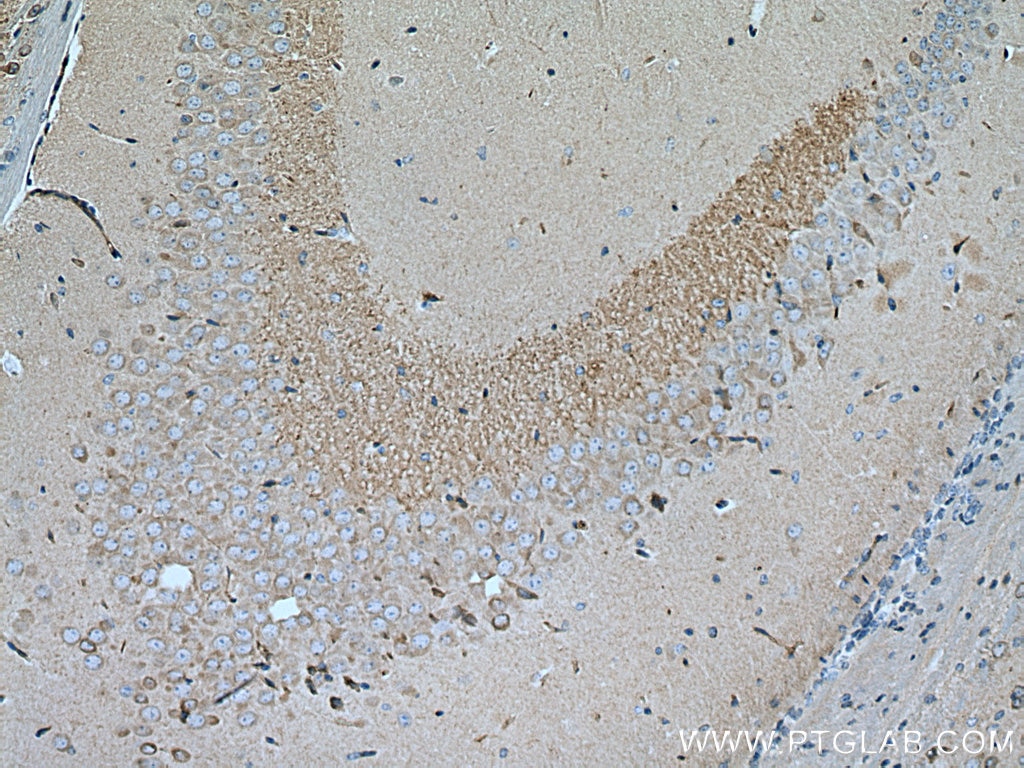
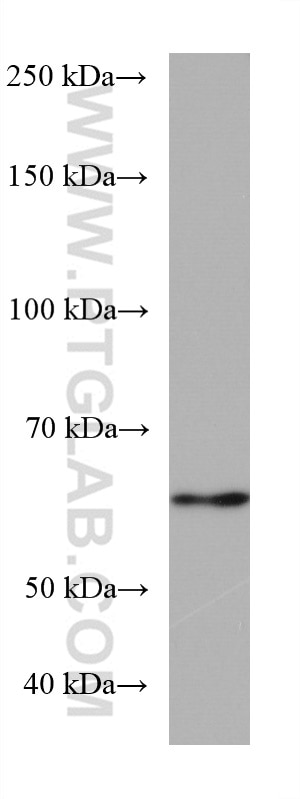
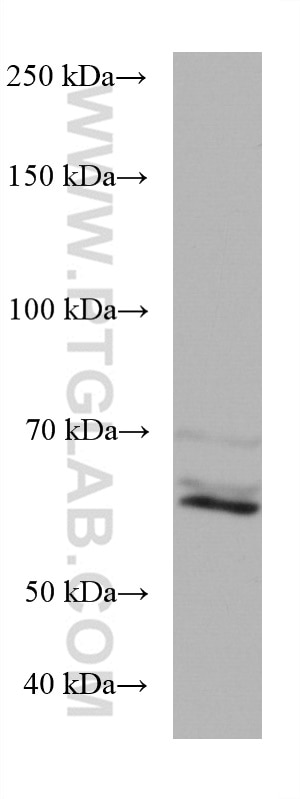
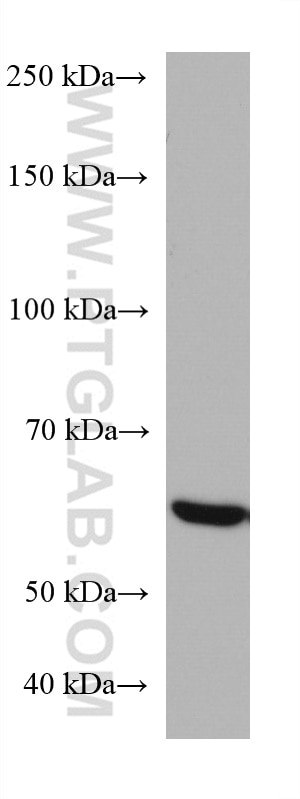
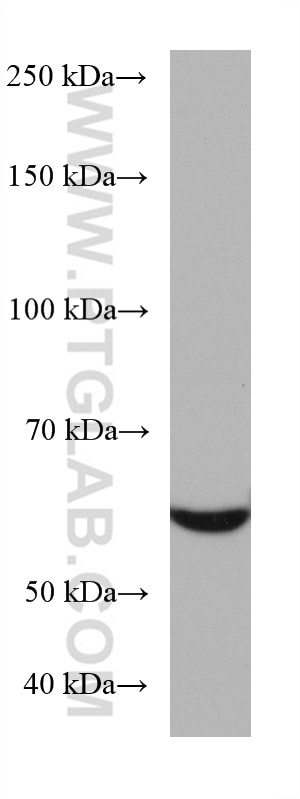
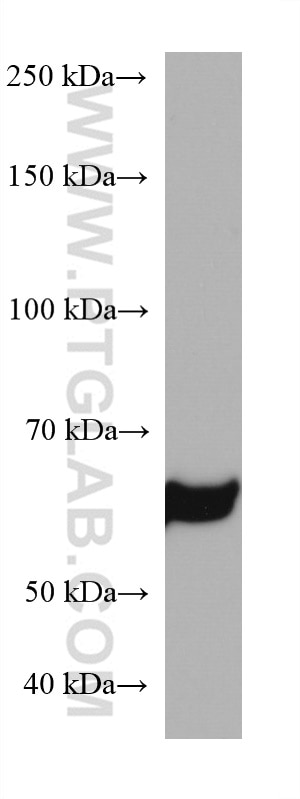
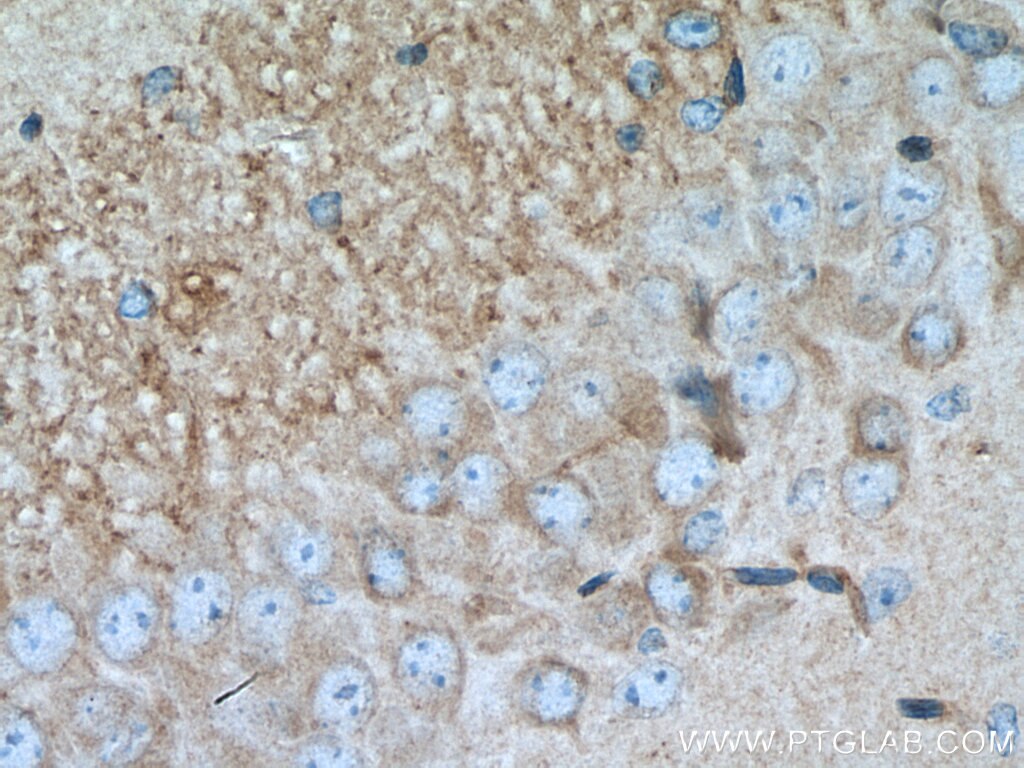
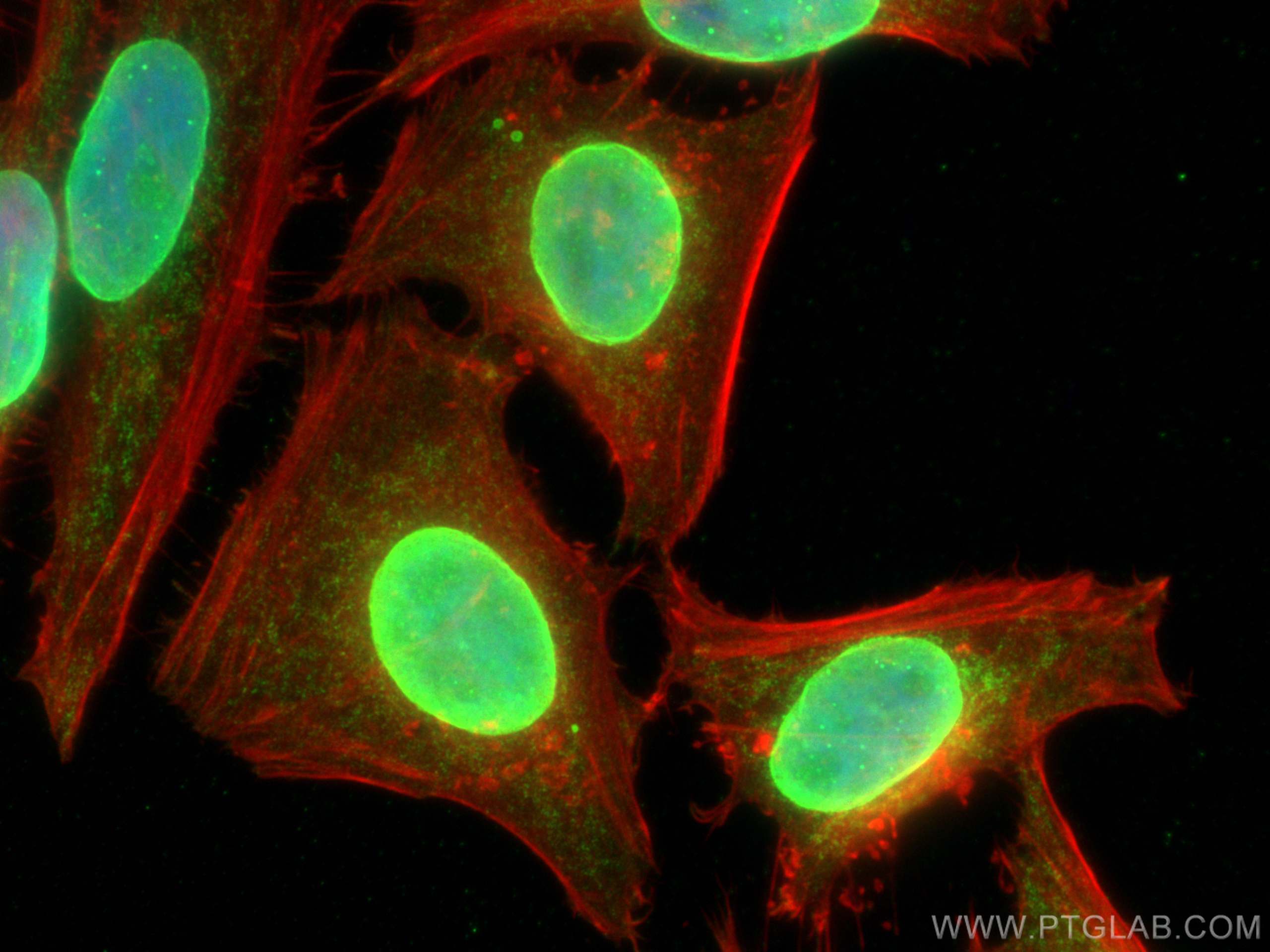
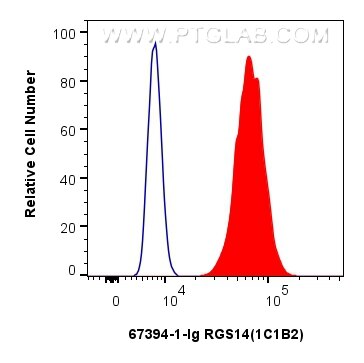
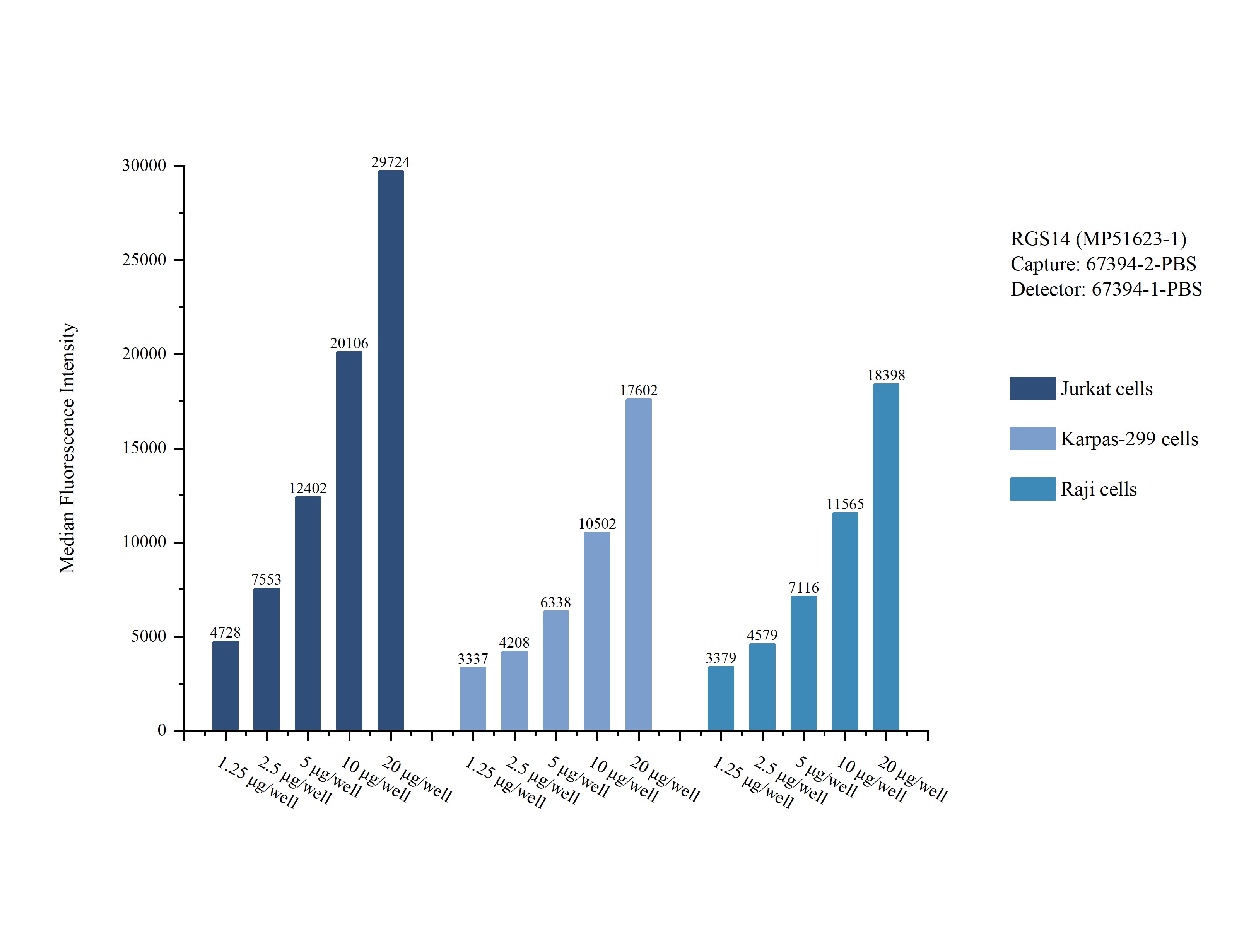
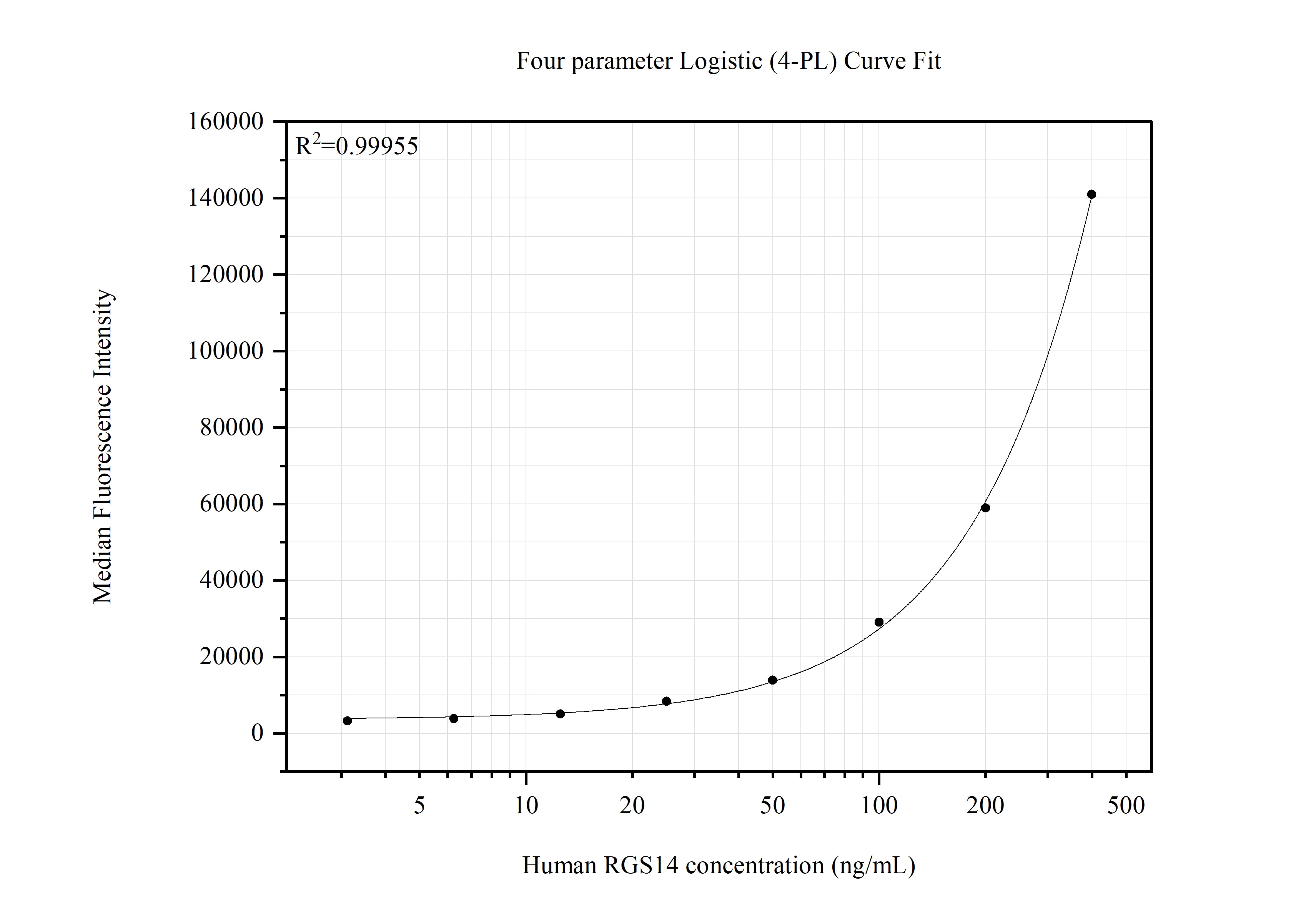
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
67394-1-PBS targets RGS14 as part of a matched antibody pair:
MP51623-1: 67394-2-PBS capture and 67394-1-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag9477 Product name: Recombinant human RGS14 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 217-566 aa of BC014094 