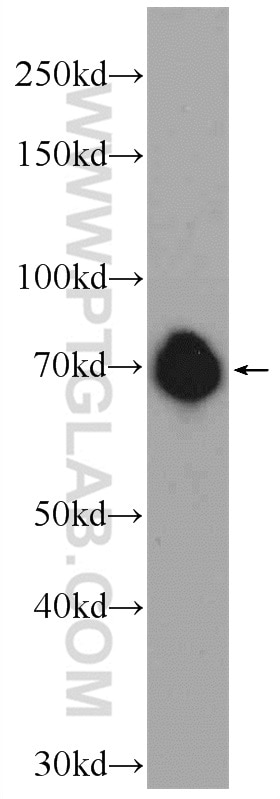
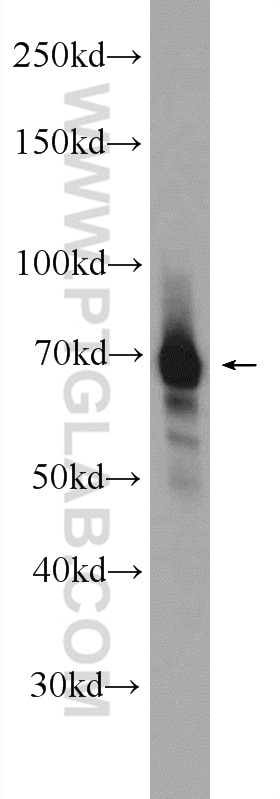
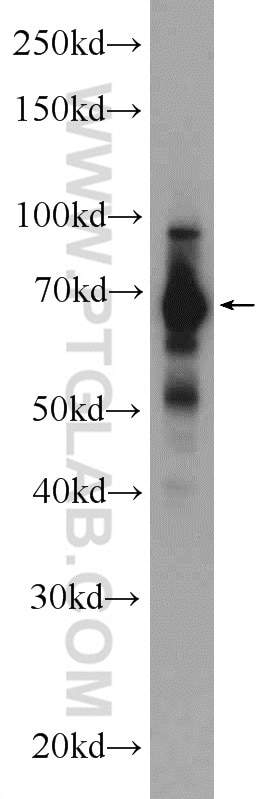
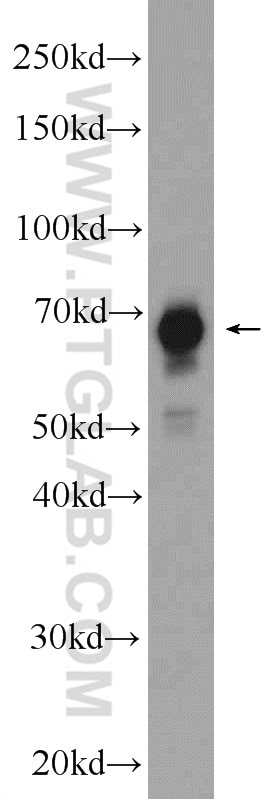
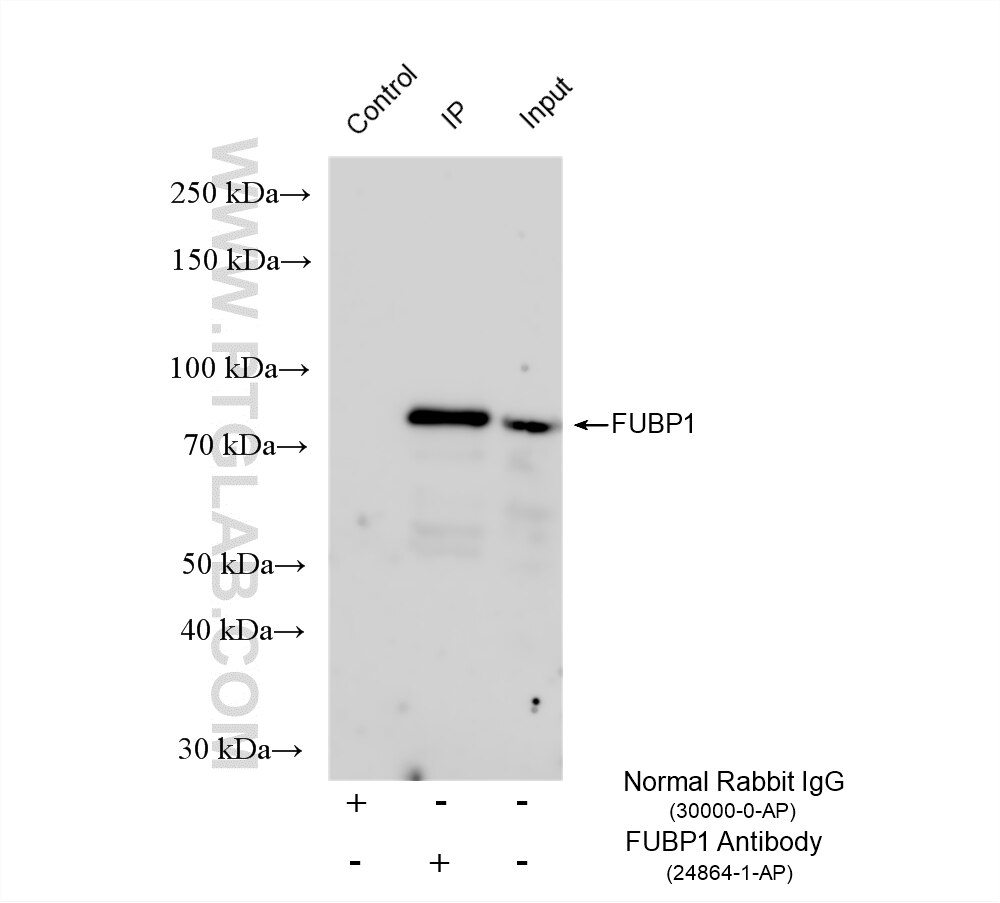
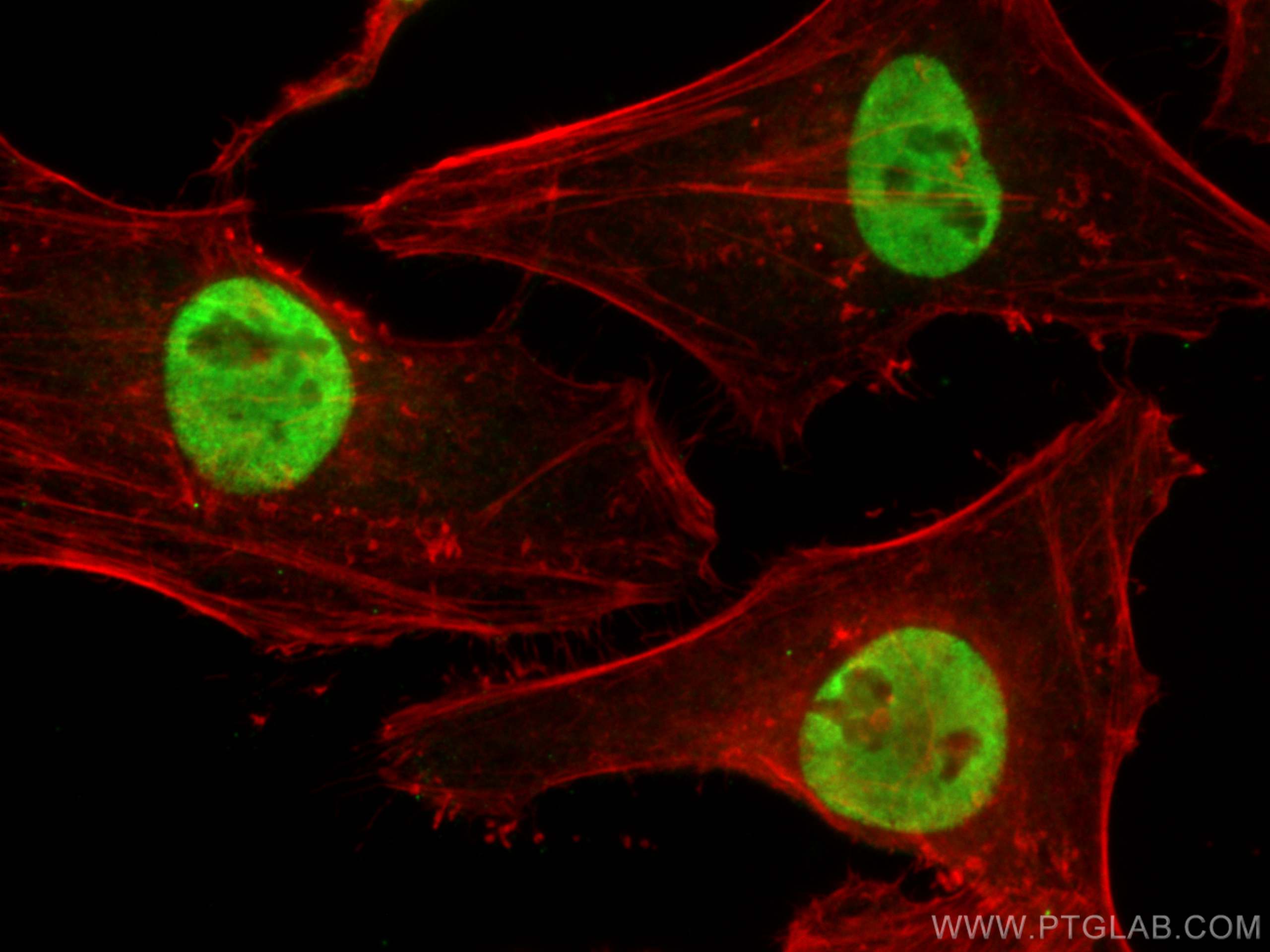
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | SH-SY5Y cells, Jurkat cells, K-562 cells, mouse brain tissue |
| Positive IP detected in | SH-SY5Y cells |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
24864-1-AP targets FUBP1 in WB, IF/ICC, IP, ChIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag13149 Product name: Recombinant human FUBP1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 303-653 aa of BC017247 Sequence: DAGVRIQFKPDDGTTPERIAQITGPPDRCQHAAEIITDLLRSVQAGNPGGPGPGGRGRGRGQGNWNMGPPGGLQEFNFIVPTGKTGLIIGKGGETIKSISQQSGARIELQRNPPPNADPNMKLFTIRGTPQQIDYARQLIEEKIGGPVNPLGPPVPHGPHGVPGPHGPPGPPGPGTPMGPYNPAPYNPGPPGPAPHGPPAPYAPQGWGNAYPHWQQQAPPDPAKAGTDPNSAAWAAYYAHYYQQQAQPPPAAPAGAPTTTQTNGQGDQQNPAPAGQVDYTKAWEEYYKKMGQAVPAPTGAPPGGQPDYSAAWAEYYRQQAAYYAQTSPQGMPQHPPAPQCRFDPASIELAL 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | far upstream element (FUSE) binding protein 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 653 aa, 69 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 69 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC017247 |
| Gene Symbol | FUBP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8880 |
| RRID | AB_2879762 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q96AE4 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
FUBP1 also termed as FBP and FUSE-binding protein 1 is 644 amino-acid protein, which localizes in the nucleus. FUBP1 binds to a single-stranded far-upstream element (FUSE) upstream of the MYC promoter and regulates the MYC expression, indicating that FBP1 functions as a growth-dependent regulator of c-Myc expression. FUBP1 binds to FUSE, and PUF60, and forms a stable tripartite complex, which represses activated but not basal c-myc transcription after transcription initiation by delaying promoter escape. FUBP1 may be acting both as activator and repressor of transcription.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for FUBP1 antibody 24864-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for FUBP1 antibody 24864-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for FUBP1 antibody 24864-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Int J Biol Sci Poly(U) binding splicing factor 60 promotes renal cell carcinoma growth by transcriptionally upregulating telomerase reverse transcriptase. | ||
Biology (Basel) In Situ Peroxidase Labeling Followed by Mass-Spectrometry Reveals TIA1 Interactome. | ||
MedComm (2020) Far upstream element-binding protein 1 confers lobaplatin resistance by transcriptionally activating PTGES and facilitating the arachidonic acid metabolic pathway in osteosarcoma | ||
J Immunother Cancer The NR_109/FUBP1/c-Myc axis regulates TAM polarization and remodels the tumor microenvironment to promote cancer development
| ||
J Adv Res LncRNA NIPA1-SO confers atherosclerotic protection by suppressing the transmembrane protein NIPA1 | ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) PRMT5 Maintains Homeostasis of the Intestinal Epithelium by Modulating Cell Proliferation and Survival |