Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
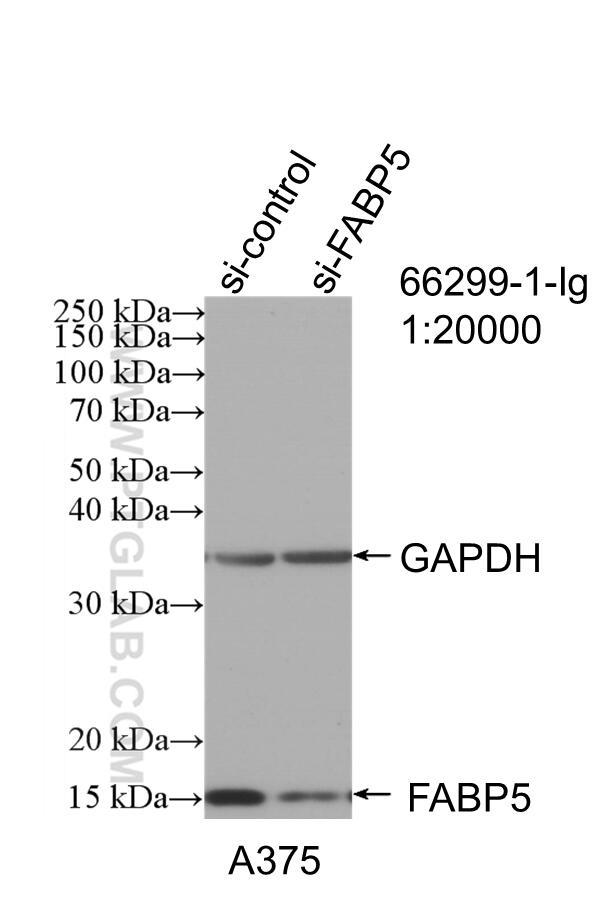
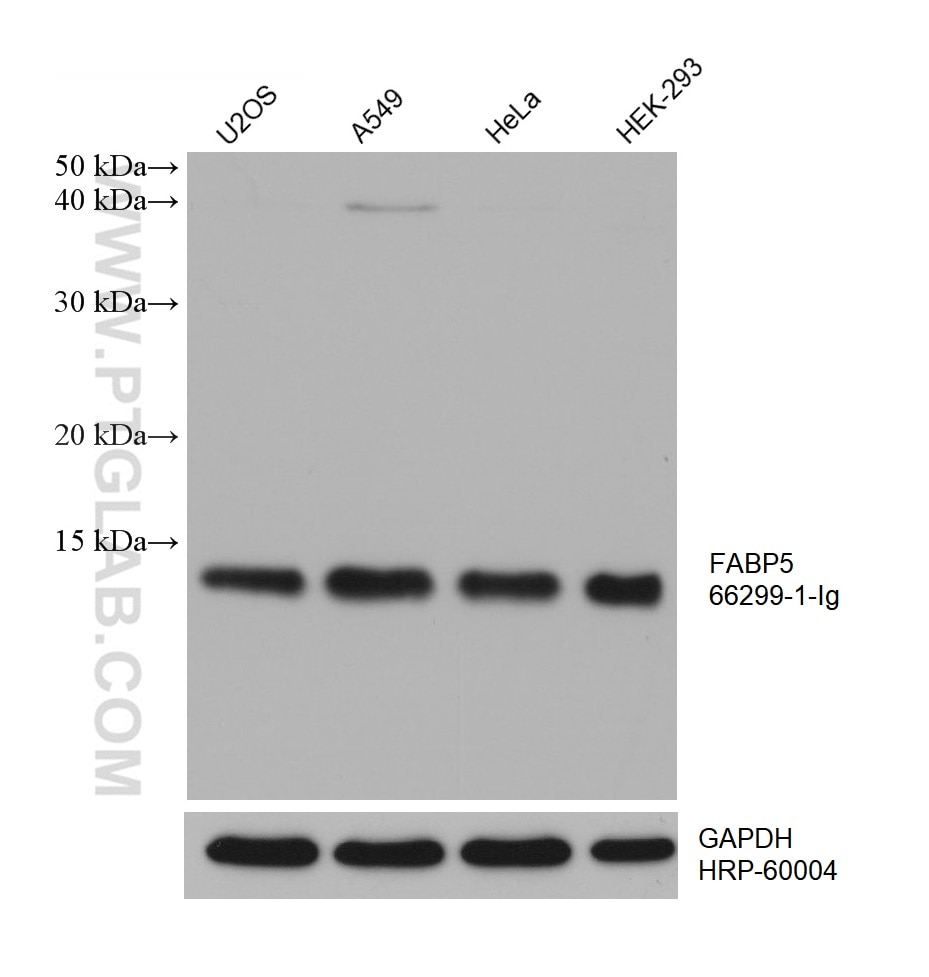
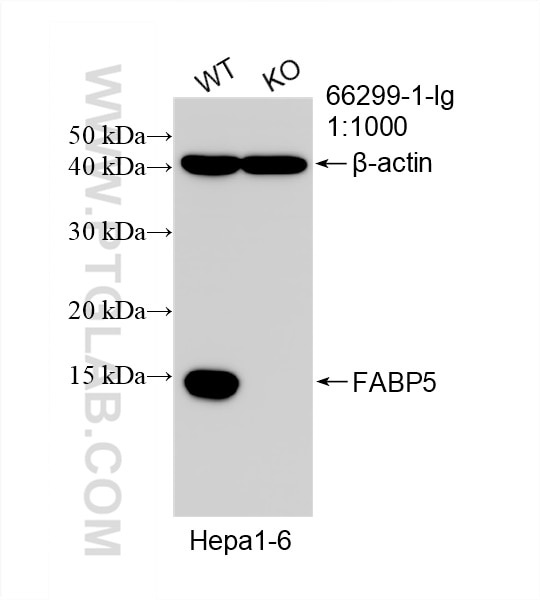
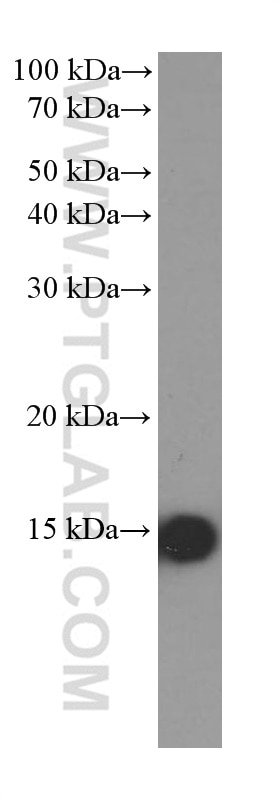
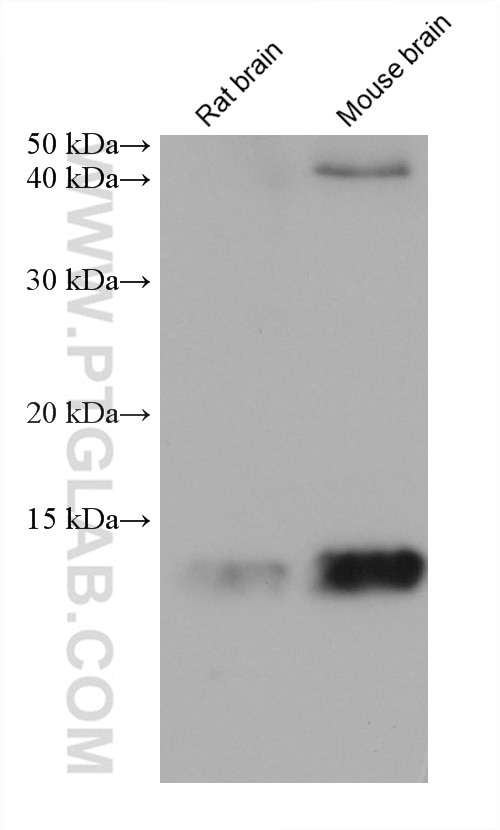
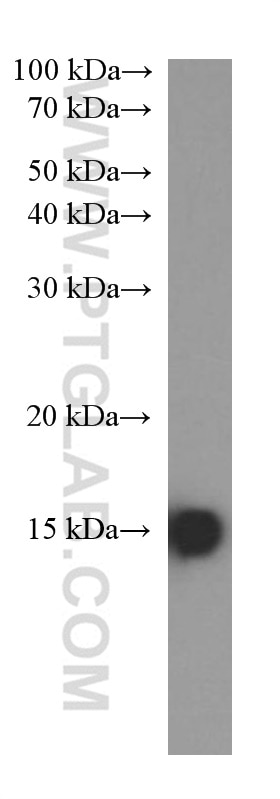
| Positive WB detected in | A375 cells, fetal human brain tissue, Hepa1-6 cells, rat brain tissue, U2OS cells, mouse brain tissue, A549 cells, HeLa cells, HEK-293 cells |
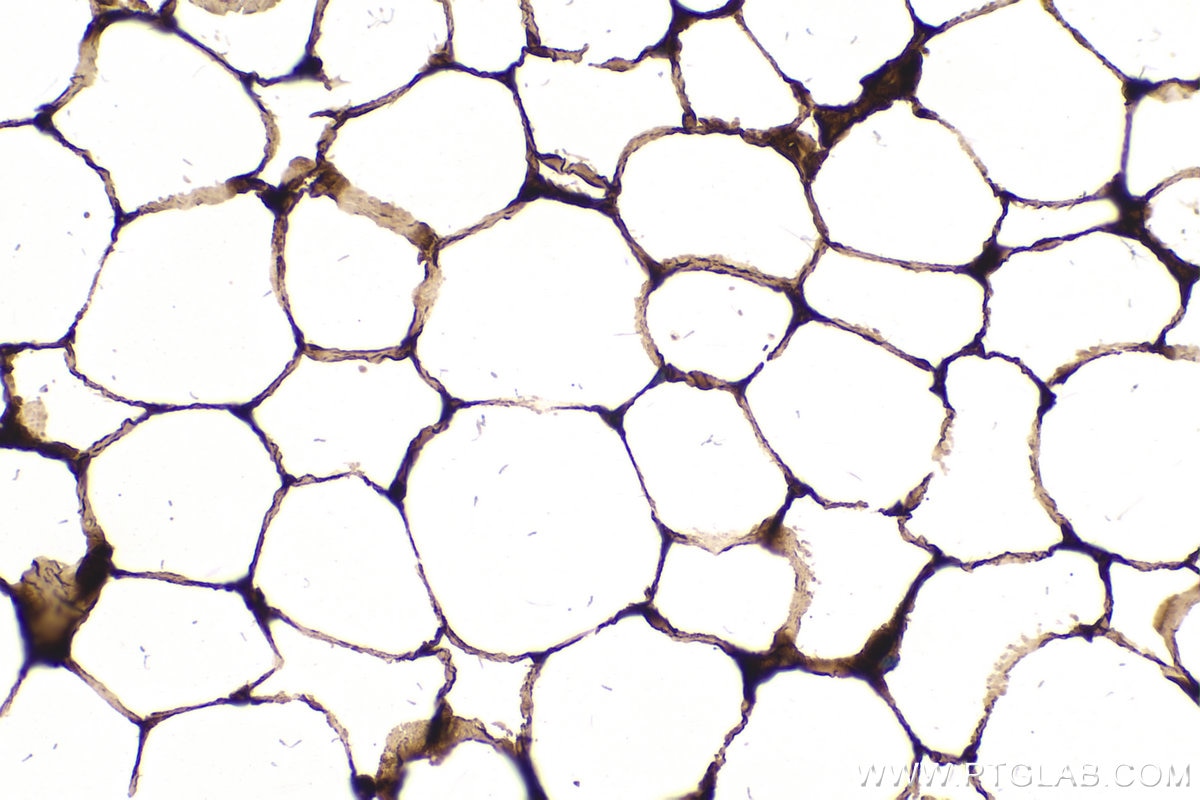
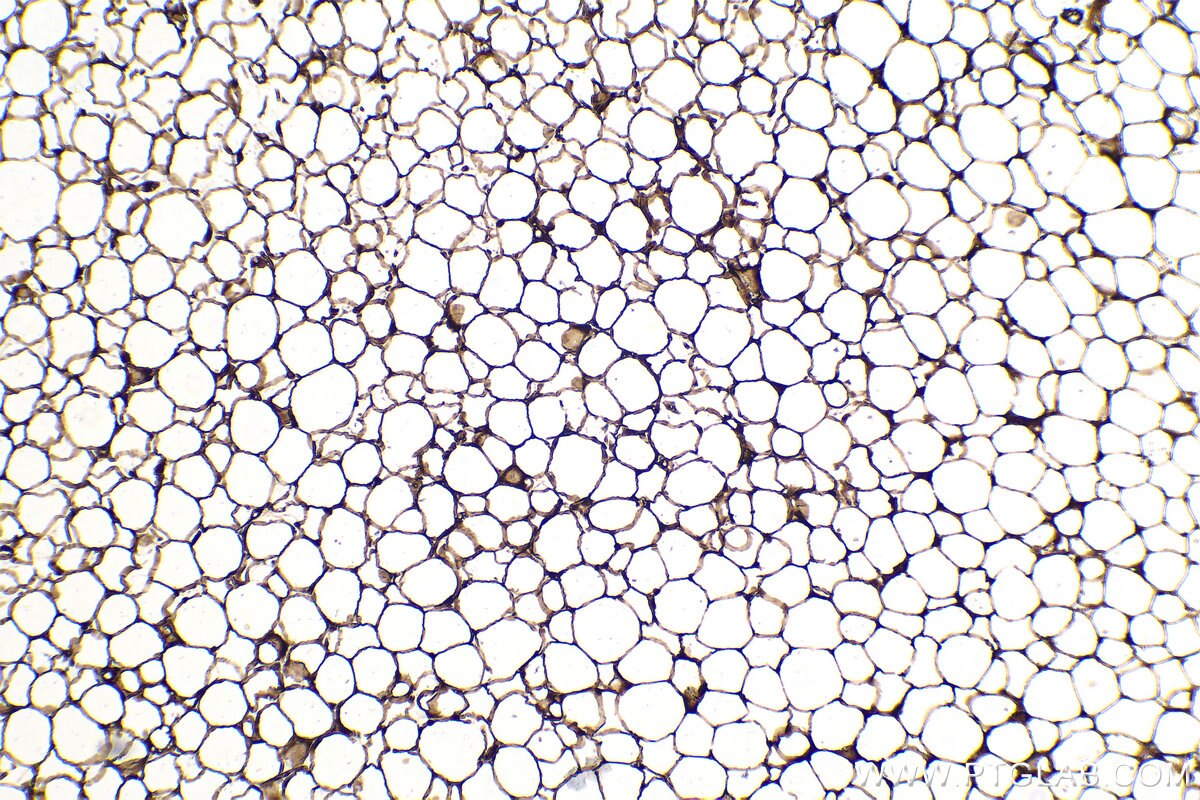
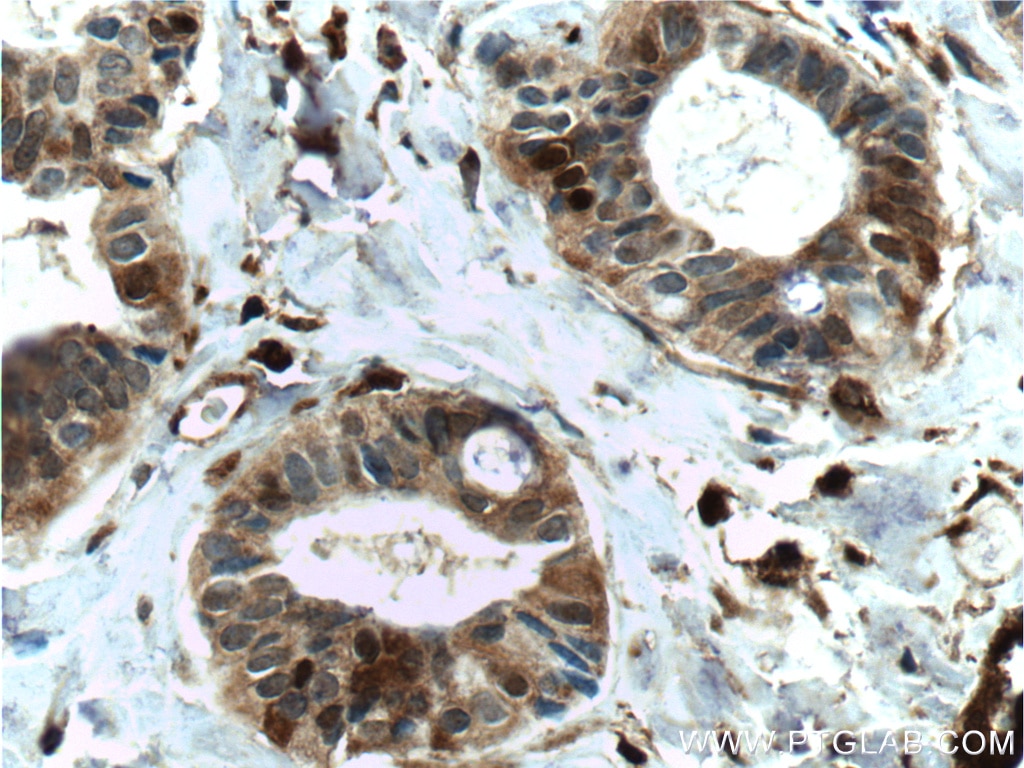
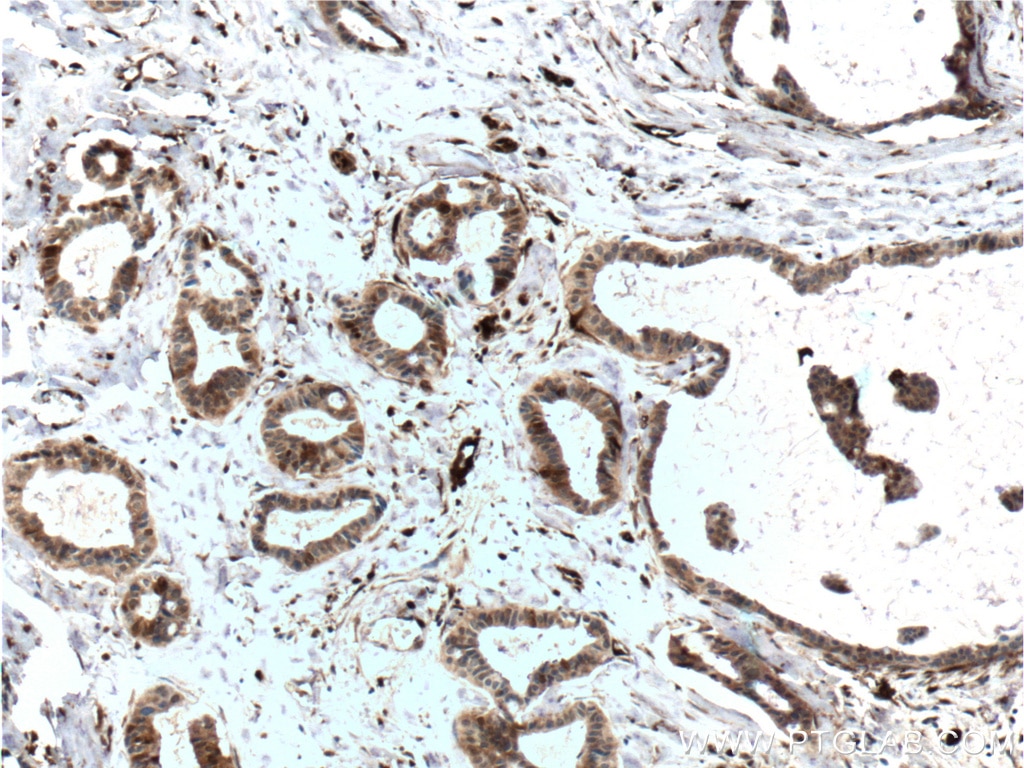
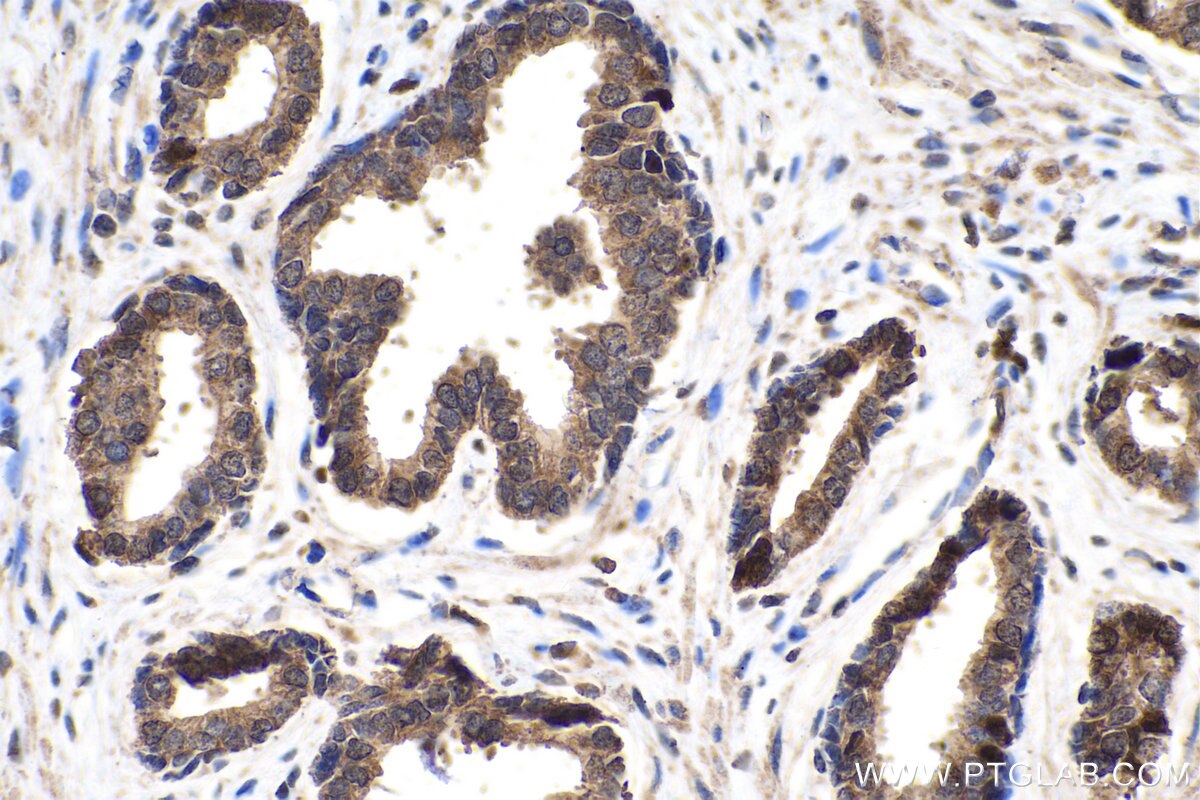
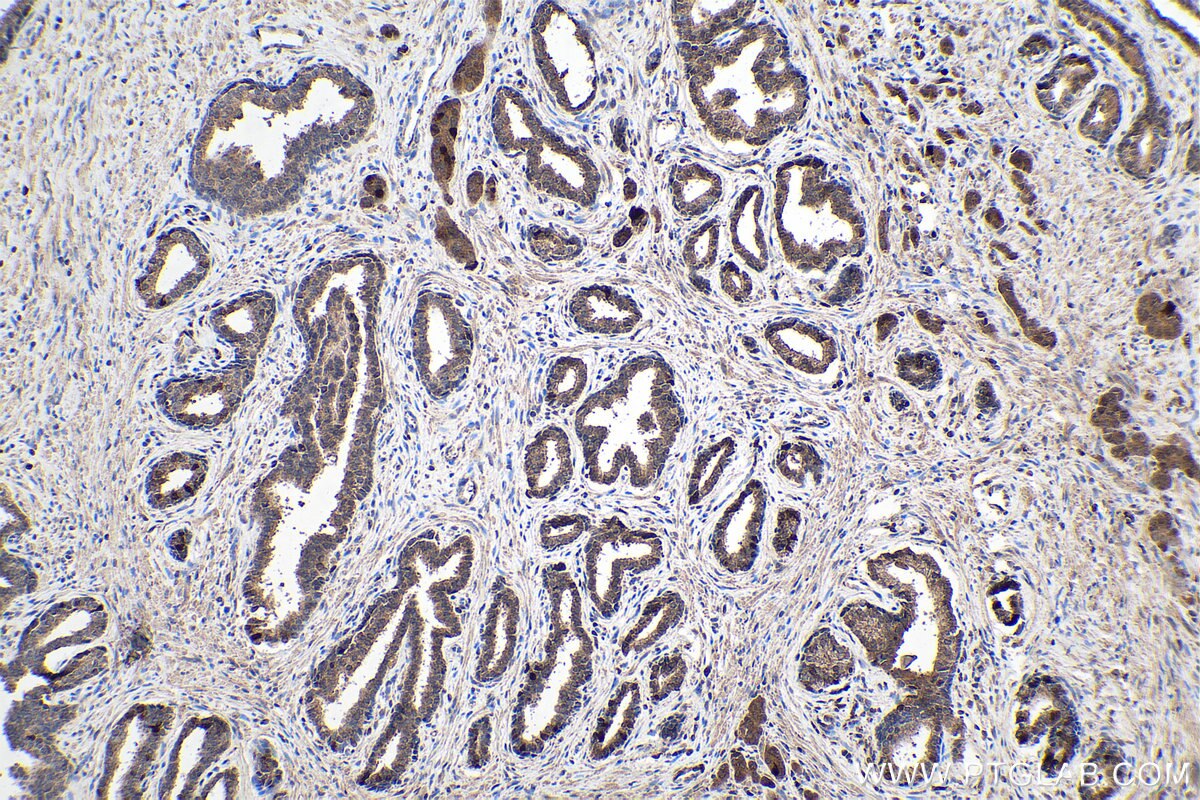
| Positive IHC detected in | human breast cancer tissue, human prostate cancer tissue, mouse brown adipose tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
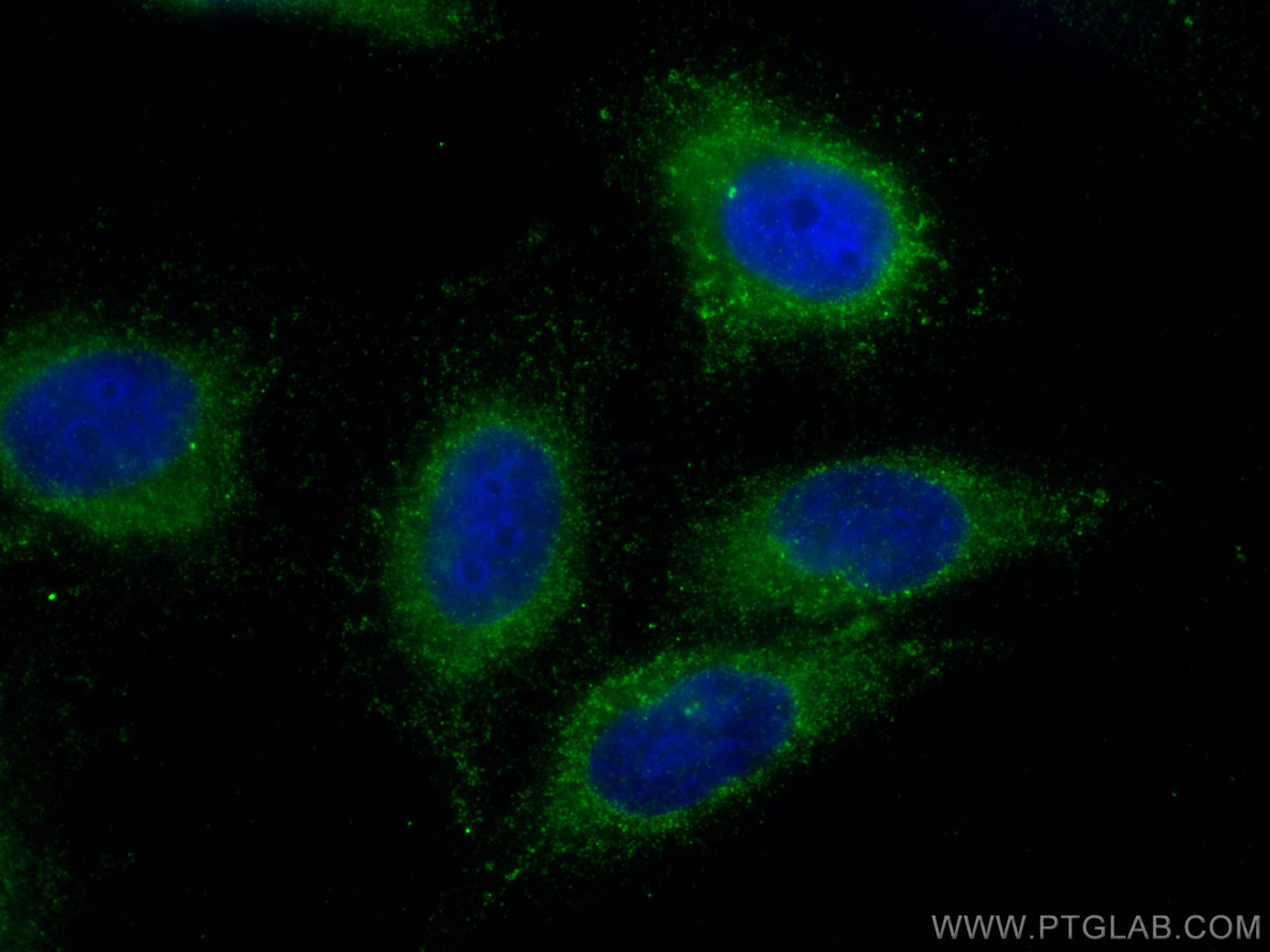
