Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
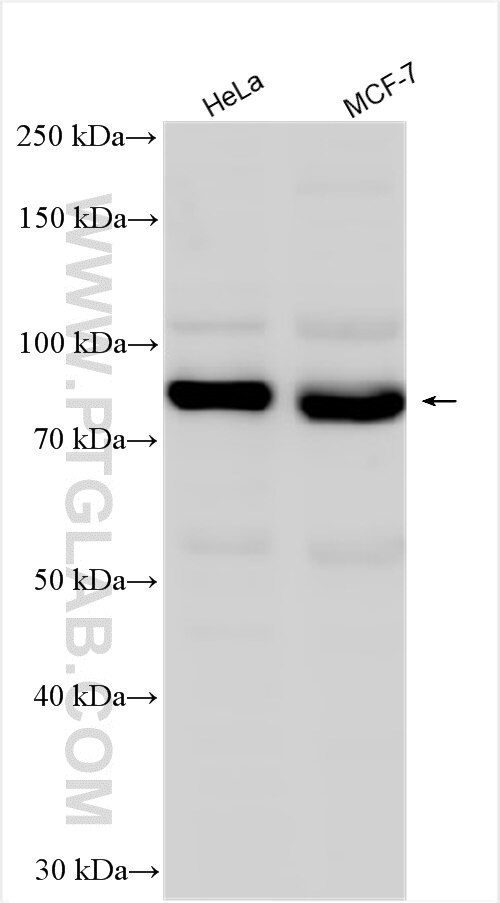
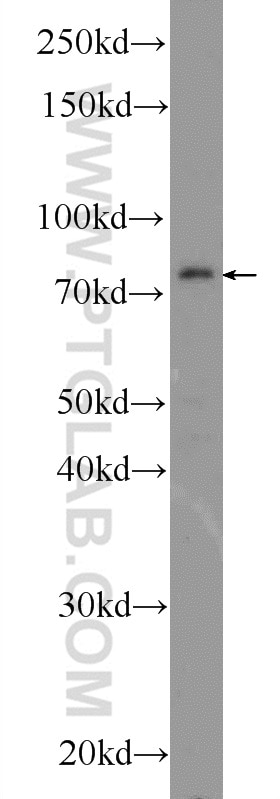
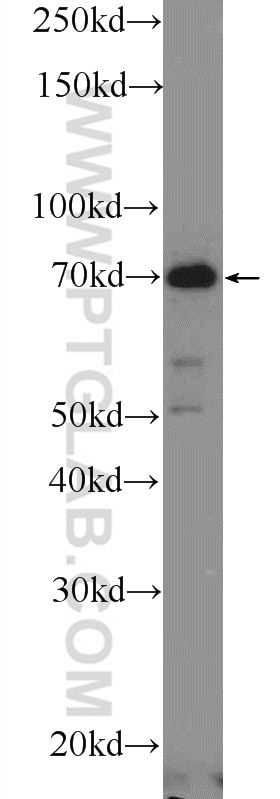
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, MDA-MB-453s cells, mouse skin tissue, MCF-7 cells |
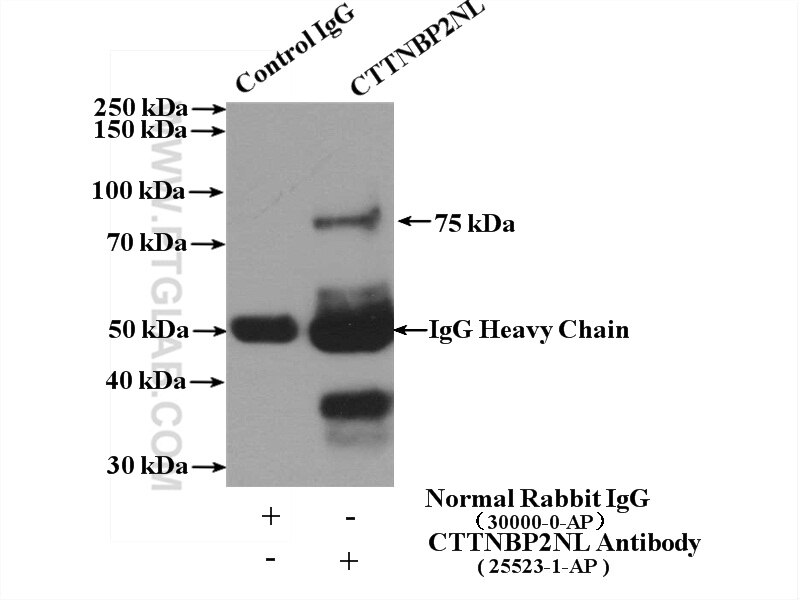
| Positive IP detected in | MCF-7 cells |
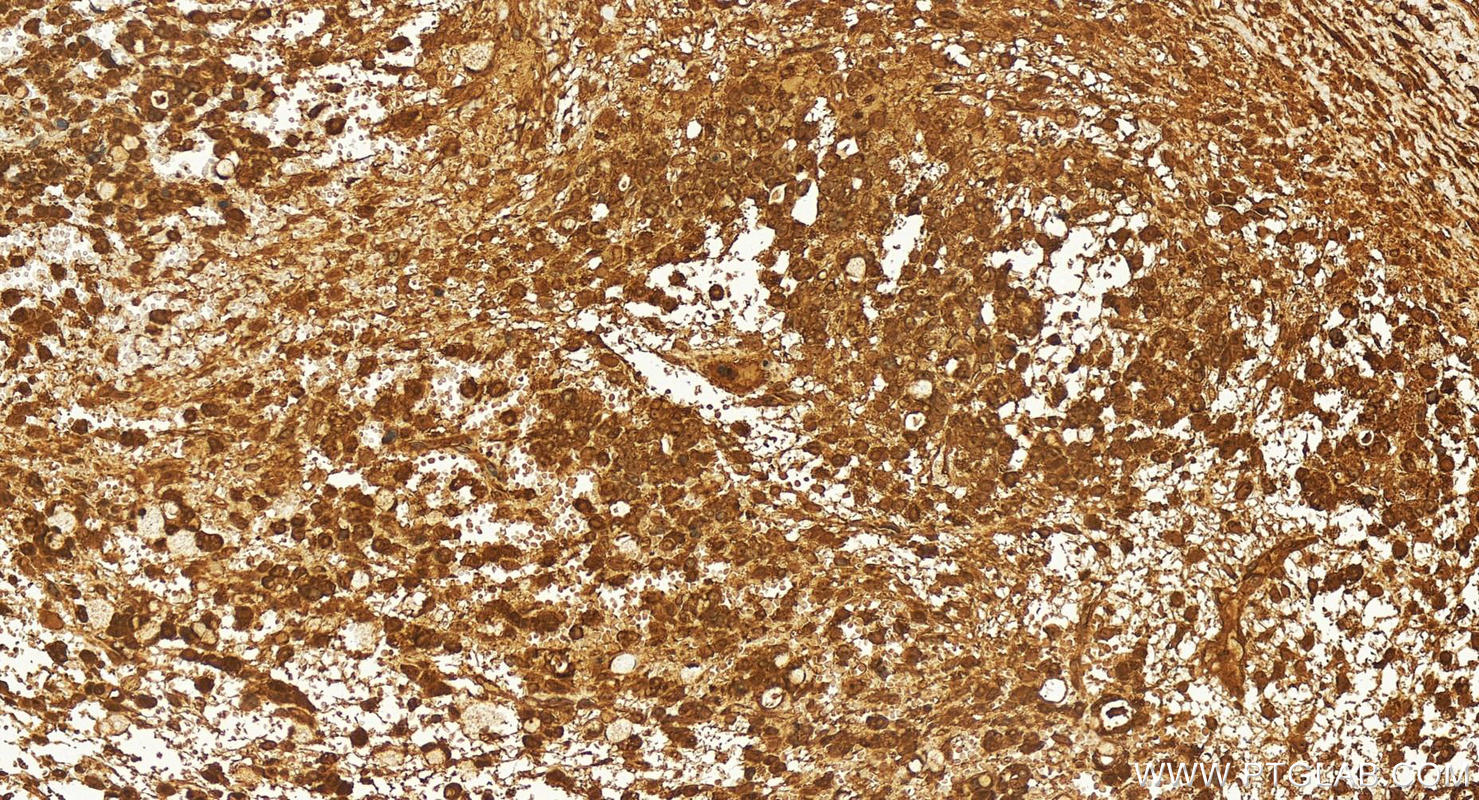
| Positive IHC detected in | human ovary cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
