Recombinant Human SPARCL1 protein (rFc Tag)
Species
Human
Purity
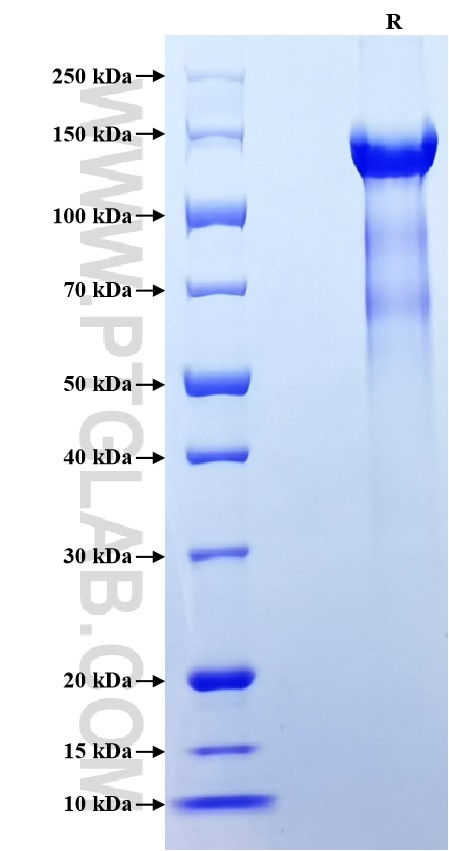
>85 %, SDS-PAGE
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg2837
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >85 %, SDS-PAGE |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human SPARCL1 protein Ile17-Phe664 (Accession# Q8N4S1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 8404 |
| Accession | Q8N4S1 |
| PredictedSize | 99.2 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 125-150 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
SPARCL1 (Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine-like 1) is an extracellular matrix glycoprotein that plays diverse roles in tissue repair, inflammation, and lipid metabolism. It is highly expressed in the brain and involved in the regulation of lipid metabolism and inflammation. SPARCL1 has been implicated in various diseases, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), where it promotes disease progression through upregulation of CCL2. Additionally, SPARCL1 regulates macrophage activation and exacerbates viral pneumonia by promoting pro-inflammatory responses. In cancer, SPARCL1 expression is often downregulated, and it has been identified as a potential prognostic biomarker in breast cancer.
References:
1. Liu, Bin et al. The Journal of clinical investigation vol. 131,20 (2021): e144801. 2. Cheng, Xu et al. Journal of inflammation research vol. 16 (2023): 2121-2127. 3. Zhao, Gan et al. Nature communications vol. 15,1 (2024): 4235. 4. Xu, Xin-Yu et al. Oncology letters vol. 29,4 (2025): 196.