Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
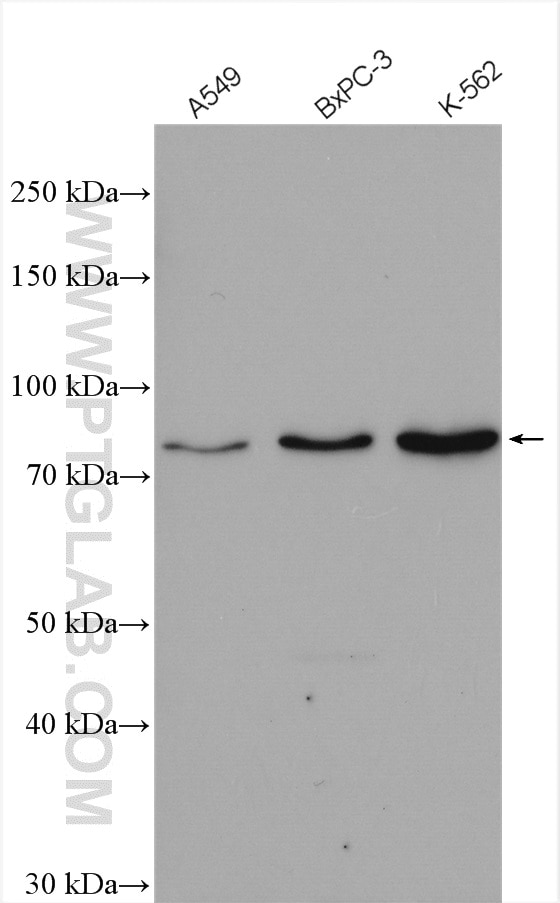
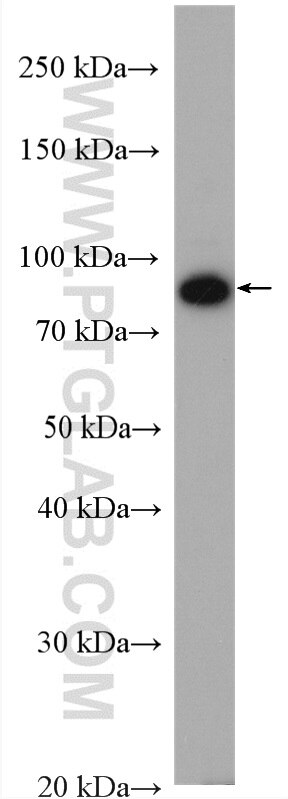
| Positive WB detected in | A549 cells, BxPC-3 cells, K-562 cells |
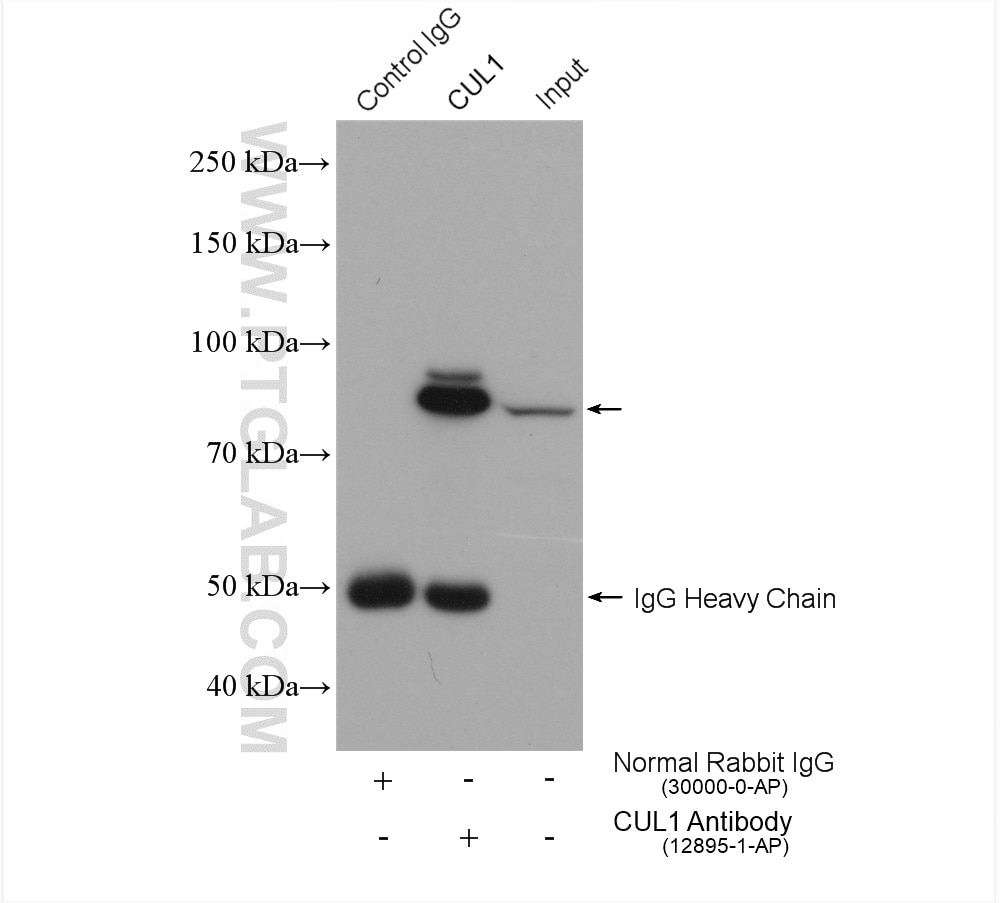
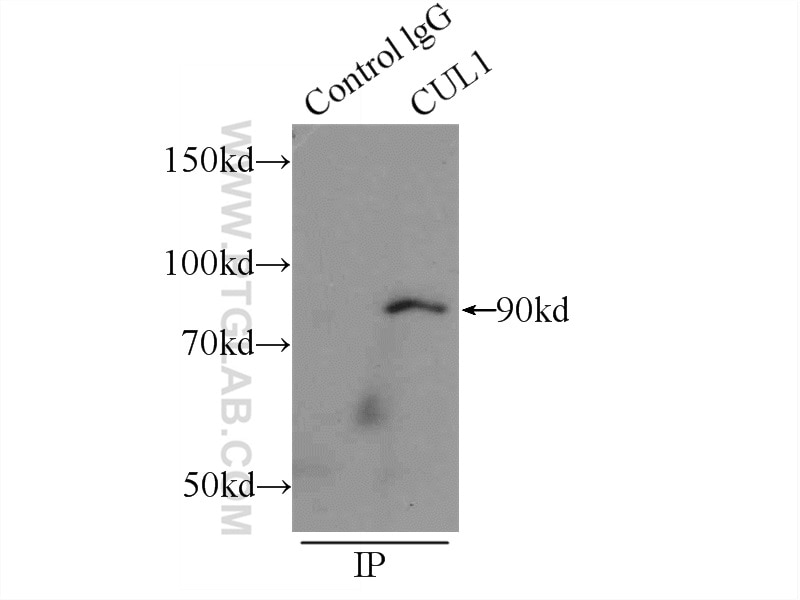
| Positive IP detected in | K-562 cells, HeLa cells |
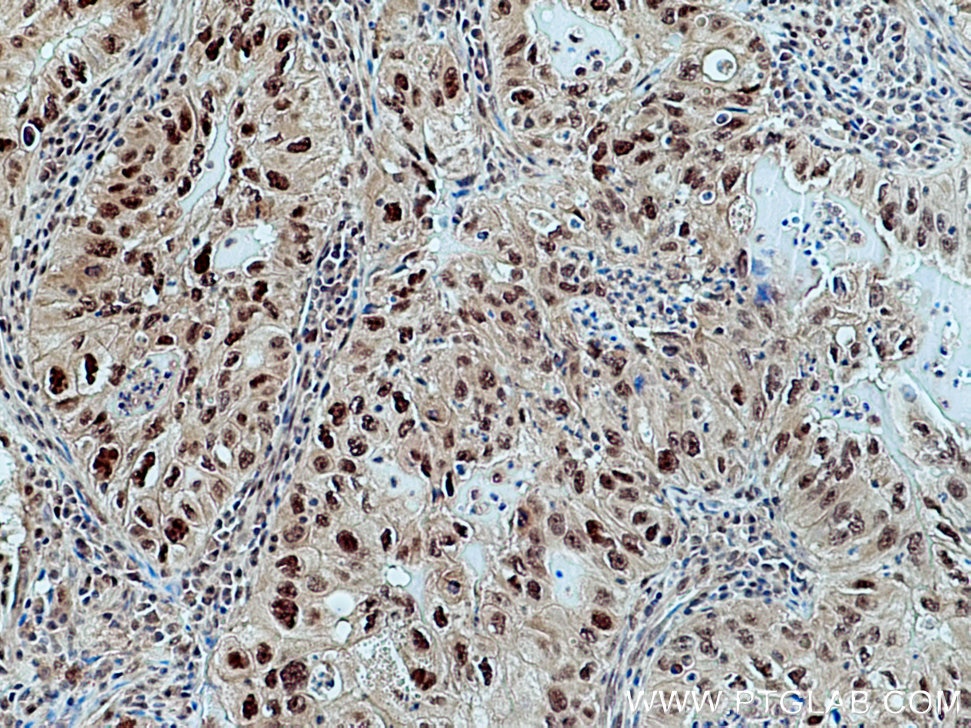
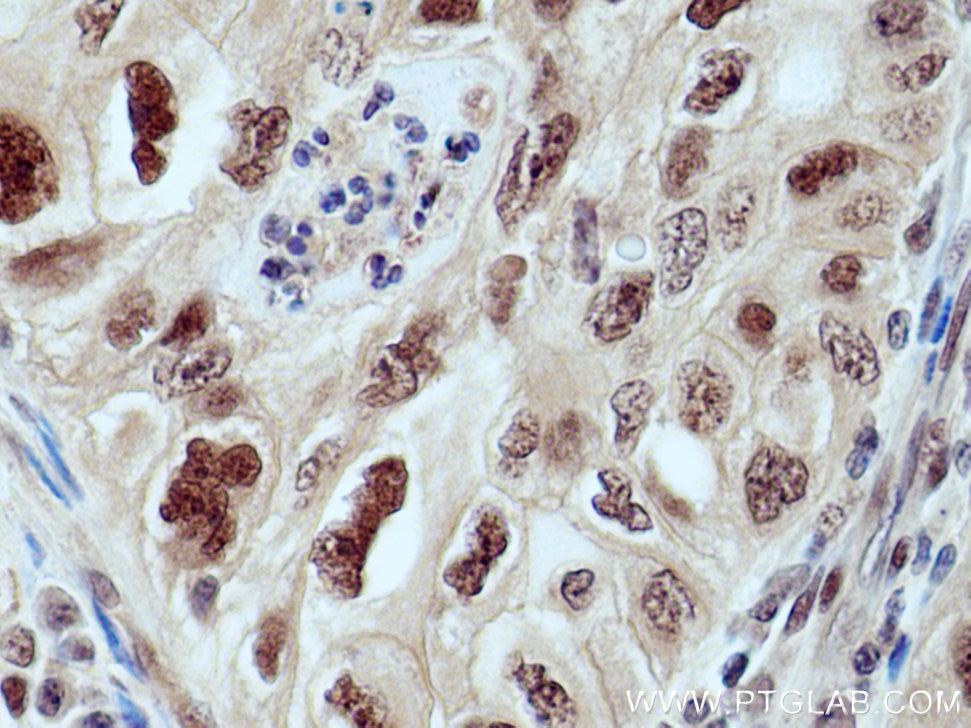
| Positive IHC detected in | human lung cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
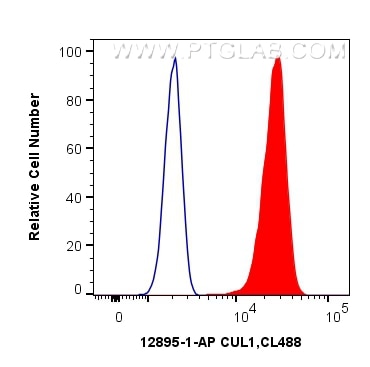
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.40 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 24 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
