Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
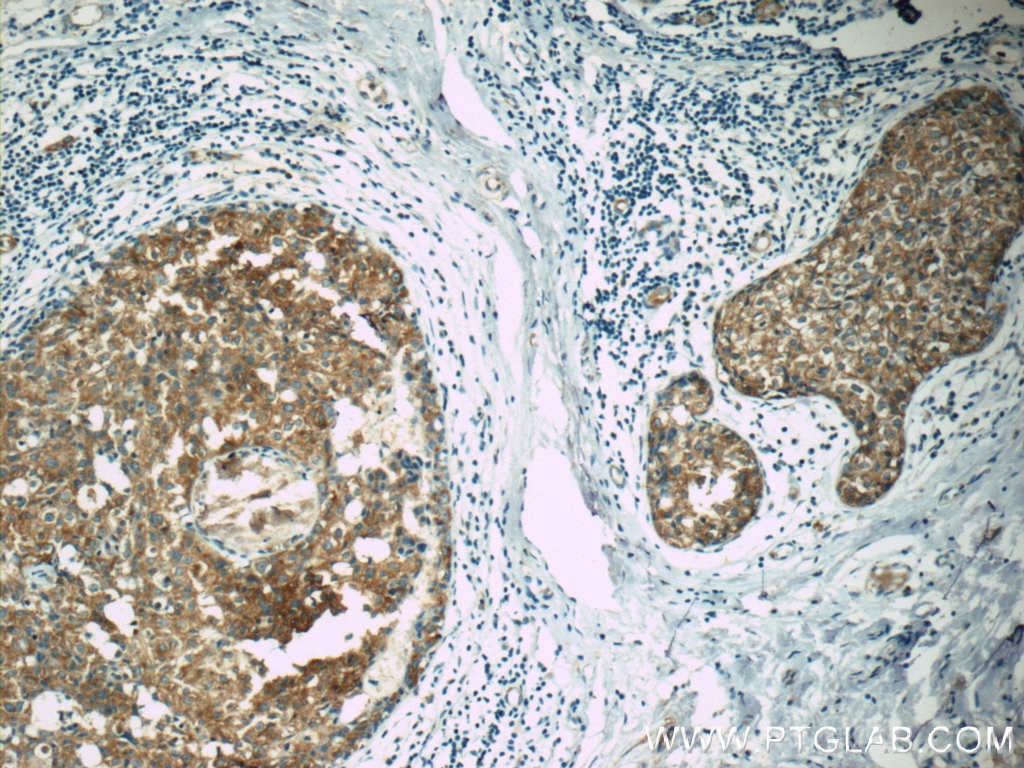
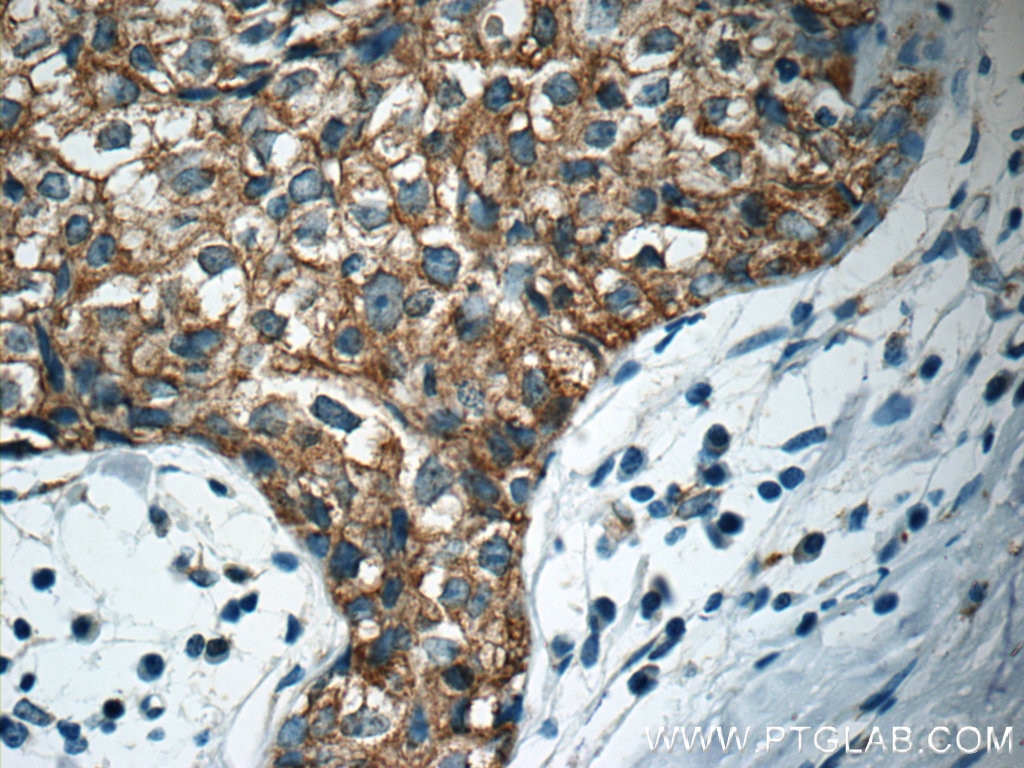
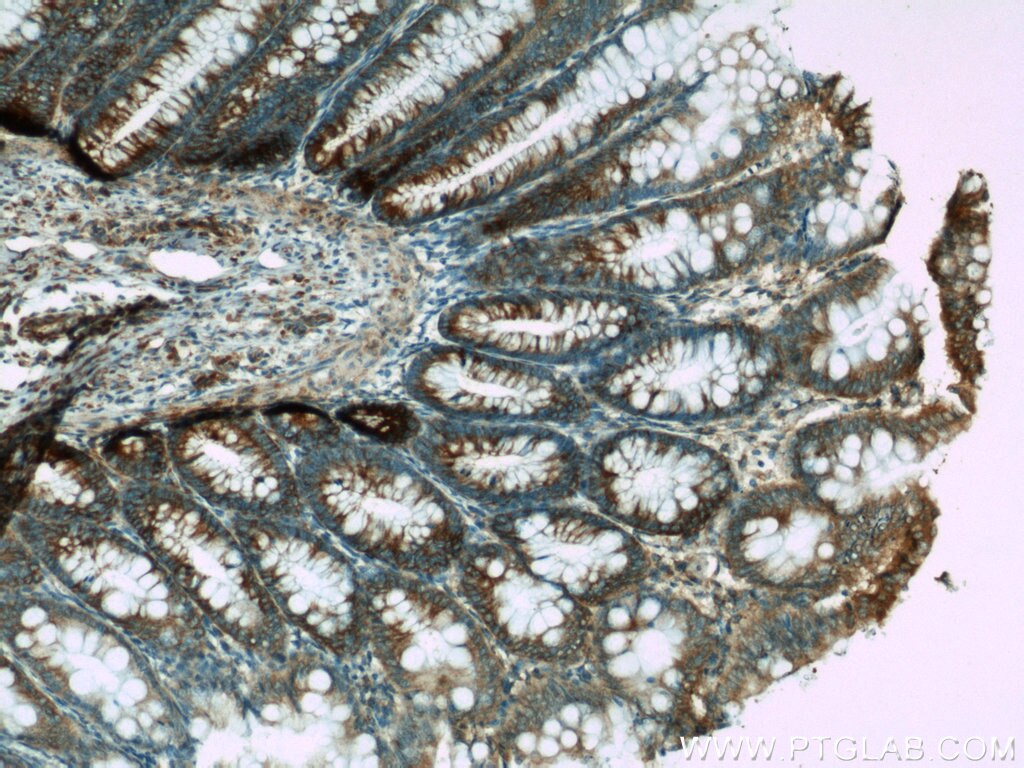
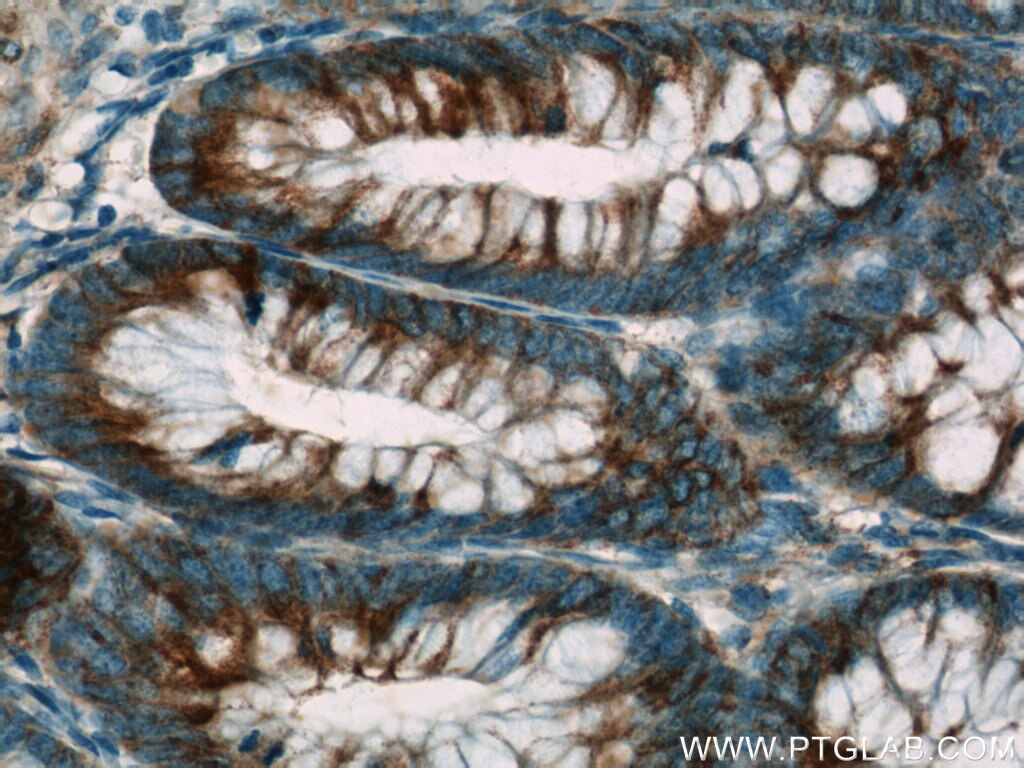
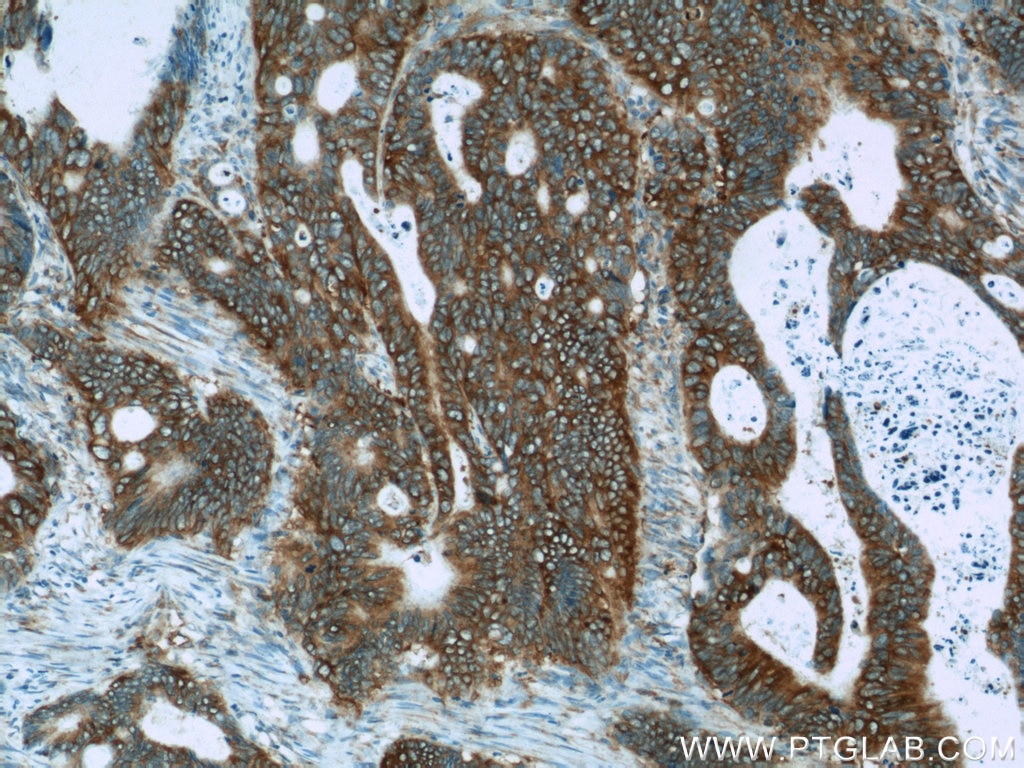
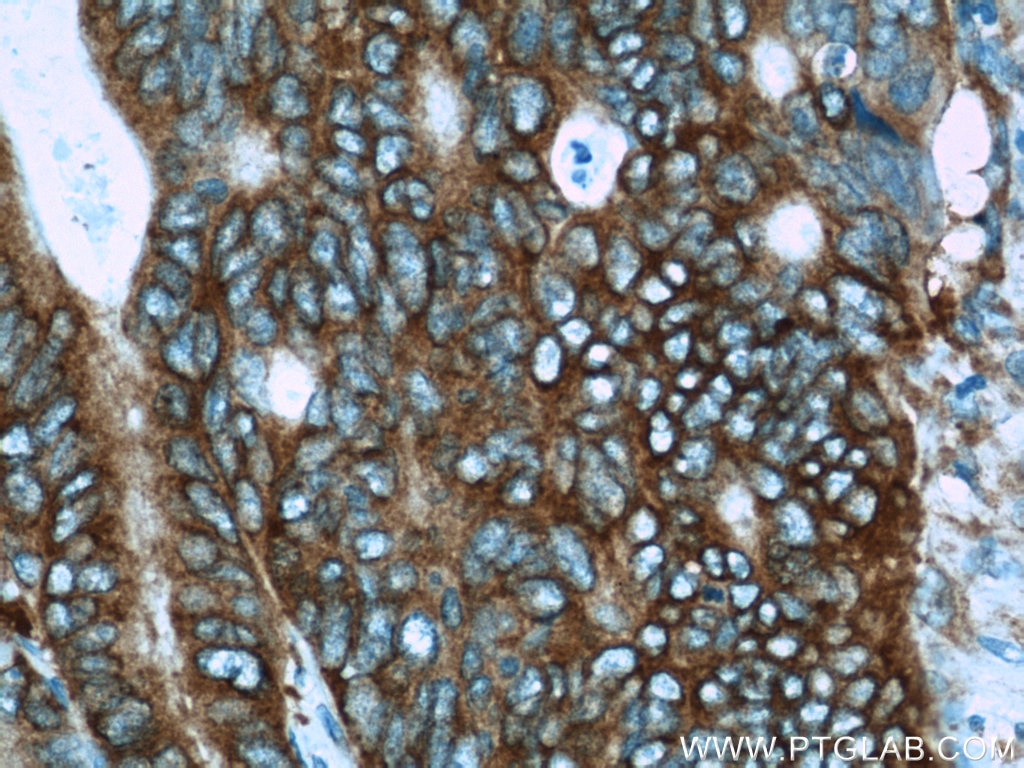
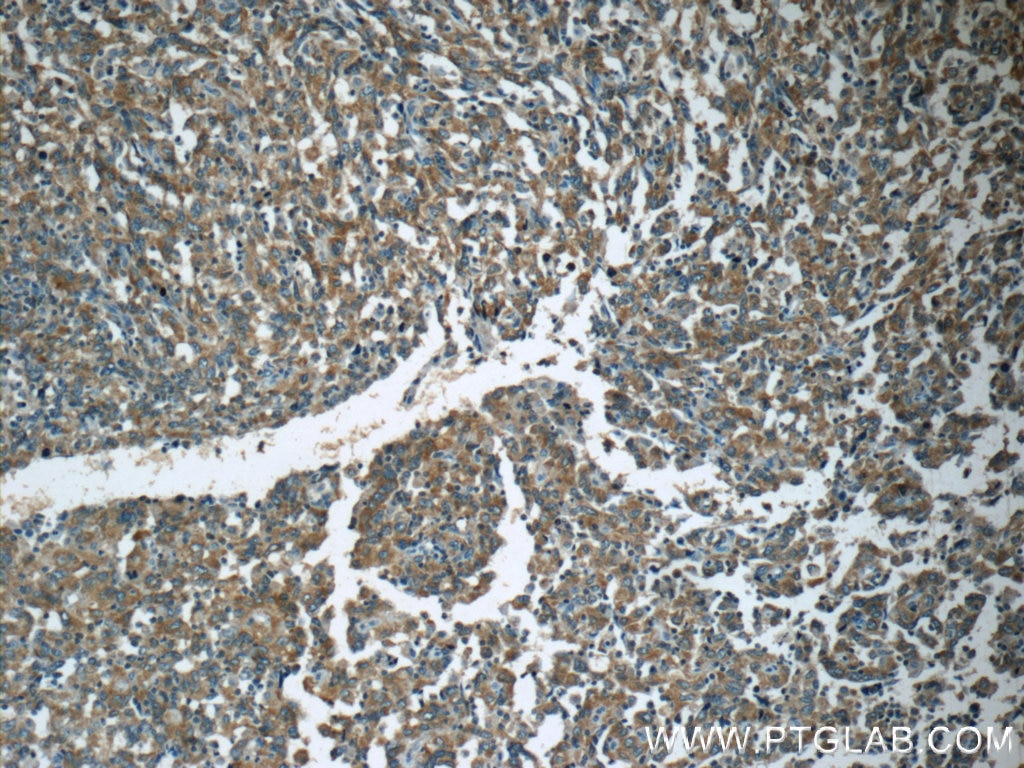
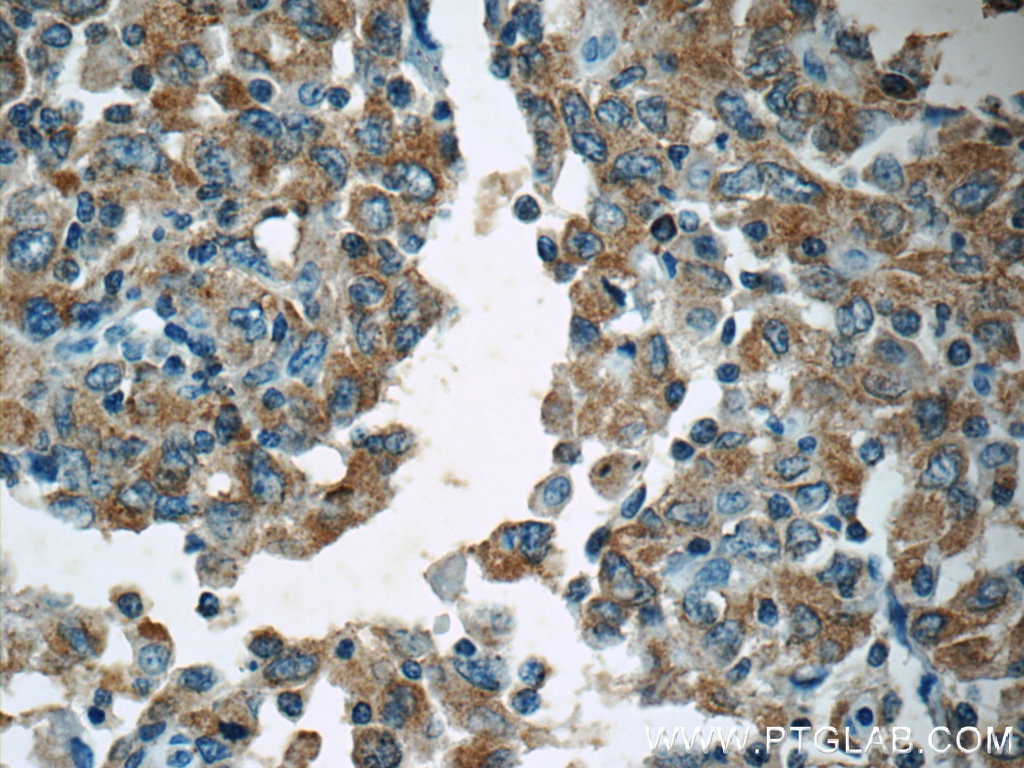
| Positive IHC detected in | human breast cancer tissue, human colon tissue, human colon cancer tissue, human endometrial cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 9 publications below |
Product Information
19782-1-AP targets APC in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
Peptide 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | adenomatous polyposis coli |
| Calculated molecular weight | 312 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_000038 |
| Gene Symbol | APC |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 324 |
| RRID | AB_2878605 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P25054 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
APC, also named as DP2.5, belongs to the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) family. APC is a tumor suppressor that regulates cell division, helps ensure that the number of chromosomes in a cell is correct following cell division, and associates with other proteins involved in cell attachment and signaling. APC promotes rapid degradation of CTNNB1 and participates in Wnt signaling as a negative regulator. It plays a critical role in several cellular processes. APC regulates beta-catenin levels through Wnt-signaling and is involved in actin cytoskeletal integrity, cell-cell adhesion and cell migration. APC activity is correlated with its phosphorylation state. Defects in APC are a cause of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) which includes also Gardner syndrome (GS). Defects in APC are a cause of hereditary desmoid disease (HDD) which also known as familial infiltrative fibromatosis (FIF). Defects in APC are a cause of medulloblastoma (MDB) which is a malignant, invasive embryonal tumor of the cerebellum with a preferential manifestation in children. Defects in APC are a cause of mismatch repair cancer syndrome (MMRCS) which also known as Turcot syndrome or brain tumor-polyposis syndrome 1 (BTPS1).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for APC antibody 19782-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Biomed Pharmacother Glycogen phosphorylase B promotes ovarian cancer progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling and is regulated by miR-133a-3p. | ||
World J Gastroenterol MiR-205 mediated APC regulation contributes to pancreatic cancer cell proliferation. | ||
Cancer Med MiR-26b suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma development by negatively regulating ZNRD1 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. | ||
J Bone Oncol BAIAP2L2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma associated with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | ||
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med Intervention Mechanism of Hunag-Lian Jie-Du Decoction on Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Psoriasis Mouse Model. |