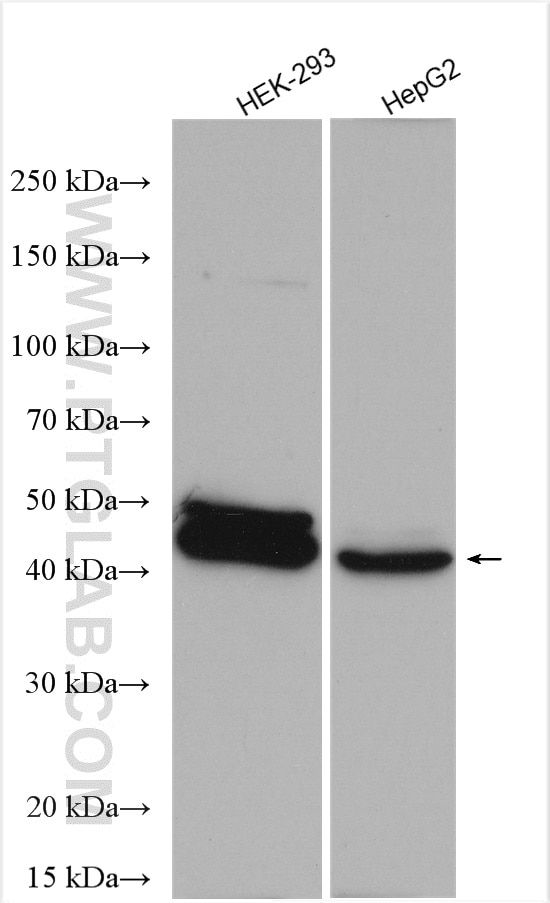
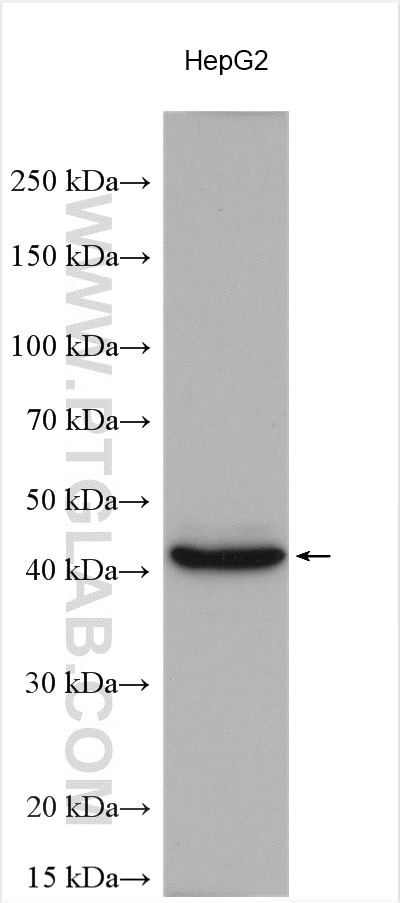
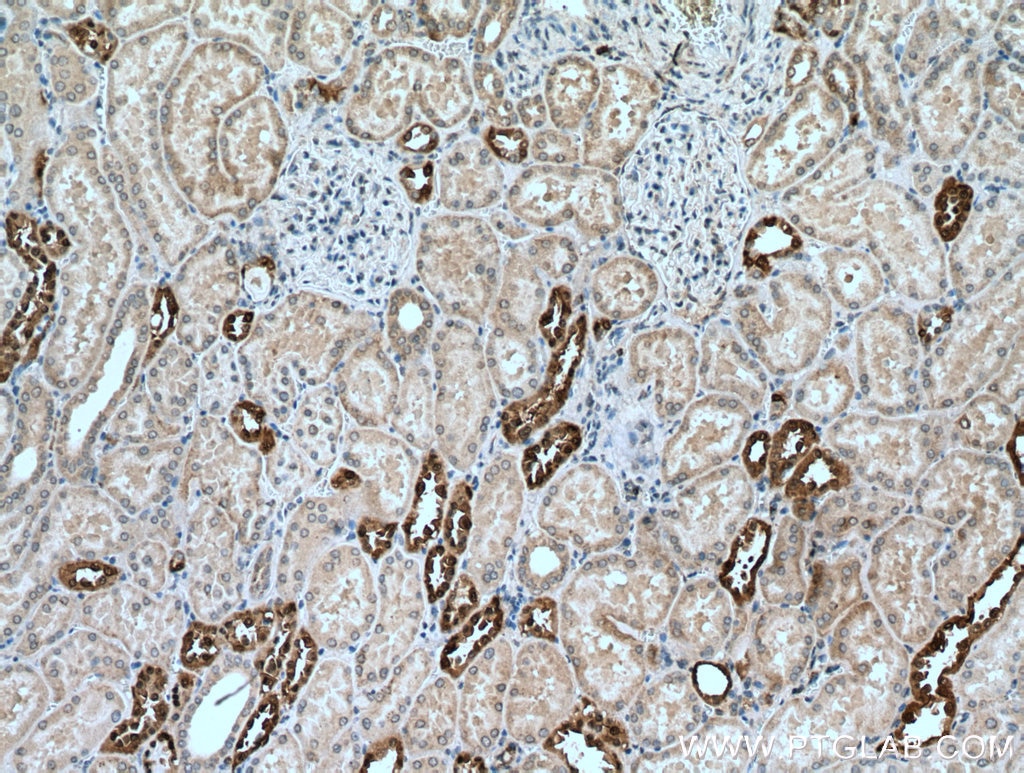
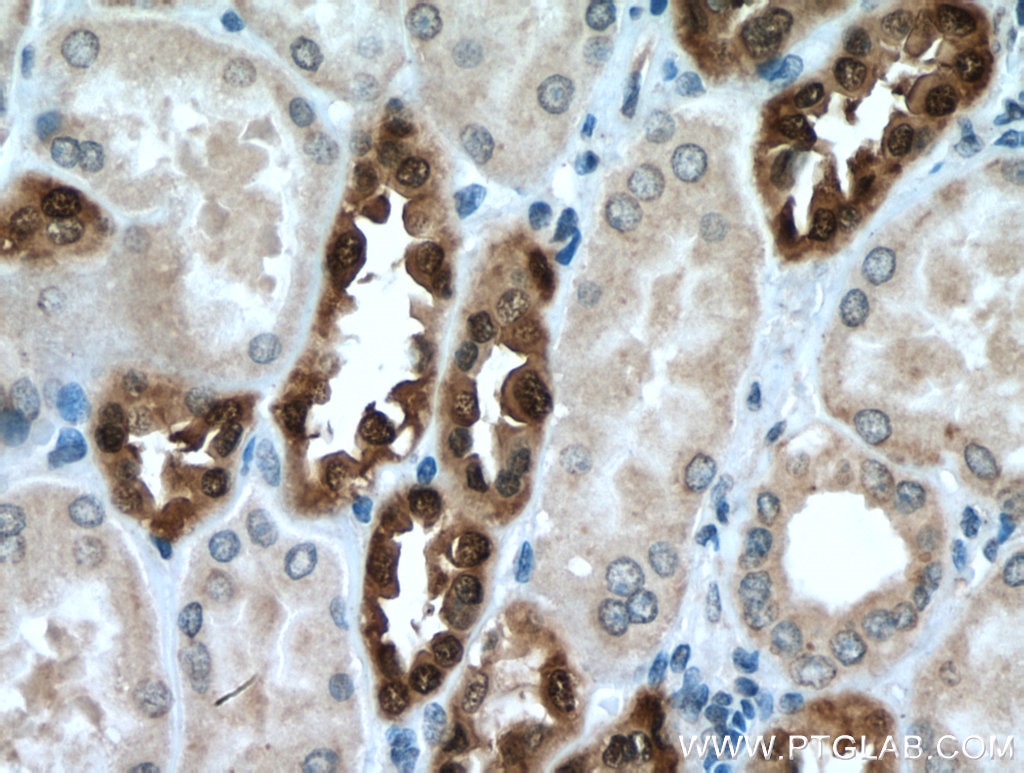
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | HEK-293 cells, HepG2 cells |
| Positive IHC detected in | human kidney tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 2 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
26718-1-AP targets DUSP9 in WB, IHC, IF, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag25167 Product name: Recombinant human DUSP9 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 343-384 aa of BC060837 Sequence: SLRLEERHSQEQGSGGQASAASNPPSFFTTPTSDGAFELAPT 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | dual specificity phosphatase 9 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 42 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 42 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC060837 |
| Gene Symbol | DUSP9 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1852 |
| RRID | AB_2880612 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q99956 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 9 (DUSP9) is also named itogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 4 (MAP kinase phosphatase 4; MKP-4). DUSP9 is a typical DUSP characterized by the presence of an MKB/KIM motif and a phosphatase domain, which shares structural homology with other DUSPs (PMID: 25519881). DUSP9 is an important downstream regulator of BMP/Smad signaling and a key factor in maintaining the stemness of mESCs (PMID: 34768967). DUSP9 is one of the key genes involved in gonadotrophin-mediated ovarian follicle development (PMID: 33676987). DUSP9 expression increases during insulin-induced adipogenesis and culminates in mature adipocytes. DUSP9 as a key regulator of insulin signaling and highlighted its potential role in insulin resistance and metabolic diseases by dephosphorylating kinases involved in metabolic processes, glucose uptake and storage. DUSP9 can also impair the action of extracellular mediators and stress inducers (i.e., proinflammatory cytokines), which can induce insulin resistance by abnormally activating MAPK or SAP pathways (PMID: 30063256, PMID: 18296638). In normal mature tissues, DUSP9 is mainly expressed in kidney, adipose tissue and placenta, while it is only minimally present in brain, ovary, testis and urinary bladder (PMID: 34768967).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for DUSP9 antibody 26718-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for DUSP9 antibody 26718-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Sci Rep Inhibition of miR-194-5p avoids DUSP9 downregulation thus limiting sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy
| ||
Adv Sci (Weinh) Malignant Hepatoblast-Like Cells Sustain Stemness via IGF2-Dependent Cholesterol Accumulation in Hepatoblastoma | ||
Front Immunol Identifying specific TLS-associated genes as potential biomarkers for predicting prognosis and evaluating the efficacy of immunotherapy in soft tissue sarcoma |