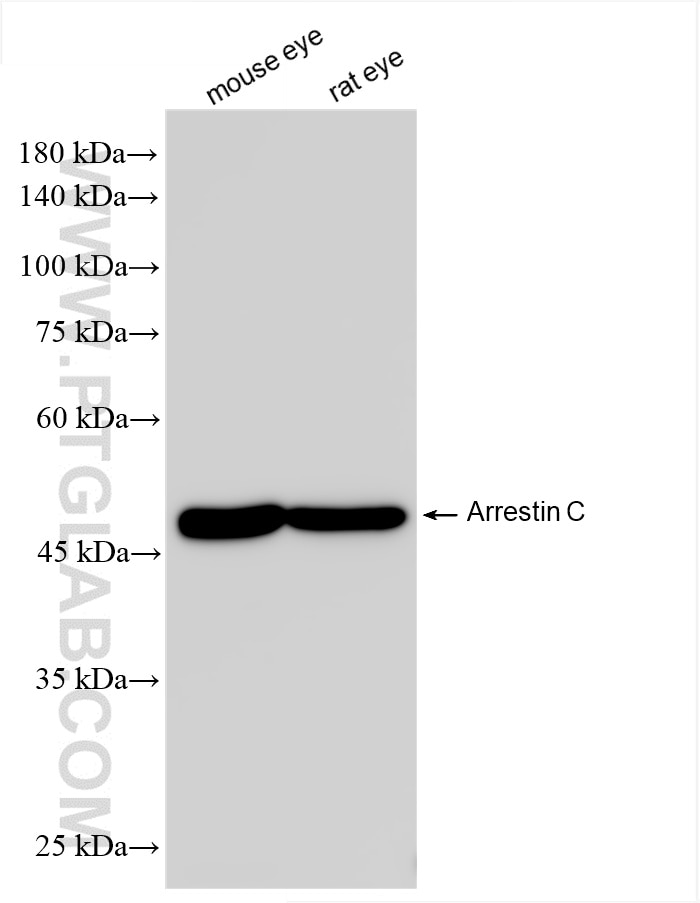
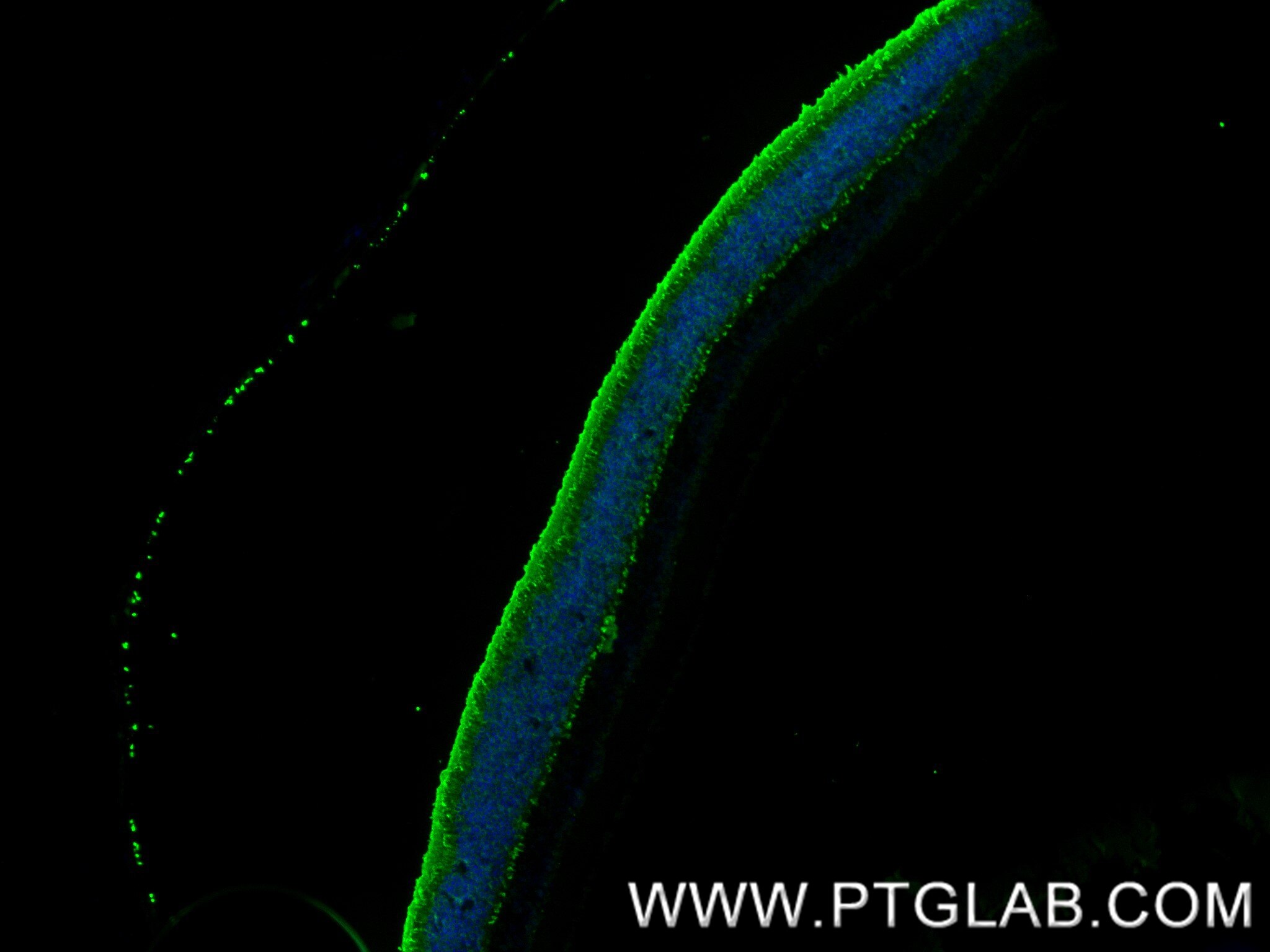
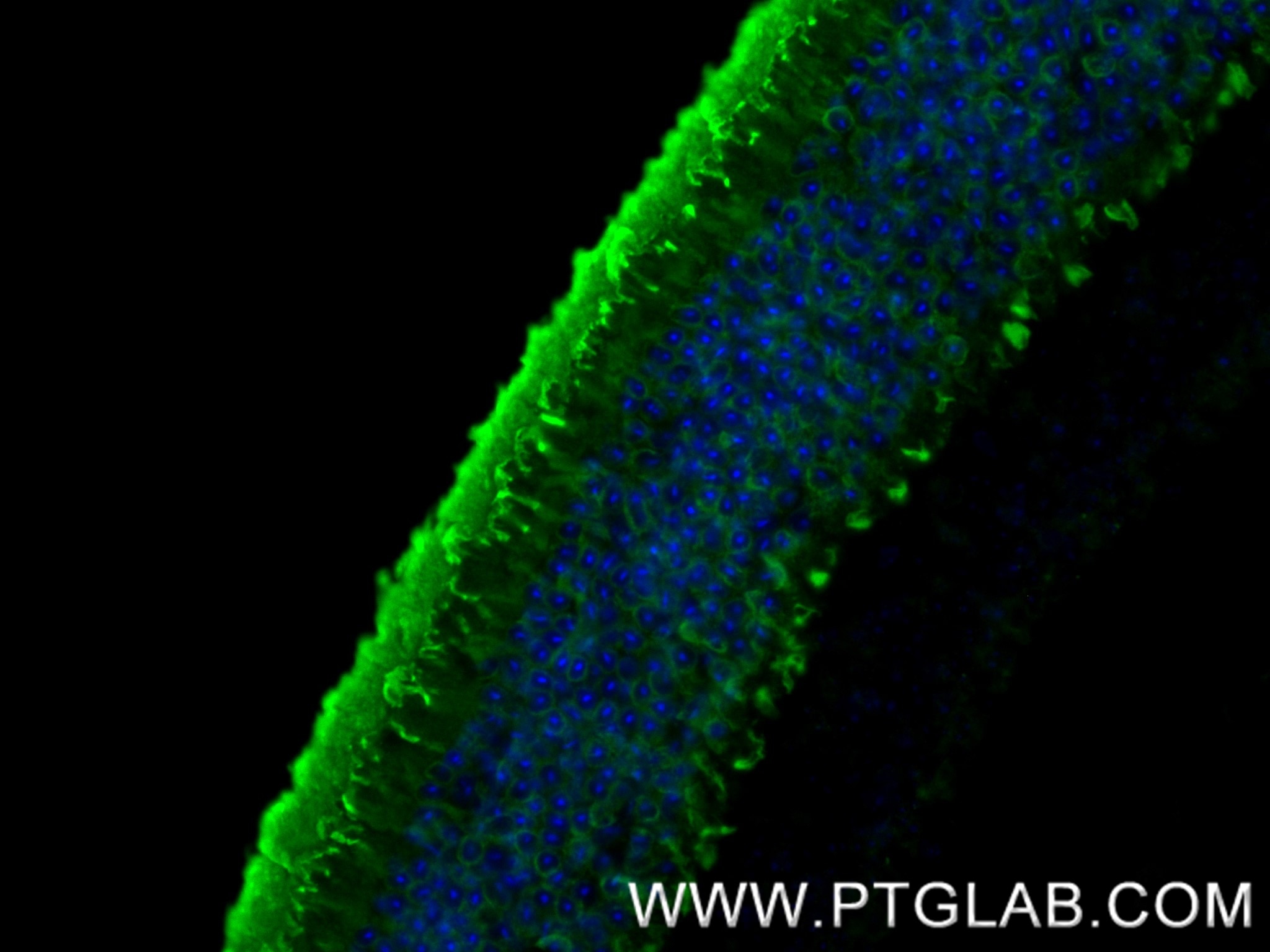
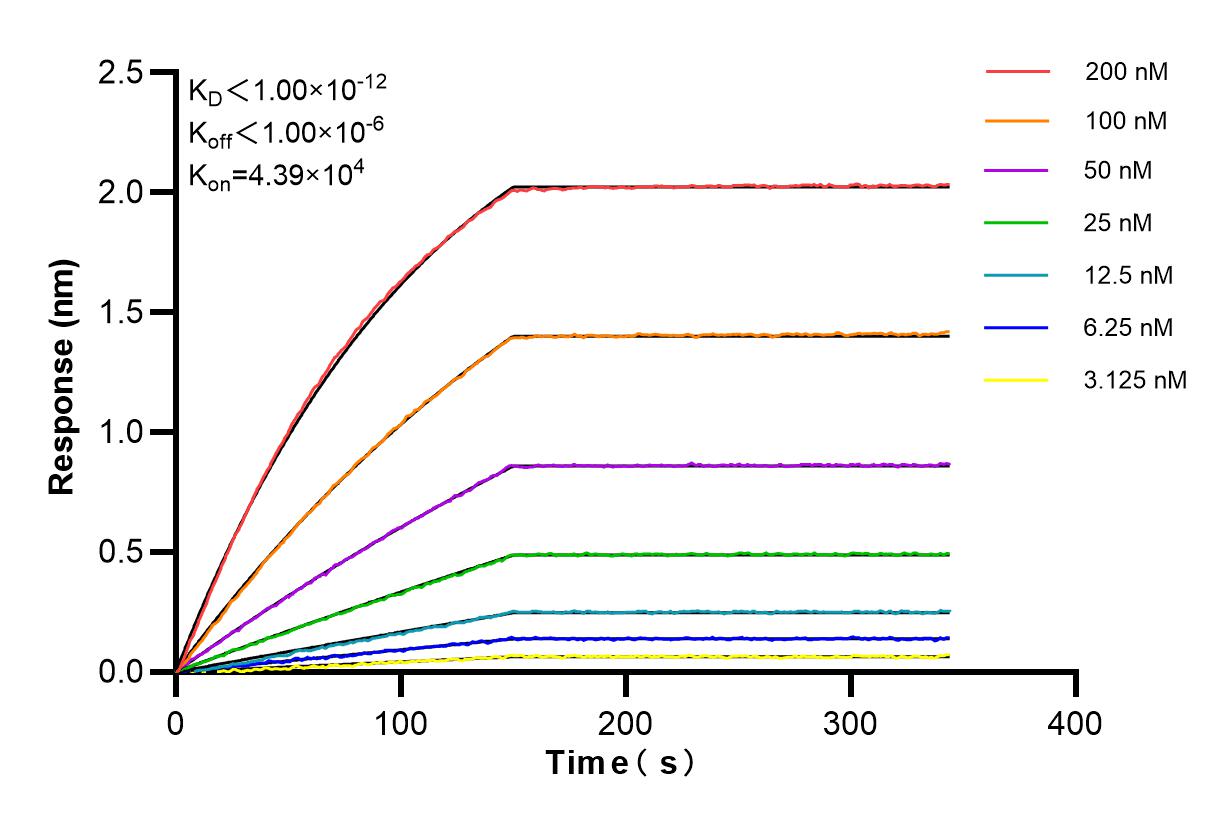
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
85067-5-PBS targets Arrestin C in WB, IF-P, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag1580 Product name: Recombinant human ARR3 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 1-300 aa of BC012096 Sequence: MSKVFKKTSSNGKLSIYLGKRDFVDHVDTVEPIDGVVLVDPEYFKCRKLFVMLTCAFRYGRDDLEVIGLTFRKDLYVQTLQVVPAESSSPQGPLTVLQERLLHKLGDNAYPFTLQMVTNLPCSVTLQPGPEDAGKPCGIDFEVKSFCAENPEETVSKRDYVRLVVRKVQFAPPEAGPGPSAQTIRRFLLSAQPLQLQAWMDREVHYHGEPISVNVSINNCTNKVIKKIKISVDQITDVVLYSLDKYTKTVFIQEFTETVAANSSFSQSFAVTPILAASCQKRGLALDGKLKHEDTNLASS 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | arrestin 3, retinal (X-arrestin) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 43 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 47-50 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC012096 |
| Gene Symbol | Arrestin C |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 407 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P36575 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Arrestin C, also known as Arrestin 3 or Retinal Cone Arrestin, is a protein encoded by the ARR3 gene. It belongs to the arrestin family, which plays a crucial role in regulating G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling and trafficking. Arrestin C is composed of two major domains: the N-domain and the C-domain, connected by a hinge region. These domains form a structure resembling two clamshells placed end-to-end. The C-terminal tail (C-tail) of Arrestin C interacts extensively with the N-domain, stabilizing its basal conformation. Arrestin C is predominantly expressed in cone photoreceptors and pinealocytes in the retina. It is involved in the shut-off mechanisms associated with high-acuity color vision by binding to phosphorylated and activated opsins, thereby inhibiting their ability to interact with transducin.