Sequence: KSLPLGVEELGQLPPVEGPGGRPLRKSFRRELGGTANAALRRESQGSLNSSASLDLGFLAFVSSKSESHRKSLGSTEGESESRPGKYCCVYLPDGTASLALARPGLTIRDMLAGICEKRGLSLPDIKVYLVGNEQALVLDQDCTVLADQEVRLENRITFELELTALERVVRISAKPTKRLQEALQPILEKHGLSPLEVVLHRPGEKQPLDLGKLVSSVAAQRLVLDTLPGVKISKARDKSPCRSQGCPPRTQDKATHPPPASPSSLVKVPSSATGKRQTCDIEGLVELLNRVQSSGAHDQRGLLRKEDLVLPEFLQLPAQGPSSEETPPQTKSAAQPIGGSLNSTTDSAL 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | regulator of G-protein signaling 14 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 566 aa, 61 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 61 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC014094 |
| Gene Symbol | RGS14 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10636 |
| RRID | AB_2882638 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O43566 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
RGS14, a member of the R12 subfamily of RGS proteins, is highly expressed in the brain and is a natural suppressor of CA2 hippocampal synaptic plasticity and learning and memory. RGS14 was first identified as a complex scaffolding protein with an unconventional domain structure that allows it to interact with various protein binding partners. RGS14 contains one RGS domain, two Raf-like Ras-binding domains (RBDs), and one GoLoco domain. The protein attenuates the signaling activity of G-proteins by binding, through its GoLoco domain, to specific types of activated, GTP-bound G alpha subunits. Acting as a GTPase activating protein (GAP), the protein increases the rate of conversion of the GTP to GDP.