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:16000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:200-1:4000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IHC | See 3 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
66299-1-Ig targets FABP5 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag3005 Product name: Recombinant human FABP5 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-135 aa of BC019385 Sequence: MATVQQLEGRWRLVDSKGFDEYMKELGVGIALRKMGAMAKPDCIITCDGKNLTIKTESTLKTTQFSCTLGEKFEETTADGRKTQTVCNFTDGALVQHQEWDGKESTITRKLKDGKLVVECVMNNVTCTRIYEKVE 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | fatty acid binding protein 5 (psoriasis-associated) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 135 aa, 15 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 15 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC019385 |
| Gene Symbol | FABP5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2171 |
| RRID | AB_2881682 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q01469 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
FABP5, also named as PA-FABP and E-FABP, belongs to the calycin superfamily and Fatty-acid binding protein (FABP) family. It is high specificity for fatty acids. FABP5 is highest affinity for C18 chain length. It may be involved in keratinocyte differentiation. FABP5 is a fatty acid-binding protein and is expressed in epidermis and endothelial cells of the microvasculature of different organs. FABP5 has also been identified as a tumor-associated antigen, which is highly expressed in various cancers. FABP5 was detected in the sera of HNSCC patients with early stage cancer. Antibodies specific for FABP5 were significantly increased in a substantial amount in patients, suggesting that FABP5 may be a potential diagnostic biomarker for HNSCC. FABP5 may serve as a biomarker for HNSCC.(PMID:19602232)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for FABP5 antibody 66299-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for FABP5 antibody 66299-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for FABP5 antibody 66299-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Carcinogenesis Serum fatty acid-binding protein 5 is a significant factor in hepatocellular carcinoma progression independent of tissue expression level.
| ||
Med Mol Morphol Expression of fatty-acid-binding protein 5 in intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: the possibility of different energy metabolisms in anatomical location. | ||
J Allergy Clin Immunol Melatonin treatment increases skin microbiota-derived propionic acid to alleviate atopic dermatitis | ||
Free Radic Biol Med Oxidative stress-induced decreased expression of FABP5 leads to mitochondrial damage and survival disorder of decidual stromal cells in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion |