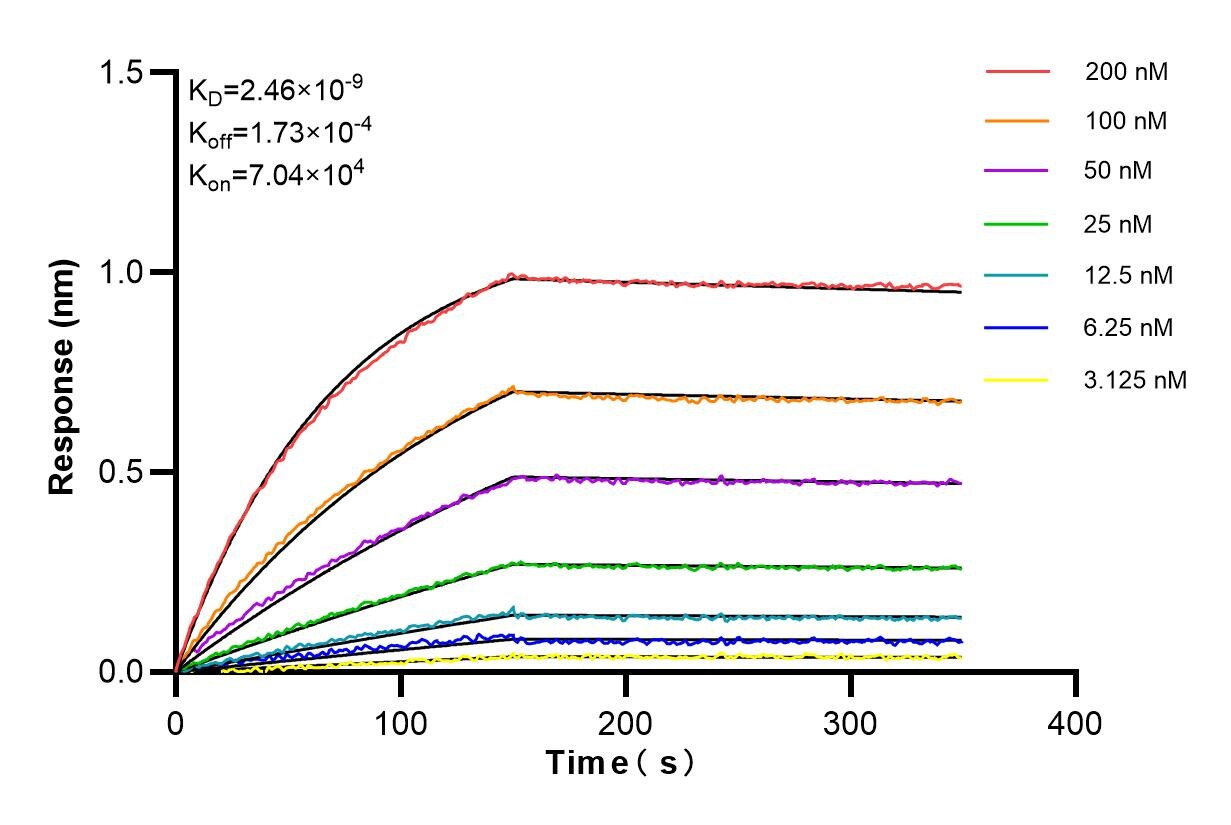
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
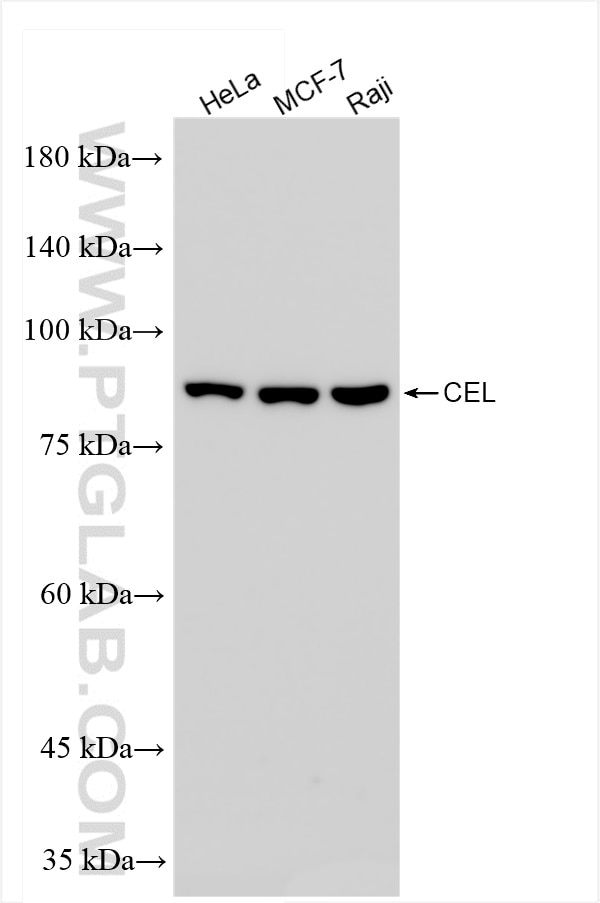
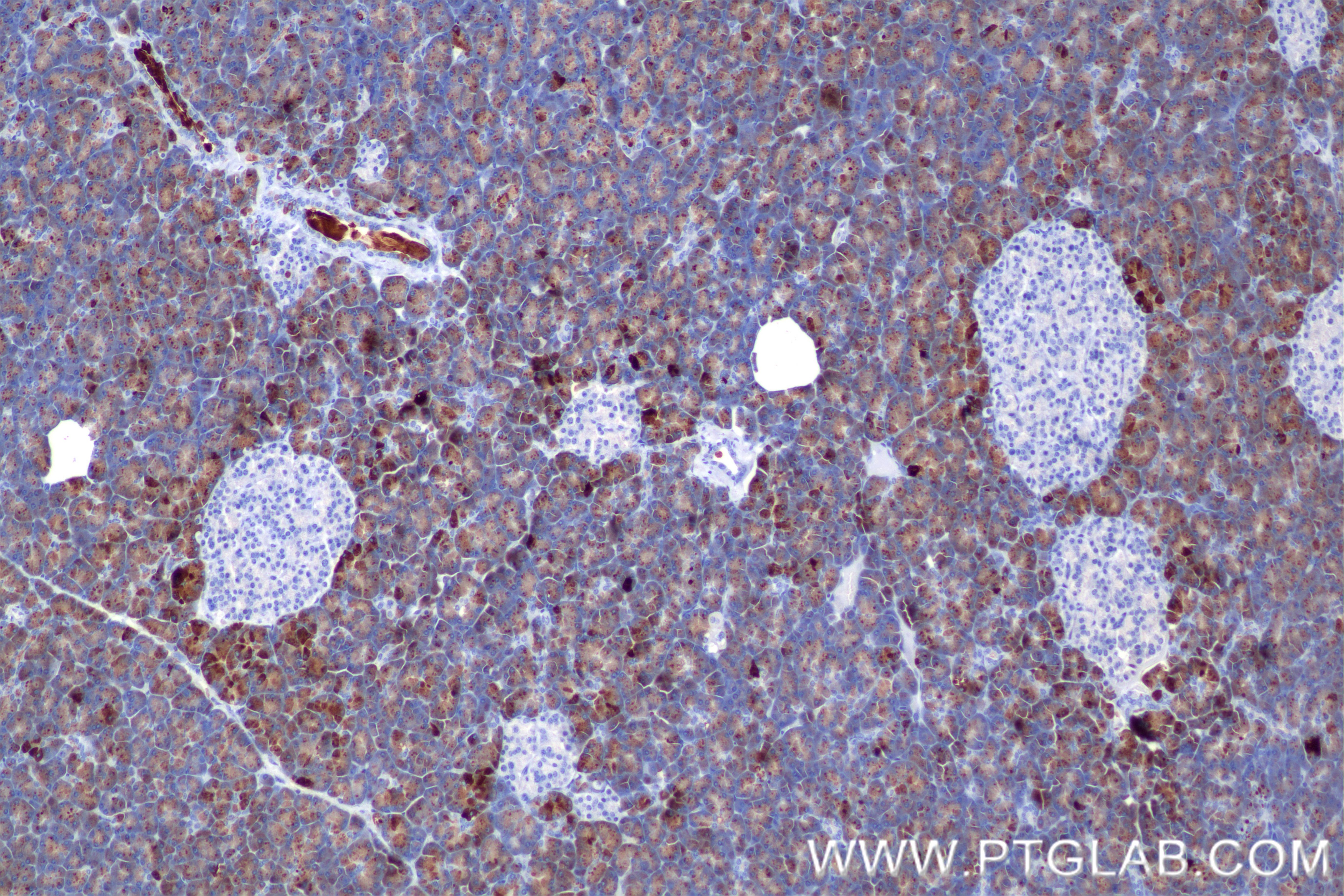
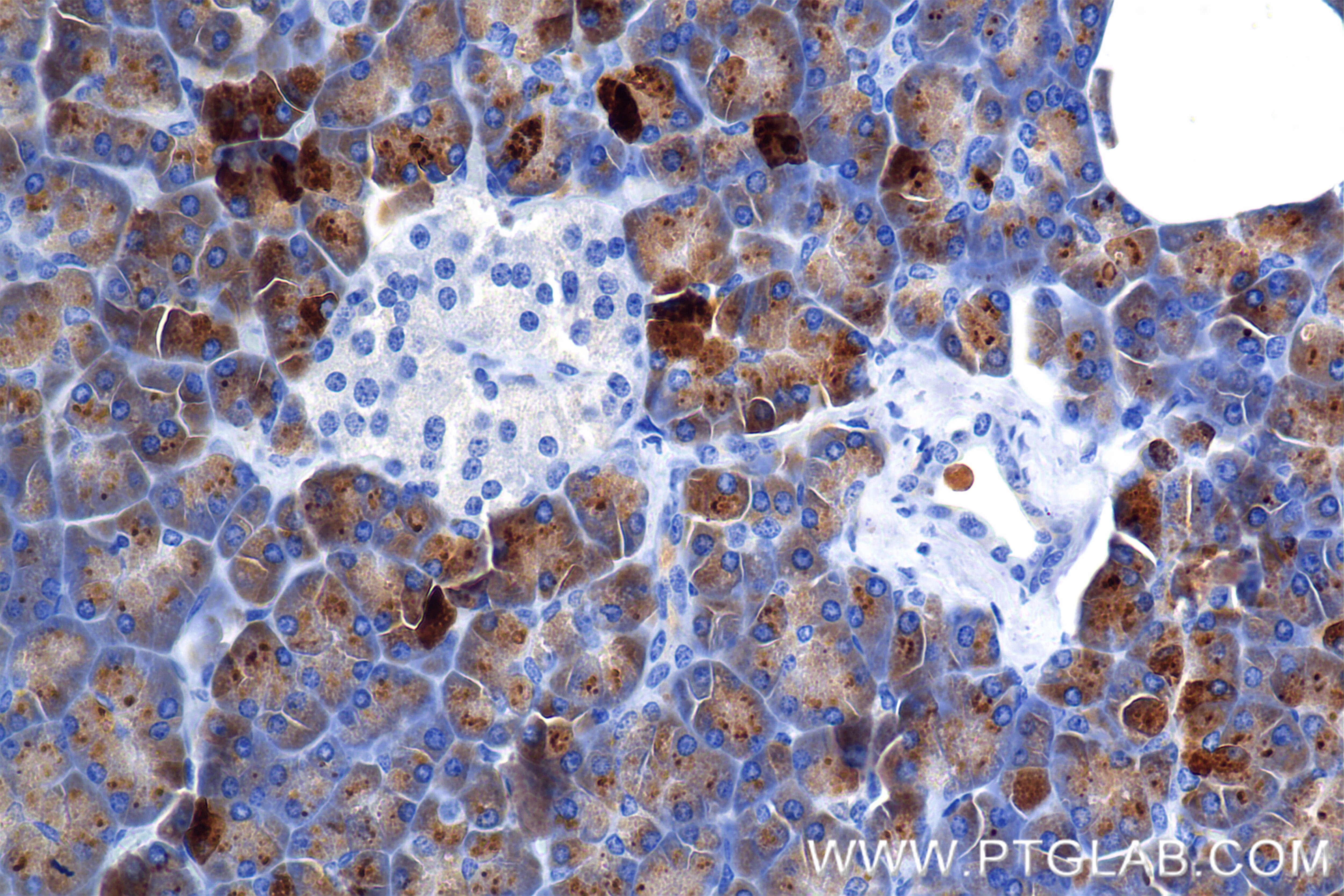
85081-4-PBS targets CEL in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag5262 Product name: Recombinant human CEL protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 371-722 aa of BC042510 Sequence: SEFTITKGLRGAKTTFDVYTESWAQDPSQENKKKTVVDFETDVLFLVPTEIALAQHRANAKSAKTYAYLFSHPSRMPVYPKWVGADHADDIQYVFGKPFATPTGYRPQDRTVSKAMIAYWTNFAKTGDPNMGDSAVPTHWEPYTTENSGYLEITKKMGSSSMKRSLRTNFLRYWTLTYLALPTVTDQEATPVPPTGDSEATPVPPTGDSETAPVPPTGDSGAPPVPPTGDSGAPPVPPTGDSGAPPVPPTGDSGAPPVPPTGDSGAPPVPPTGDAGPPPVPPTGDSGAPPVPPTGDSGAPPVTPTGDSETAPVPPTGDSGAPPVPPTGDSEAAPVPPTDDSKEAQMPAVIRF 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | carboxyl ester lipase (bile salt-stimulated lipase) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 79 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 79 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC042510 |
| Gene Symbol | CEL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1056 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P19835 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Bile salt-activated lipase, previously named cholesterol esterase or bile salt-stimulated (or dependent) lipase, is a 74 kDa lipolytic enzyme capable of hydrolyzing cholesteryl esters, tri-, di-, and mono-acylglycerols, phospholipids, lysophospholipids, and ceramide(PMID:12454261). The same enzyme is present as a major protein in milk and as a minor constituent in liver, activated macrophages, and endothelial cells(PMID:11733511). Defects in CEL are a cause of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 8 with exocrine dysfunction (MODY8)(PMID:16369531). The full length protein has 11 glycosylation sites. It has 2 isoforms produced by alternative splicing.