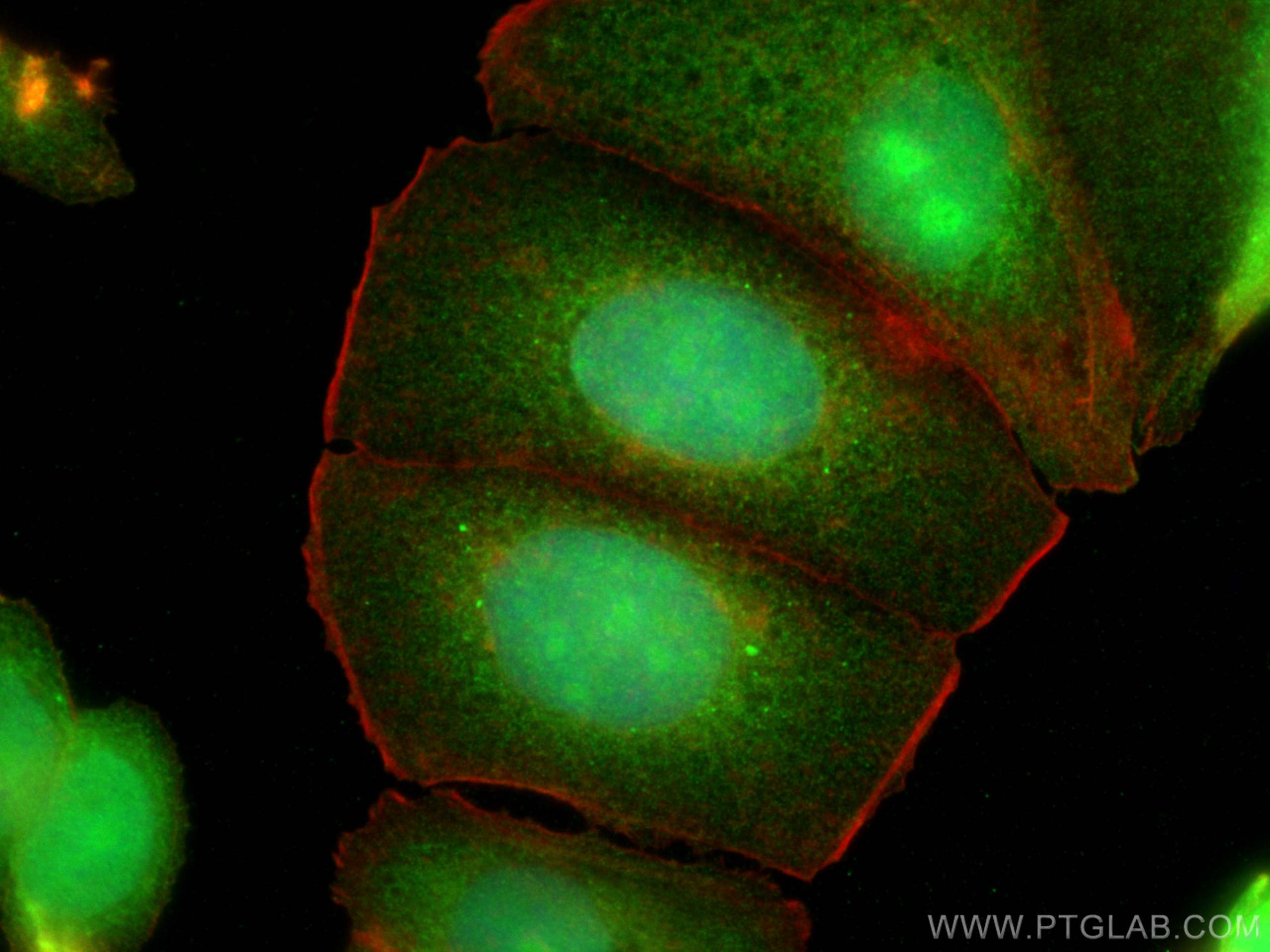
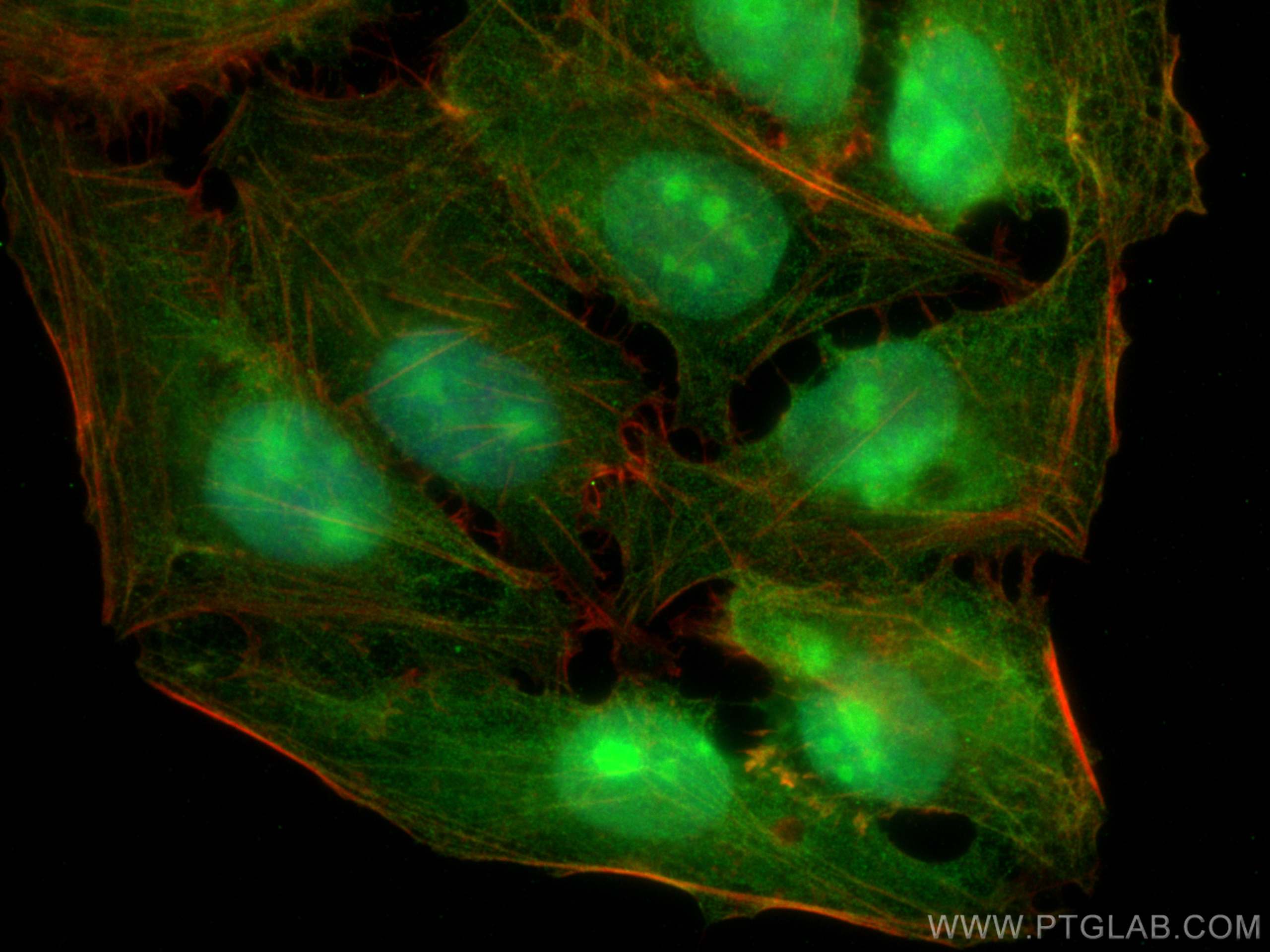
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | U2OS cells, MCF-7 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:12000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
25523-1-AP targets CTTNBP2NL in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag22137 Product name: Recombinant human CTTNBP2NL protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 271-479 aa of BC016029 Sequence: KKIVKDLEASHQHSSPNEQLKKPVTVSKGTATEPLMLMSVFCQTESFPAERTHGSNIAKMTNTGLPGPATPAYSYAKTNGHCDPEIQTTRELTAGNNVENQVPPREKSVALAQEKPVENGGCPVGIETPVPMPSPLSSSGSSLSPSSTASSSLTSSPCSSPVLTKRLLGSSASSPGYQSSYQVGINQRFHAARHKFQSQADQDQQASGL 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | CTTNBP2 N-terminal like |
| Calculated molecular weight | 639 aa, 70 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 70-75 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC016029 |
| Gene Symbol | CTTNBP2NL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 55917 |
| RRID | AB_2880117 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9P2B4 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for CTTNBP2NL antibody 25523-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for CTTNBP2NL antibody 25523-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for CTTNBP2NL antibody 25523-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for CTTNBP2NL antibody 25523-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |