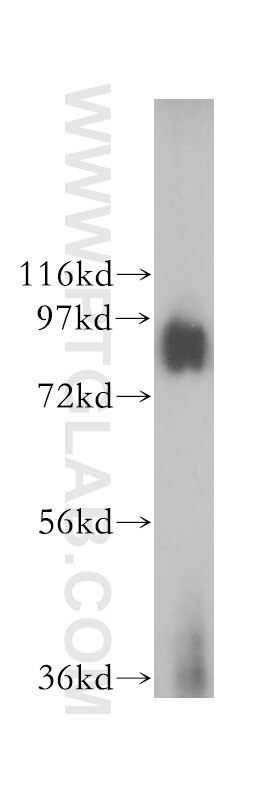
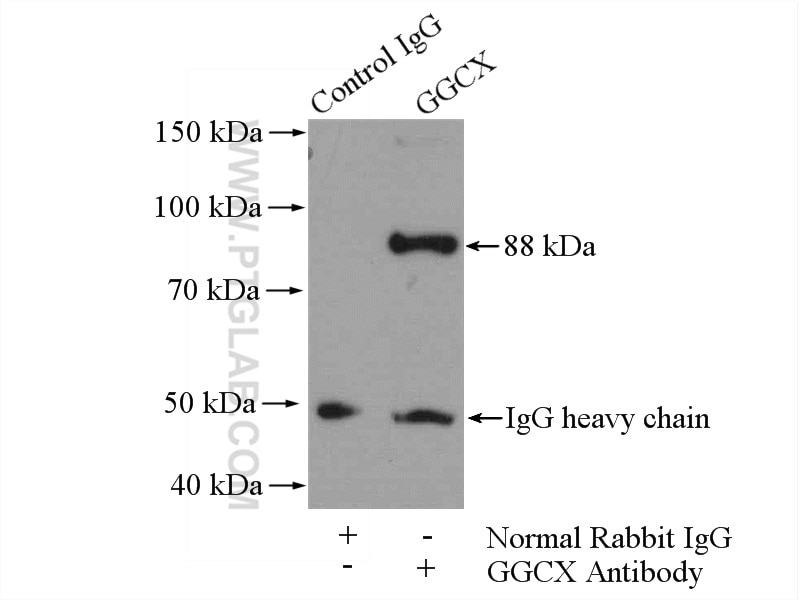
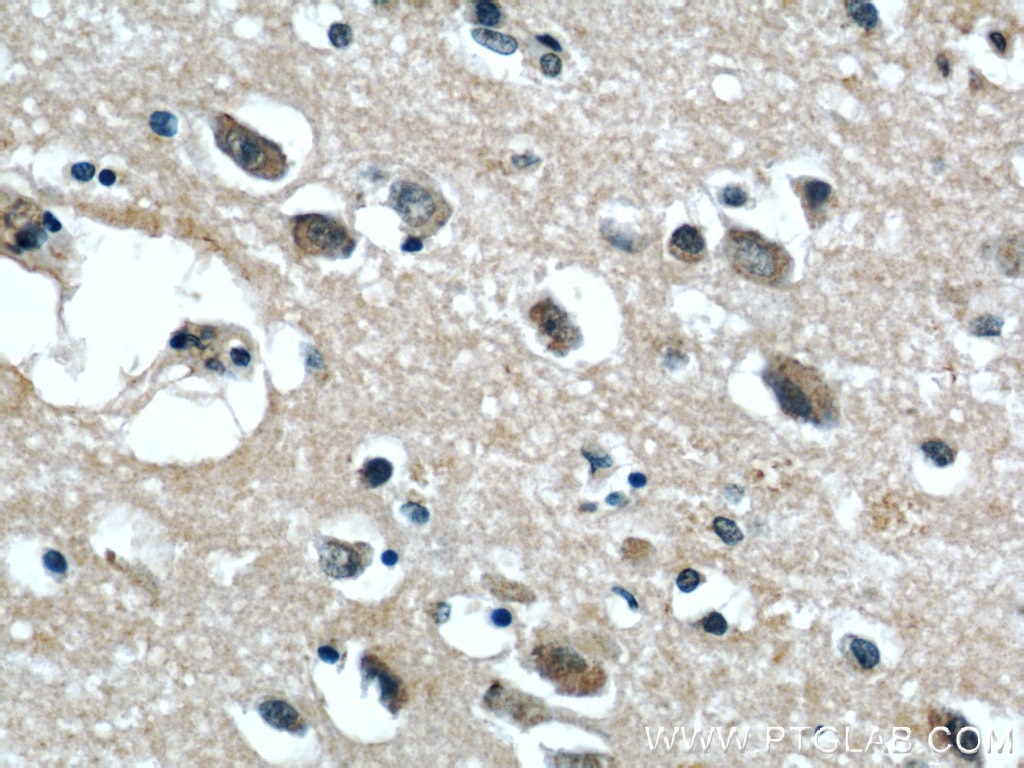
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | MCF7 cells, HEK-293 cells, HepG2 cells, L02 cells, MCF-7 cells, mouse liver tissue, PC-3 cells |
| Positive IP detected in | mouse liver tissue |
| Positive IHC detected in | human liver tissue, human brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:4000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
16209-1-AP targets GGCX in WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, pig |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag9185 Product name: Recombinant human GGCX protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 383-758 aa of BC013979 Sequence: LTQGYNNWTNGLYGYSWDMMVHSRSHQHVKITYRDGRTGELGYLNPGVFTQSRRWKDHADMLKQYATCLSRLLPKYNVTEPQIYFDIWVSINDRFQQRIFDPRVDIVQAAWSPFQRTSWVQPLLMDLSPWRAKLQEIKSSLDNHTEVVFIADFPGLHLENFVSEDLGNTSIQLLQGEVTVELVAEQKNQTLREGEKMQLPAGEYHKVYTTSPSPSCYMYVYVNTTELALEQDLAYLQELKEKVENGSETGPLPPELQPLLEGEVKGGPEPTPLVQTFLRRQQRLQEIERRRNTPFHERFFRFLLRKLYVFRRSFLMTCISLRNLILGRPSLEQLAQEVTYANLRPFEAVGELNPSNTDSSHSNPPESNPDPVHSEF 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | gamma-glutamyl carboxylase |
| Calculated molecular weight | 758 aa, 88 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 88 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC013979 |
| Gene Symbol | GGCX |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2677 |
| RRID | AB_2110874 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P38435 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
GGCX(Gamma-glutamyl carboxylase) is also named as GC and belongs to the vitamin K-dependent gamma-carboxylase family. This 94 kDa (including all modifications, such as the five N-linked glycosylations), is a 5-pass transmembrane protein and a key regulator of blood coagulation(PMID:20518534). It mediates the vitamin K-dependent carboxylation of glutamate residues to calcium-binding gamma-carboxyglutamate (Gla) residues with the concomitant conversion of the reduced hydroquinone form of vitamin K to vitamin K epoxide. Defects in GGCX are a cause of combined deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors type 1 (VKCFD1) and pseudoxanthoma elasticum-like disorder with multiple coagulation factor deficiency (PXEL-MCFD)(PMID:9845520;17110937).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for GGCX antibody 16209-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for GGCX antibody 16209-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for GGCX antibody 16209-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Blood Characterization of vitamin K-dependent carboxylase mutations that cause bleeding and nonbleeding disorders. | ||
Methods Enzymol Functional Study of the Vitamin K Cycle Enzymes in Live Cells.
| ||
JCI Insight VKOR paralog VKORC1L1 supports vitamin K-dependent protein carboxylation in vivo. | ||
Nat Commun GGCX promotes Eurasian avian-like H1N1 swine influenza virus adaption to interspecies receptor binding
| ||
Curr Issues Mol Biol The GgcxK325Q Mutation Does Not Affect the Calcium Homeostasis of the Epididymis and Male Fertility in Mice |