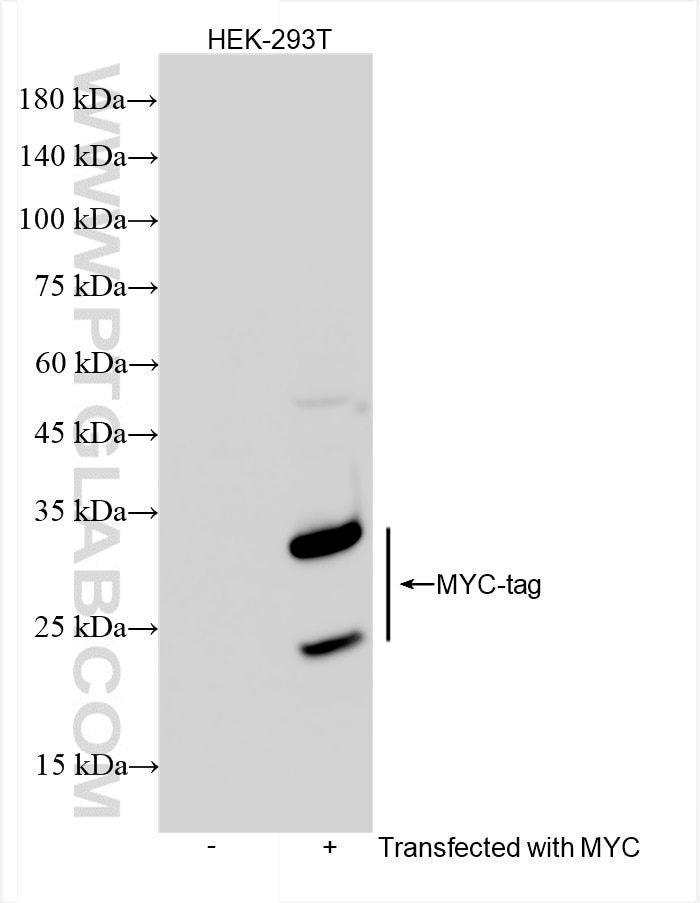
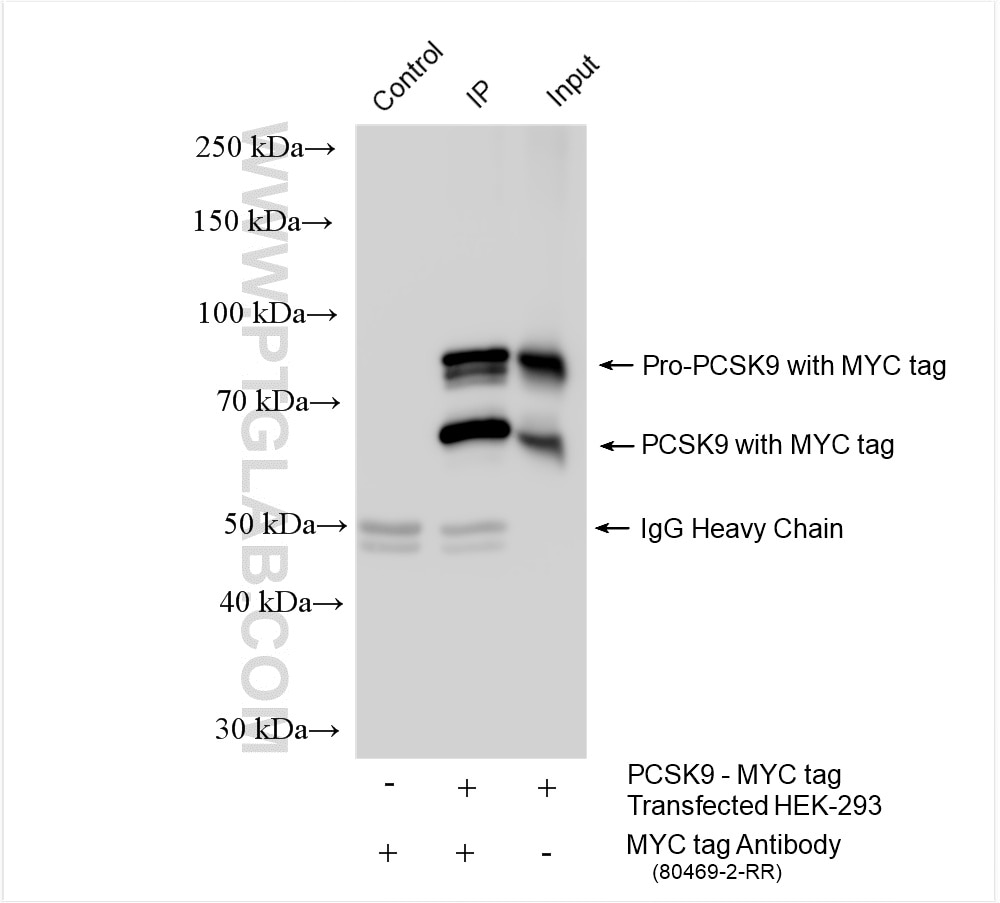
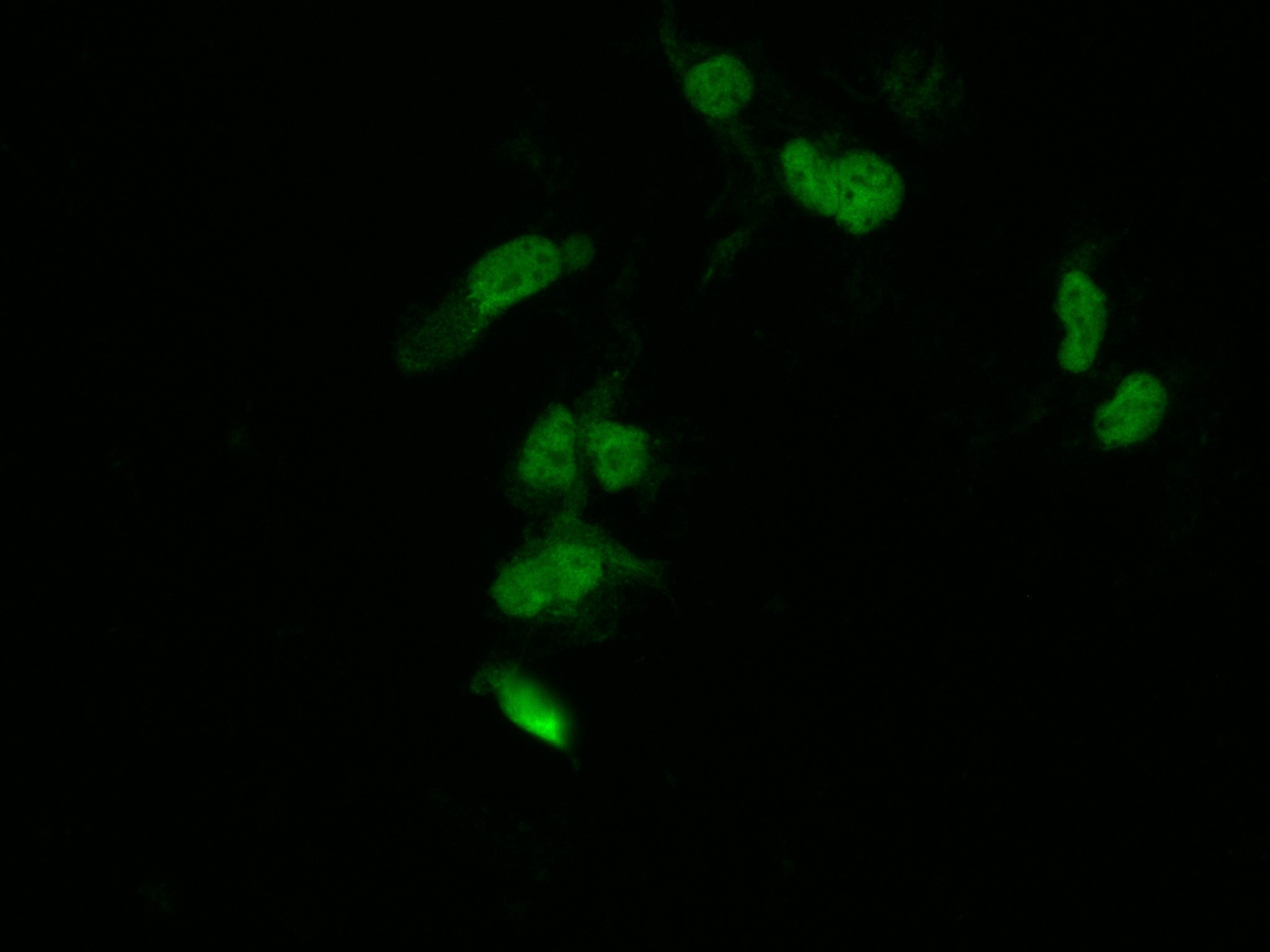
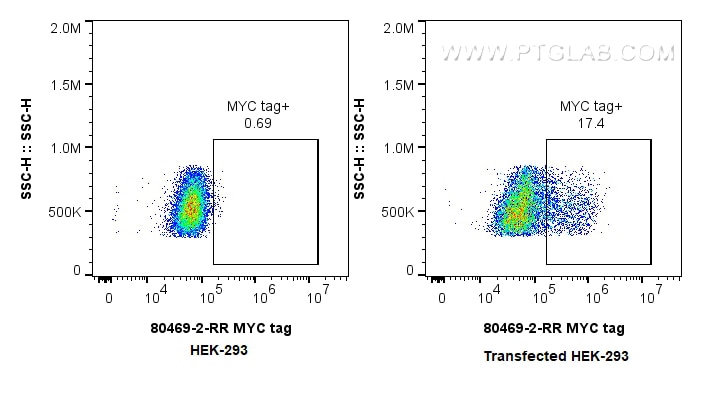
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
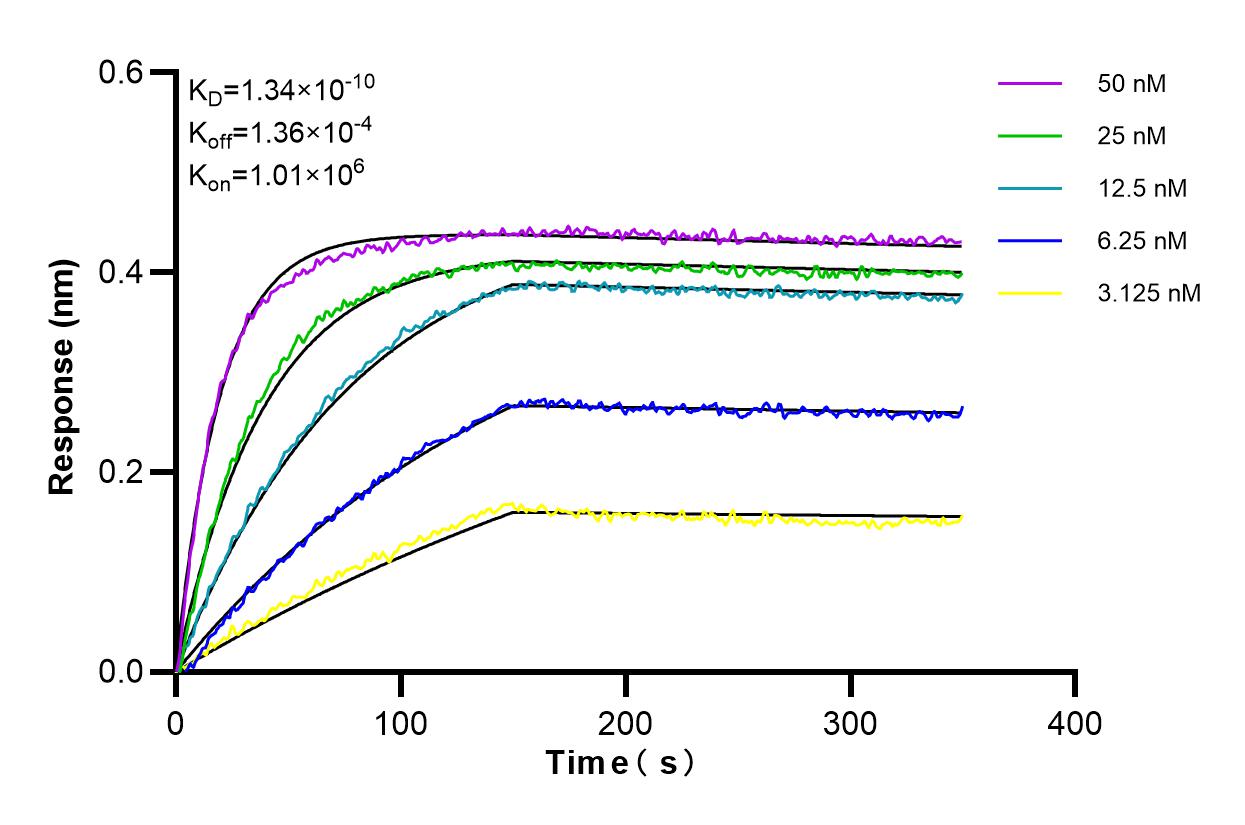
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
80469-2-PBS targets MYC tag in WB, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with recombinant protein samples.
| Tested Reactivity | recombinant protein |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag9409 Product name: Recombinant MYC-tag protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Sequence: EQKLISEEDLEQKLISEEDLEQKLISEEDL 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | Myc tag |
| Gene Symbol | Myc tag |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 99 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | MYCTAG |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
The myc-tag is a short synthetic polypeptide sequence derived from c-MYC protein that can be added to recombinant proteins to enable isolation and study when an antibody is not available. This antibody recognizes the MYC tag EQKLISEEDL. MYC tag is a part of c-MYC protein. So there's weaker 62-65 kDa bands for endogenous c-MYC protein. What is the molecular weight of myc? 1203Da: the ten amino acid myc tag sequence is EQKLISEEDL (in single letter code). What are the applications for myc tag? The addition of the myc tag to a particular protein can be useful when an antibody is not available to the protein of interest. Using recombinant DNA technology, the myc tag can be fused to the protein and then an antibody against the myc tag can be used to probe (PMID: 24490106). This is a reliable method and can be used in a number of different techniques, including purification using chromatography, tracking the protein in localization studies using immunofluorescence, or quantifying levels using Western Blot (PMID: 24490106). What is the structure of myc tag? The c-myc gene from which this tag is derived has a molecular weight of 49kDa, but the myc tag represents only a small portion of the C-terminus of this gene. The short polypeptide sequence can be fused to the N-terminus or the C-terminus of any protein without influencing function, although it is advised to avoid fusing it to a secretory signal. A cleavage site behind this tag is also sometimes engineered to allow removal with a specific protease.