Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
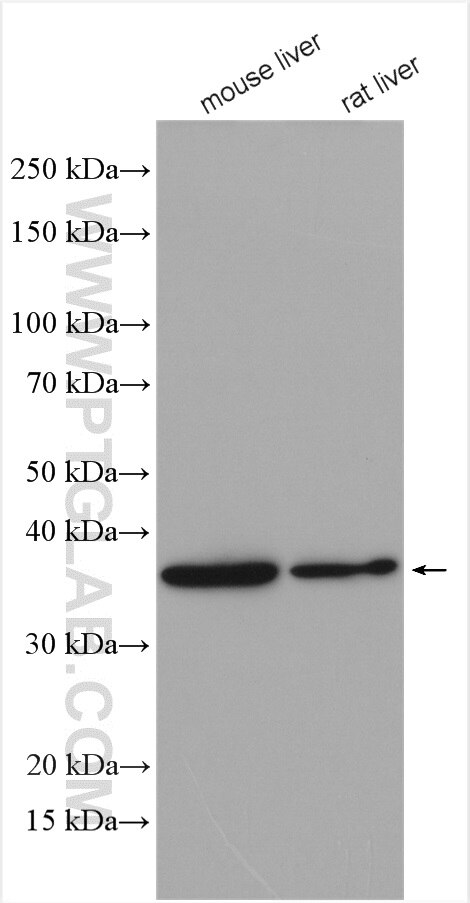
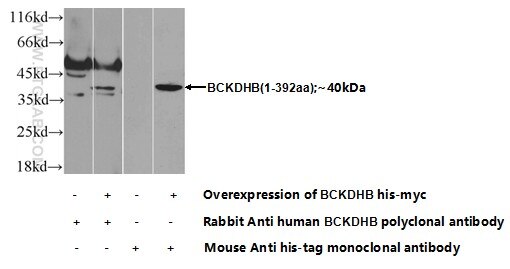
| Positive WB detected in | mouse liver tissue, Transfected HEK-293 cells, rat liver tissue |
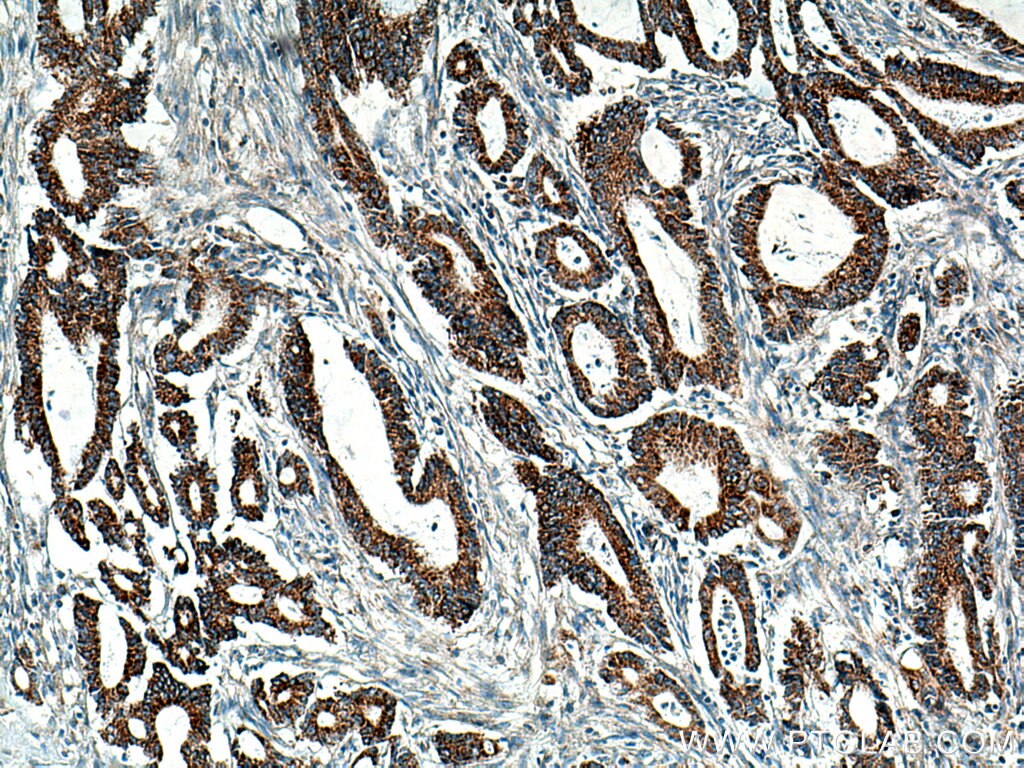
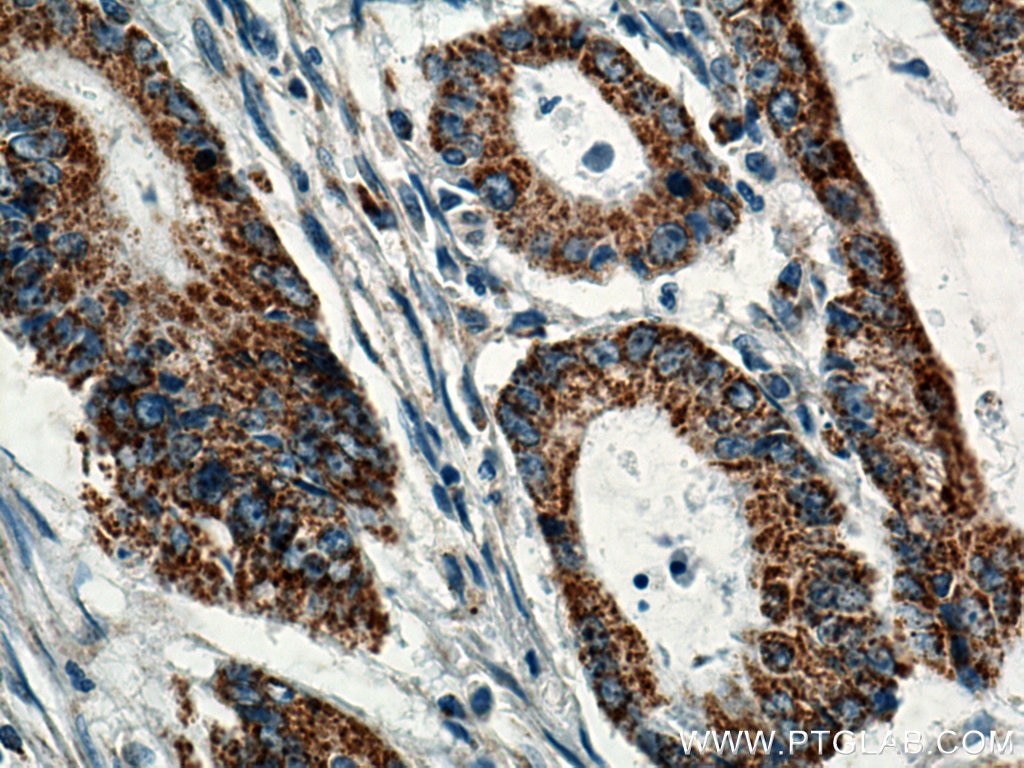
| Positive IHC detected in | human colon cancer tissue, human stomach tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 8 publications below |
| IHC | See 4 publications below |
| RIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
13685-1-AP targets BCKDHB in WB, IHC, RIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, sheep |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag4552 Product name: Recombinant human BCKDHB protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 41-392 aa of BC040139 Sequence: TVEDAAQRRQVAHFTFQPDPEPREYGQTQKMNLFQSVTSALDNSLAKDPTAVIFGEDVAFGGVFRCTVGLRDKYGKDRVFNTPLCEQGIVGFGIGIAVTGATAIAEIQFADYIFPAFDQIVNEAAKYRYRSGDLFNCGSLTIRSPWGCVGHGALYHSQSPEAFFAHCPGIKVVIPRSPFQAKGLLLSCIEDKNPCIFFEPKILYRAAAEEVPIEPYNIPLSQAEVIQEGSDVTLVAWGTQVHVIREVASMAKEKLGVSCEVIDLRTIIPWDVDTICKSVIKTGRLLISHEAPLTGGFASEISSTVQEECFLNLEAPISRVCGYDTPFPHIFEPFYIPDKWKCYDALRKMINY 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | branched chain keto acid dehydrogenase E1, beta polypeptide |
| Calculated molecular weight | 392 aa, 43 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 37 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC040139 |
| Gene Symbol | BCKDHB |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 594 |
| RRID | AB_2877972 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P21953 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase E1 component beta chain (BCKDHB; BCKDE1B; BCKDH E1-beta) is a subunit of the BCKDH complex, which is a mitochondrial enzyme in the degradation pathway for branched-chain amino acids (BCAA). Together with BCKDHA, BCKDHB forms the E1 subunit of this complex, whereas DBT and DLD are the E2 and E3 subunits, respectively. A deficiency of the BCKDH complex in humans causes maple syrup urine disease (MSUD), a severe neurometabolic disorder diagnosed by the detection alloisoleucine in plasma (MIM 248600). (PMID: 30709776)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for BCKDHB antibody 13685-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for BCKDHB antibody 13685-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Cancer Integrative proteogenomic profiling of high-risk prostate cancer samples from Chinese patients indicates metabolic vulnerabilities and diagnostic biomarkers | ||
Sci Transl Med BCKDHA-BCKDHB digenic gene therapy restores metabolic homeostasis in two mouse models and a calf with classic maple syrup urine disease | ||
Anim Sci J MiR-330-5p negatively regulates ovine preadipocyte differentiation by targeting branched-chain aminotransferase 2. | ||
Cell Rep SIRT4 is an early regulator of branched-chain amino acid catabolism that promotes adipogenesis. | ||
Cell Rep Branched-chain amino acid catabolism breaks glutamine addiction to sustain hepatocellular carcinoma progression | ||
Nat Commun AMPK induces degradation of the transcriptional repressor PROX1 impairing branched amino acid metabolism and tumourigenesis |