Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
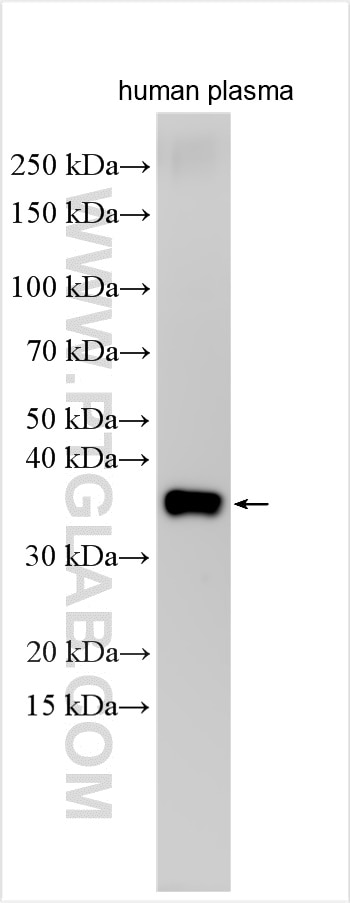
| Positive WB detected in | human plasma |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
55164-1-AP targets STX1A in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Peptide 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | syntaxin 1A (brain) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 33 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 35 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_004603 |
| Gene Symbol | STX1A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6804 |
| RRID | AB_3086433 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q16623 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Syntaxins are a family of transmembrane proteins that belong to the SNARE complex (PMID: 11737951). In conjunction with other SNAREs and with the cytoplasmic NSF and SNAP proteins, syntaxins mediate vesicle fusion in diverse vesicular transport processes along the exocytic and endocytic pathways (PMID: 11737951). Syntaxin 1A (STX1A) and 1B (STX1B), two closely related isoforms of syntaxin 1, are involved in synaptic vesicle docking and fusion during neurotransmitter release (PMID: 7690687; 1321498; 18691641). Syntaxin 1A is associated with a variety of neurological diseases, including epilepsy, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), migraine, etc (PMID: 26918652; 25445064; 22250207). This antibody recognizes human STX1A.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for STX1A antibody 55164-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |