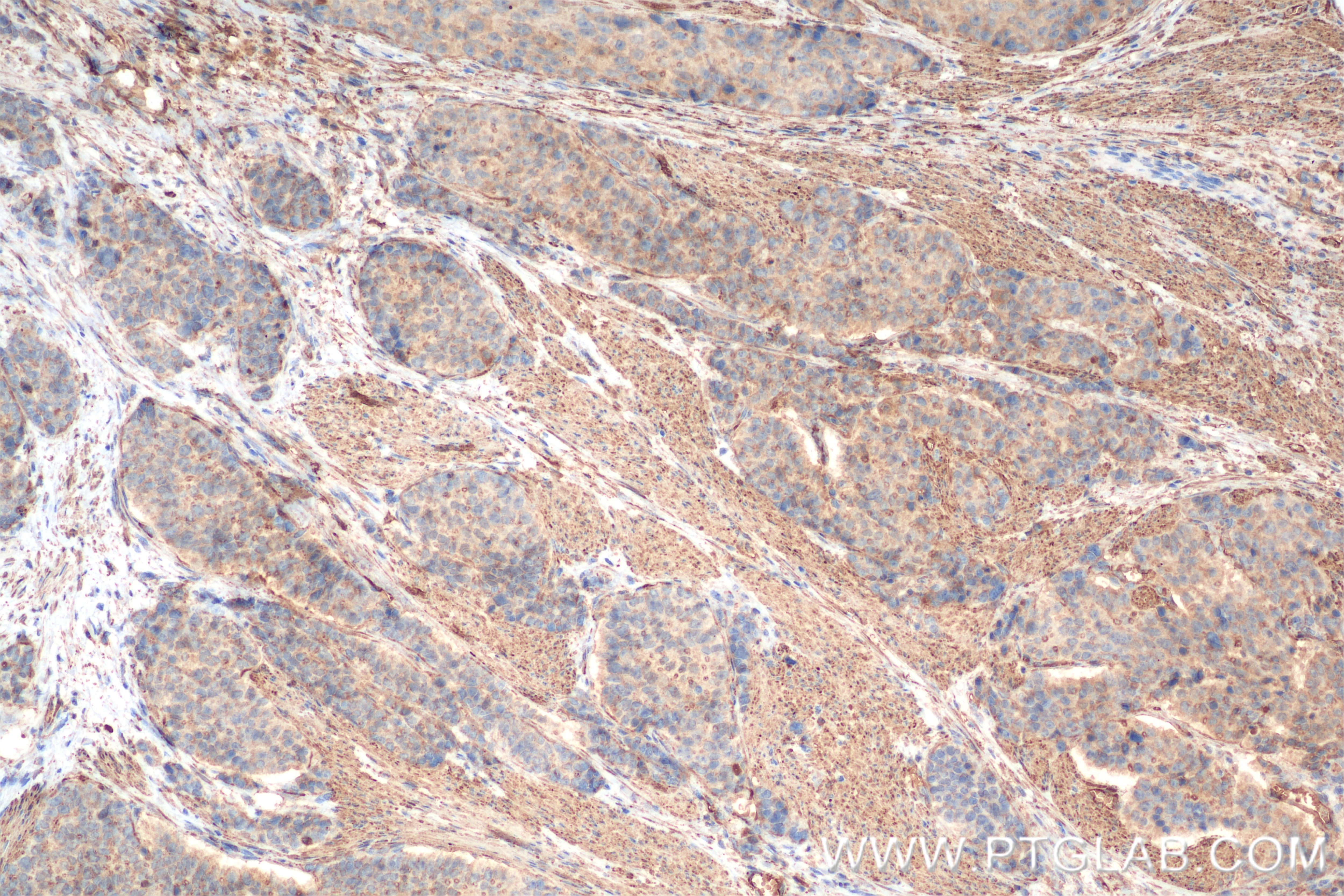
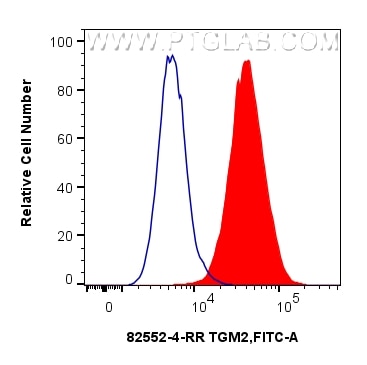
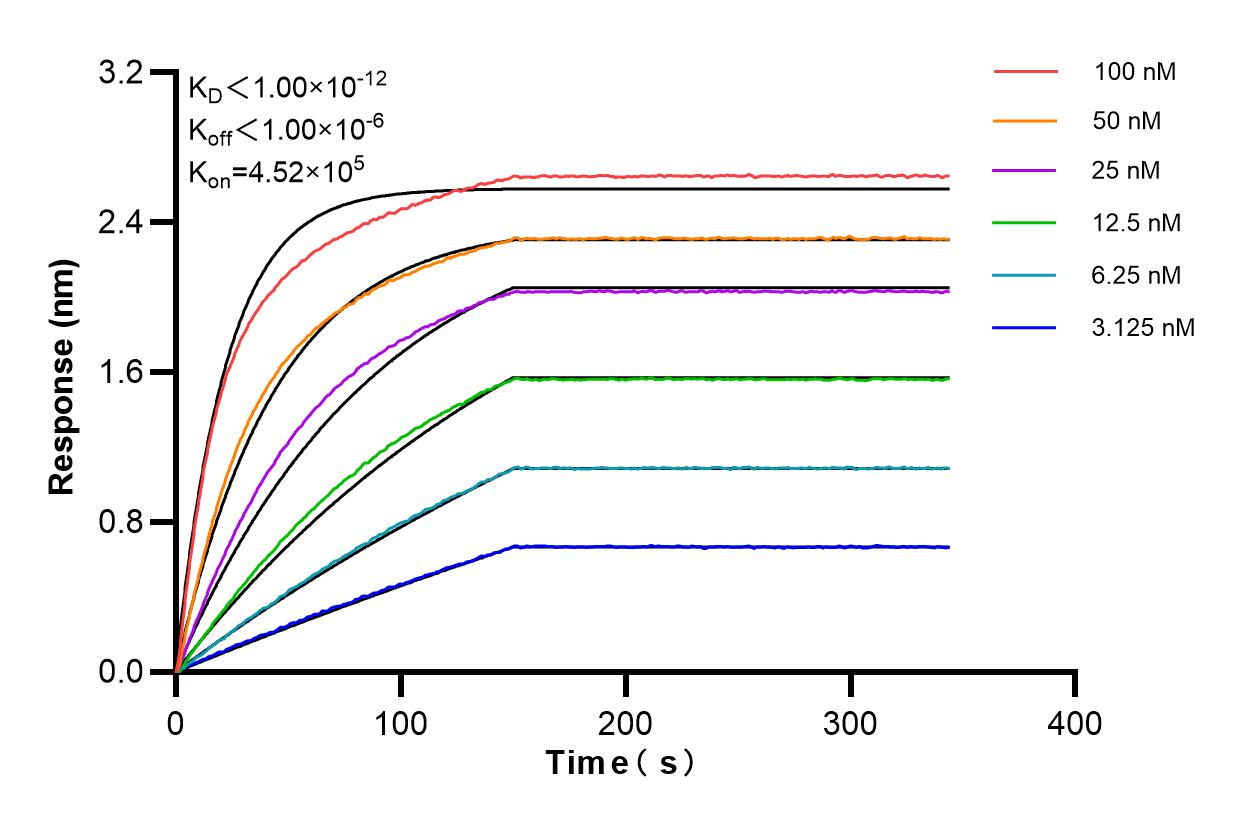
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
82552-4-PBS targets TGM2 in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag7439 Product name: Recombinant human TGM2 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-349 aa of BC003551 Sequence: MAEELVLERCDLELETNGRDHHTADLCREKLVVRRGQPFWLTLHFEGRNYEASVDSLTFSVVTGPAPSQEAGTKARFPLRDAVEEGDWTATVVDQQDCTLSLQLTTPANAPIGLYRLSLEASTGYQGSSFVLGHFILLFNAWCPADAVYLDSEEERQEYVLTQQGFIYQGSAKFIKNIPWNFGQFEDGILDICLILLDVNPKFLKNAGRDCSRRSSPVYVGRVVSGMVNCNDDQGVLLGRWDNNYGDGVSPMSWIGSVDILRRWKNHGCQRVKYGQCWVFAAVACTVLRCLGIPTRVVTNYNSAHDQNSNLLIEYFRNEFGEIQGDKSEMIWNFHCWVESWMTRPDLQP 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | transglutaminase 2 (C polypeptide, protein-glutamine-gamma-glutamyltransferase) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 77 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 77-80 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC003551 |
| Gene Symbol | TGM2 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7052 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000198959 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P21980 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Transglutaminase 2 (TGM2) is a ubiquitous and multifunctional calcium-dependent enzyme belonging to the transglutaminase family. It is best known for its canonical activity of catalyzing the cross-linking of proteins by forming stable ε-(γ-glutamyl)lysine isopeptide bonds, which contributes to extracellular matrix stabilization and wound healing. Beyond this, TGM2 exhibits GTPase activity, allowing it to function as a signaling G-protein in intracellular processes. It is implicated in a wide range of physiological functions, including cell adhesion, proliferation, and apoptosis, as well as pathological conditions such as celiac disease, fibrosis, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer metastasis, where its dysregulated expression often contributes to disease progression.