Recombinant Human NRP2 protein (rFc Tag)(HPLC verified)
Species
Human
Purity
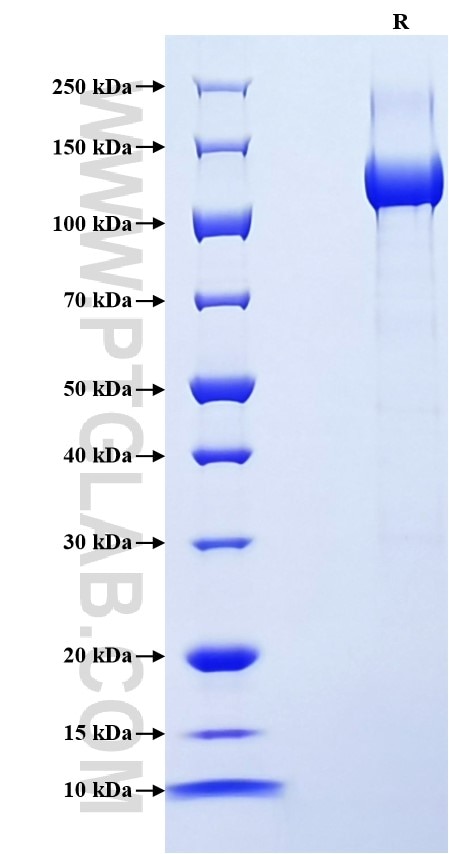
>90 %, SDS-PAGE
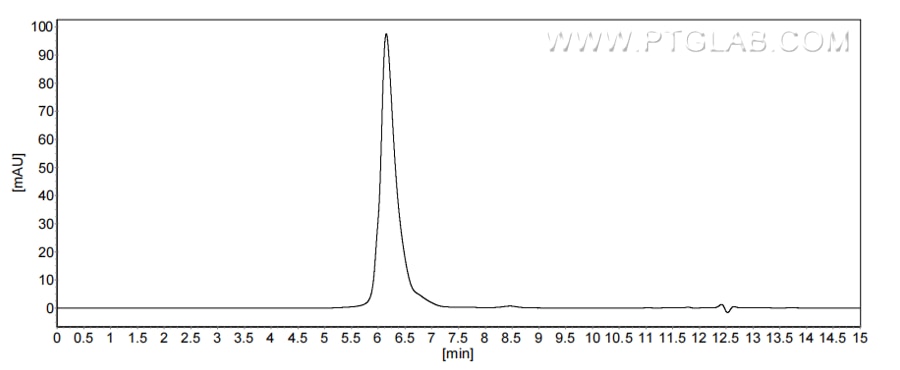
>90%, SEC-HPLC
Tag
rFc Tag
Activity
not tested
Cat no : Eg3125
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
| Purity | >90 %, SDS-PAGE >90%, SEC-HPLC |
| Endotoxin | <0.1 EU/μg protein, LAL method |
| Activity |
Not tested |
| Expression | HEK293-derived Human NRP2 protein Arg21-Pro864 (Accession# O60462-1) with a rabbit IgG Fc tag at the C-terminus. |
| GeneID | 8828 |
| Accession | O60462-1 |
| PredictedSize | 121.1 kDa |
| SDS-PAGE | 110-140 kDa, reducing (R) conditions |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH 7.4. Normally 5% trehalose and 5% mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Reconstitution | Briefly centrifuge the tube before opening. Reconstitute at 0.1-0.5 mg/mL in sterile water. |
| Storage Conditions |
It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
|
| Shipping | The product is shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store it immediately at the recommended temperature. |
Background
NRP2 (Neuropilin-2) is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the neuropilin family. It acts as a multifunctional receptor that binds to a variety of ligands, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and signaling proteins (e.g., Sema3C and Sema3F), and plays important roles in neurodevelopment, angiogenesis, and immunomodulation. NRP2 is a cell surface molecule that is widely present in pancreatic cancer cells and is upregulated in various malignant tumors, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric carcinoma, thyroid carcinoma and prostate cancer. It plays a crucial role in tumor cell growth, migration, invasion and angiogenesis, and monoclonal antibodies against NRP2 have been proposed as a potential strategy for pancreatic cancer treatment.
References:
1. Zhao Z, et al. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(30):e2303872. 2. Luo S, et al. FASEB J. 2022;36(2):e22079. 3. Kang Y, et al. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(8):8938-8951. 4. Schulz A, et al. Front Oncol. 2020;9:1461. 5. Luo X, et al. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:113.