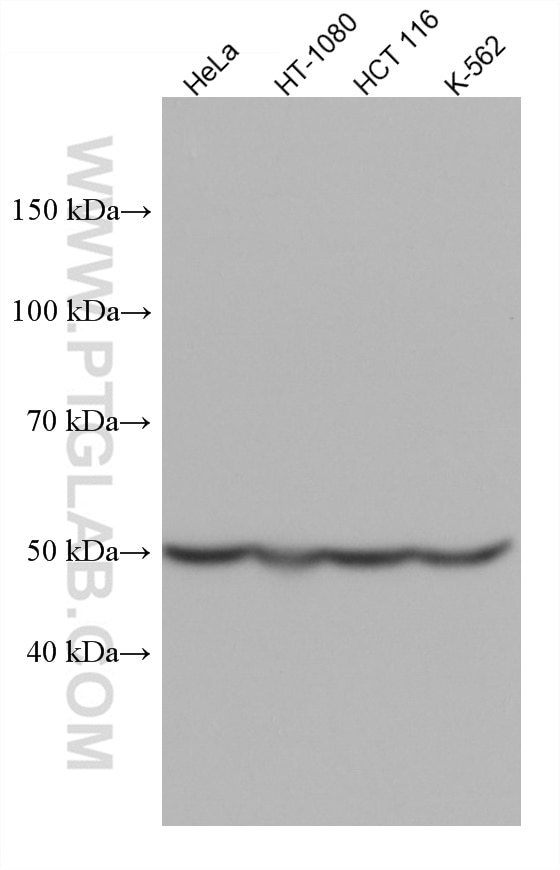
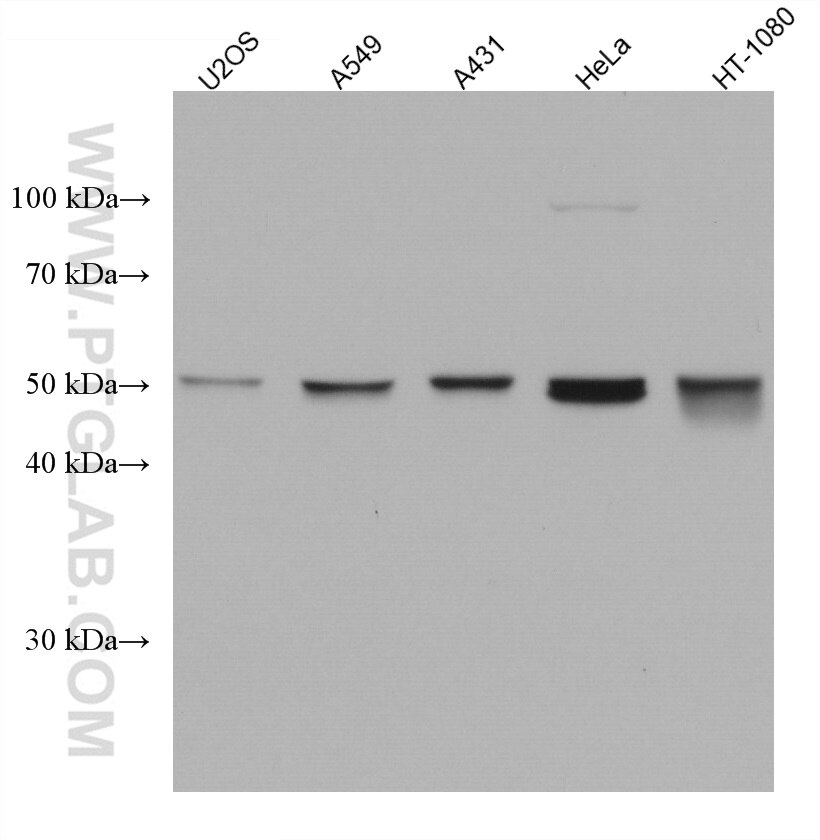
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
67750-1-PBS targets RUVBL1 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag16688 Product name: Recombinant human RUVBL1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-214 aa of BC002993 Sequence: MKIEEVKSTTKTQRIASHSHVKGLGLDESGLAKQAASGLVGQENAREACGVIVELIKSKKMAGRAVLLAGPPGTGKTALALAIAQELGSKVPFCPMVGSEVYSTEIKKTEVLMENFRRAIGLRIKETKEVYEGEVTELTPCETENPMGGYGKTISHVIIGLKTAKGTKQLKLDPSIFESLQKERVEAGDVIYIEANSGAVKRQGRCDTYATEFD 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | RuvB-like 1 (E. coli) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 456 aa, 50 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 50 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC002993 |
| Gene Symbol | RUVBL1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8607 |
| RRID | AB_2918519 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9Y265 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
RUVBL1 is a member of the AAA (ATPase associated with diverse cellular activities) family of proteins that is associated with several chromatin-remodelling complexes and has important roles in transcriptional regulation, the DNA damage response, telomerase activity, snoRNP assembly, cellular transformation and cancer metastasis[PMID: 21617703]. It consists of 456 amino acids (50 kDa) and interacts with TATA-binding protein (TBP), which is a central component for transcriptional regulation by forming complexes with various transcription regulators. RUVBL1 is a component of a large nuclear protein complex, possibly the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. RUVBL1 is also highly homologous to RuvB proteins that function as a DNA helicase promote branch migration of the Holliday junction[PMID: 9588198].