Recombinant Mouse gp130/IL6ST protein (rFc Tag)(HPLC verified)
Species
Mouse
Purity
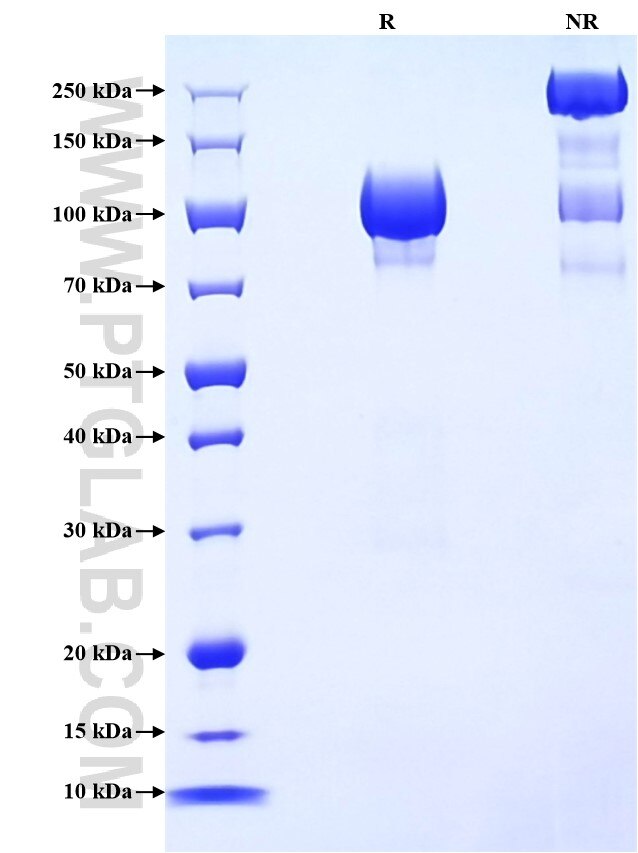
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
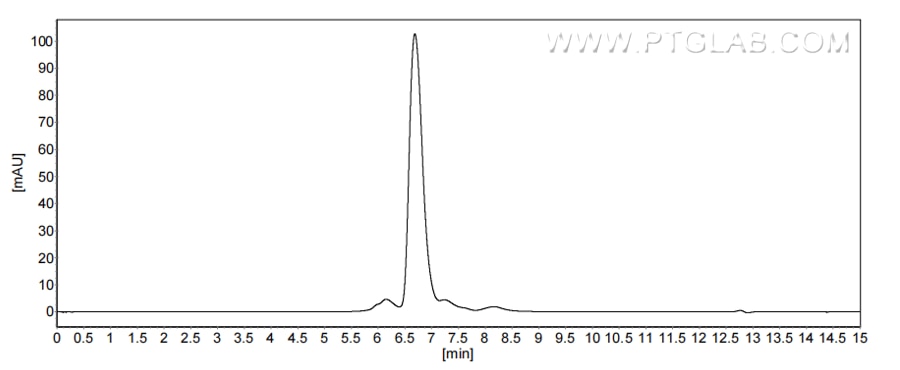
>90 %, SEC-HPLC
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg1631
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90 %, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Mouse gp130 protein Gln23-Glu617 (Accession# Q00560) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 16195 |
| Accession | Q00560 |
| PredictedSize | 92.9 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 90-125 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
Glycoprotein 130 (gp130, also known as IL6ST, CD130 or IL6-beta) is a ubiquitously expressed, signal-transducing receptor that serves as the signal transduction unit for IL-6 family of cytokines, including IL-6, IL-11, IL-27, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), OSM, ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), cardiotrophin 1 (CT-1), and cardiotrophin-like cytokine (CLC). These cytokines signal through the gp130/Jak/STAT pathway. Binding of IL-6 to IL-6R induces gp130 homodimerization and formation of a high-affinity receptor complex, which activates Jaks. That causes phosphorylation of gp130 tyrosine residues which in turn activates STAT3. gp130 is a type I transmembrane protein, and can also exist as a soluble form (sgp130). sgp130 binds to sIL-6R/IL-6 complexes and prevents their interactions with membrane-anchored gp130 on target cells.
References:
1. T Taga, et al. (1997) Annu Rev Immunol. 15:797-819. 2. J S Silver, et al. (2010) J Leukoc Biol. 88(6):1145-56. 3. P C Heinrich, et al. (1998) Biochem J. 334 ( Pt 2):297-314. 4. F A Montero-Julian, et al. (1997) Clin Cancer Res. 3(8):1443-51.