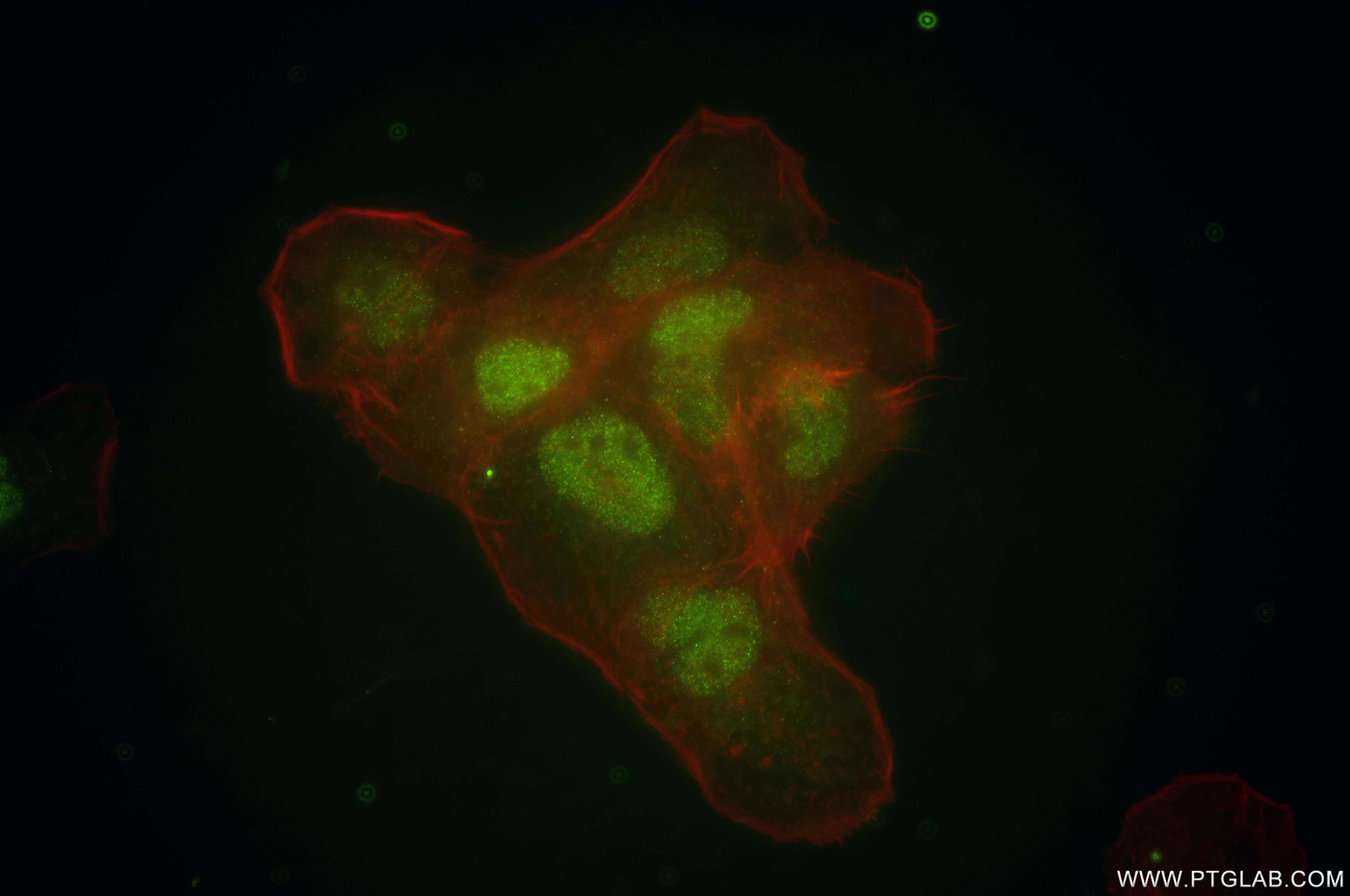
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
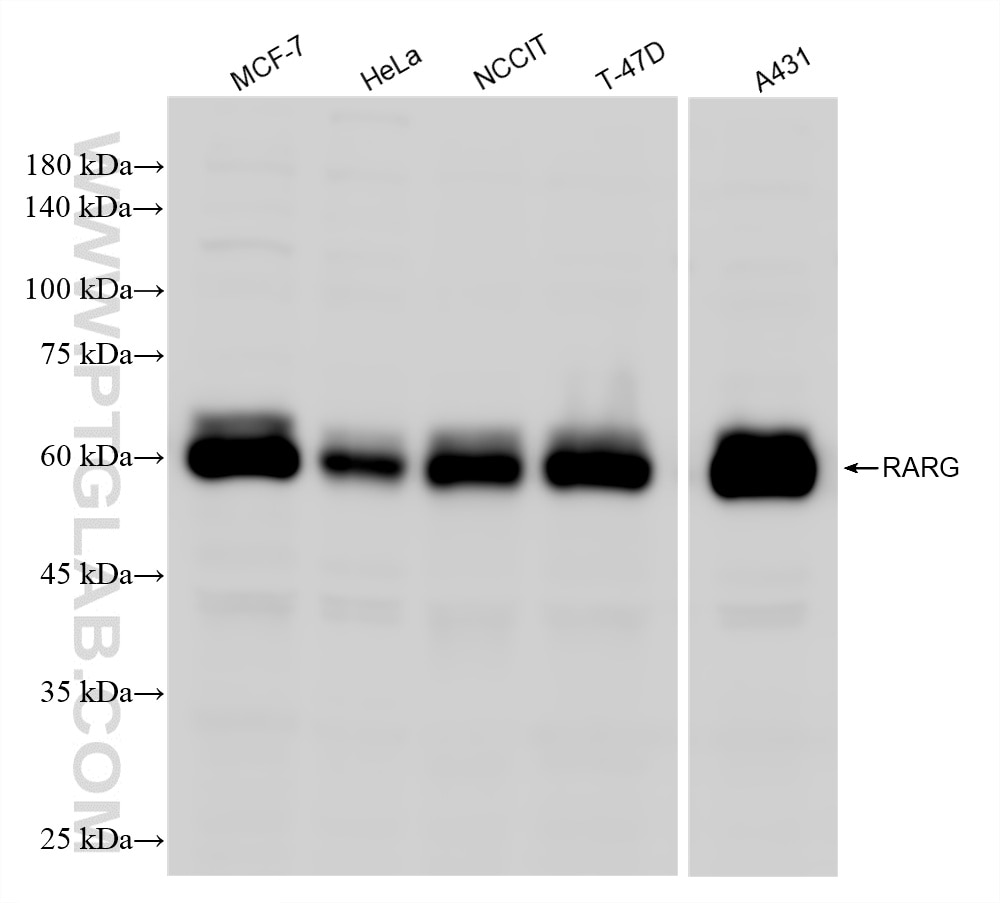
| Positive WB detected in | MCF-7 cells, HeLa cells, NCCIT cells, T-47D cells, A431 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
86098-1-RR targets RARG in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag1991 Product name: Recombinant human RARG protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-300 aa of BC019098 Sequence: MATNKERLFAAGALGPGSGYPGAGFPFAFPGALRGSPPFEMLSPSFRGLGQPDLPKEMASLSVETQSTSSEEMVPSSPSPPPPPRVYKPCFVCNDKSSGYHYGVSSCEGCKGFFRRSIQKNMVYTCHRDKNCIINKVTRNRCQYCRLQKCFEVGMSKEAVRNDRNKKKKEVKEEGSPDSYELSPQLEELITKVSKAHQETFPSLCQLGKYTTNSSADHRVQLDLGLWDKFSELATKCIIKIVEFAKRLPGFTGLSIADQITLLKAACLDILMLRICTRYTPEQDTMTFSDGLTLNRTQMH 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | retinoic acid receptor, gamma |
| Calculated molecular weight | 454 aa, 50 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 50-60kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC019098 |
| Gene Symbol | RARG |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5916 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P13631 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Retinoic acid receptors (RARs) are nuclear hormone receptors that act as ligand-dependent transcriptional regulators. In their liganded state, RARs activate transcription, whereas in their nonliganded form, they repress transcription of their target genes. RARs have numerous target genes, which have retinoic response elements in their promoter regions (PMID:17574023). RARG is a member of the retinoid acid receptor (RAR) family, along with RARA, which is known to be involved PML/RARA fusion of acute promyelocytic leukemia, and RARB. and rearrangement that conferred to leukemic cells acute promyelocytic leukemia-like morphologic and immunophenotypic features (PMID:20935257).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RARG antibody 86098-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |