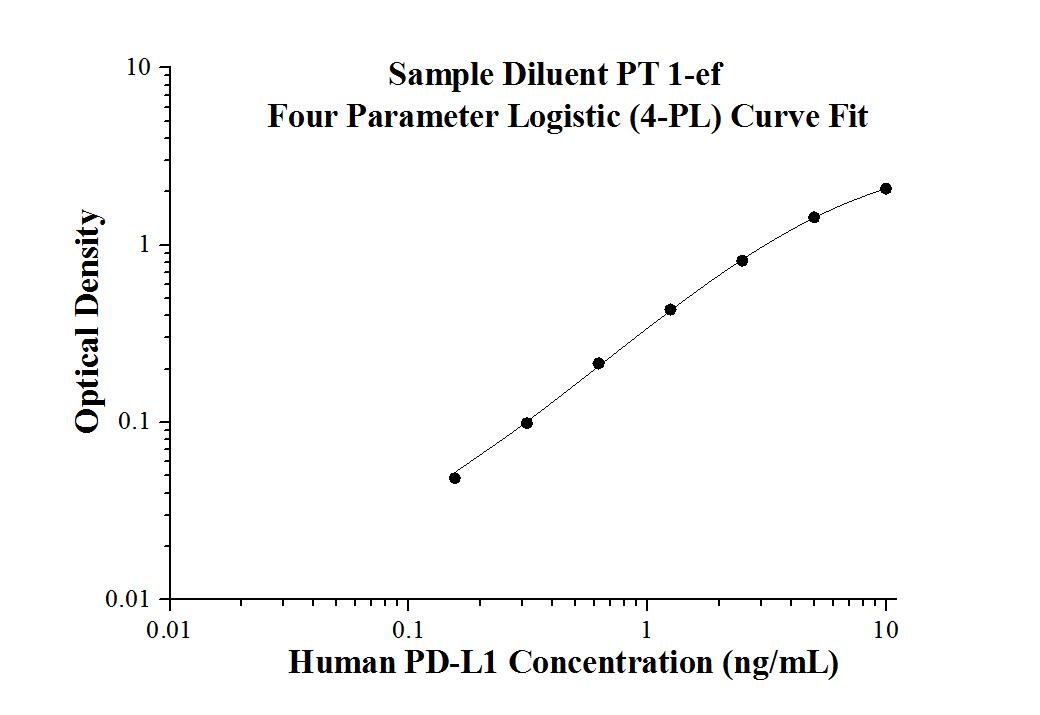
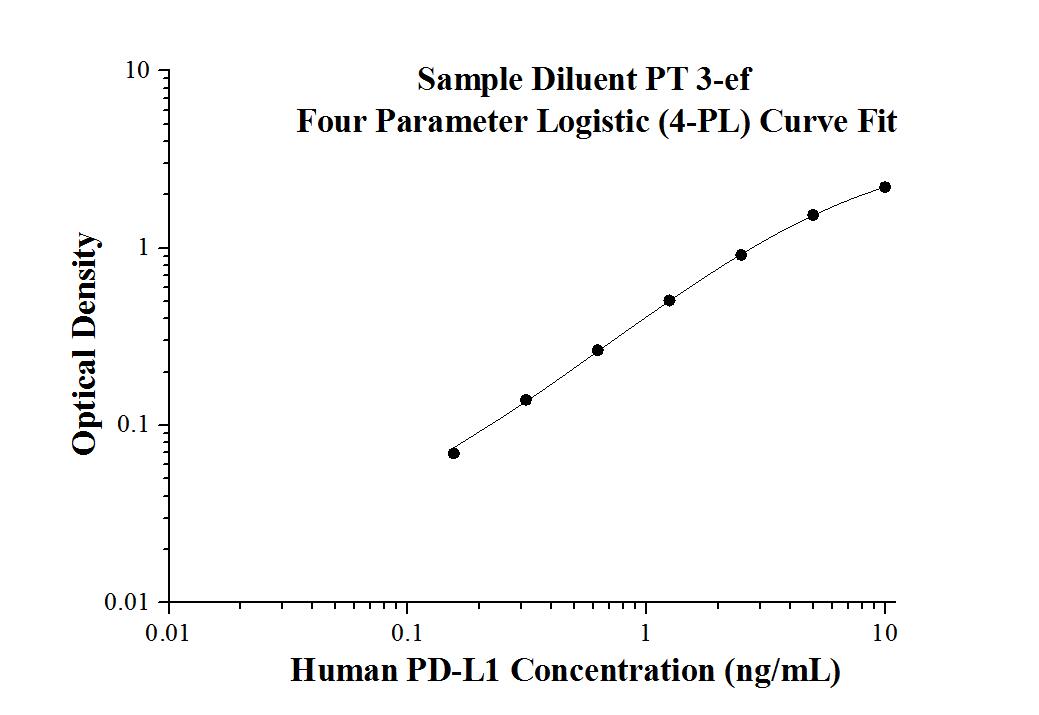
Human PD-L1 ELISA Kit
Cat no : KE00074
Synonyms
CD274, B7 H1, B7-H1, hPD-L1, PD L1
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
KE00074 is a solid phase sandwich Enzyme Linked-Immuno-Sorbent Assay (Sandwich ELISA). The PD-L1 ELISA kit is to be used to detect and quantify protein levels of endogenous PD-L1. The assay recognizes human PD-L1. An antibody specific for PD-L1 has been pre-coated onto the microwells. The PD-L1 protein in samples is captured by the coated antibody after incubation. Following extensive washing, another antibody specific for PD-L1 is added to detect the captured PD-L1 protein. For signal development, horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated antibody is added, followed by Tetramethyl-benzidine (TMB) reagent. Solution containing sulfuric acid is used to stop color development and the color intensity which is proportional to the quantity of bound protein is measurable at 450 nm with the correction wavelength set at 630 nm.
| Product name | Human PD-L1 ELISA Kit |
| Tests | 1 X 96 well plate |
| Sample type | Serum, Plasma, Cell culture supernatants, Cell lysates |
| Assay type | Sandwich |
| Sensitivity | 0.04 ng/mL |
| Range | 0.156-10 ng/mL |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Tested applications | Sandwich ELISA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 29126 |
Recovery
| Sample Type | Average | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Human plasma | 94% | 74%-125% |
| Cell culture supernatants | 105% | 87%-127% |
| Cell lysates | 100% | 74%-126% |
IntraAssay
| Sample | n | mean ( ng/mL) | SD | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | 8.26 | 0.64 | 7.8 |
| 2 | 20 | 2.02 | 0.14 | 6.8 |
| 3 | 20 | 0.49 | 0.02 | 4.6 |
InterAssay
| Sample | n | mean ( ng/mL) | SD | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24 | 7.43 | 0.38 | 5.1 |
| 2 | 24 | 1.90 | 0.12 | 6.1 |
| 3 | 24 | 0.47 | 0.03 | 7.0 |
Background Information
PD-L1 (programmed cell death ligand 1, also known as CD274 or B7-H1) is a 290 aa type I transmembrane protein. PD-L1 is expressed constitutively on T cells, B cells, DCs, macrophages, mesenchymal stem cells and cultured bone marrow-derived mast cells. In addition, PD-L1 is also expressed on many nonhematopoietic cell types, including vascular endothelial cells, epithelial cells, muscle cells, hepatocytes, pancreatic islet cells, astrocytes in the brain, placental syncytiotrophoblasts, and cells in cornea, iris-ciliary body and retina of eye. PD-L1 is frequently upregulated in a wide variety of solid tumors, including melanoma, ovarian, lung, glioblastoma, breast, and pancreatic cancers. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are two ligands of PD-1. Engagement of PD-1 by PD-L1 or PD-L2 transduces a signal that inhibits T-cell proliferation, cytokine production, and cytolytic function. It is critical for the regulation of T cell function during tolerance, autoimmunity and infection. Besides the membrane-bound form, PD-L1 can also exist as a soluble form (sPD-L1) generated either by proteolytic cleavage of membrane-bound form or by translation of alternative spliced mRNA.
Properties
| Storage Instructions | All the reagents are stored at 2-8℃ for 6 months or -20℃ for 12 months. Refer to the protocol for further storage instructions. |
| Synonyms | CD274, B7 H1, B7-H1, hPD-L1, PD L1 |
Publications
| Species | Sample Type | Title |
|---|---|---|
Crit Care Lymphocyte subset expression and serum concentrations of PD-1/PD-L1 in sepsis - pilot study. | ||
Lung Cancer Chemotherapy-induced PDL-1 expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes chemoresistance in NSCLC | ||
Microorganisms Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1 Induces Soluble PD-L1 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. | ||
Clin Exp Immunol CMTM6: increased circulating level and up-regulated expression in labial salivary glands in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. | ||
Invest New Drugs A novel bivalent anti-c-MET/PD-1 bispecific antibody exhibits potent cytotoxicity against c-MET/PD-L1-positive colorectal cancer | ||
Exp Ther Med Role of soluble programmed death-1 (sPD-1) and sPD-ligand 1 in patients with cystic echinococcosis. |