12895-1-AP targets CUL1 in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag3585 Product name: Recombinant human CUL1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 111-462 aa of BC034318 Sequence: YCDSLLKKSSKNPEEAELEDTLNQVMVVFKYIEDKDVFQKFYAKMLAKRLVHQNSASDDAEASMISKLKQACGFEYTSKLQRMFQDIGVSKDLNEQFKKHLTNSEPLDLDFSIQVLSSGSWPFQQFCTFALPSELERSYQRFTAFYASRHSGRKLTWLYQLSKGELVTNCFKNRYTLQASTFQMAILLQYNTEDAYTVQQLTDSTQIKMDILAQVLQILLKSKLLVLEDENANVDEVELKPDTLIKLYLGYKNKKLRVNINVPMKTEQKQEQETTHKNIEEDRKLLIQAAIVRIMKMRKVLKHQQLLGEVLTQLSSRFKPRVPVIKKCIDILIEKEYLERVDGEKDTYSYLA 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | cullin 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 90 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 80-90 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC034318 |
| Gene Symbol | CUL1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8454 |
| RRID | AB_2086291 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q13616 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
The cullin family proteins are scaffold proteins for the Ring finger type E3 ligases. Humans express seven cullin proeins: CUL1-3, CUL4A, CUL4B, CUL5, and CUL7. Each cullin protein can form an E3 ligase similar to the prototype Ring-type E3 ligase Skp1-CUL1-F-box complex. The Cullin-RING-finger type E3 ligases are important regulators in early embryonic development, as highlighted by genetic studies demonstrating that knock-out of CUL1, CUL3, or CUL4A in mice results in early embryonic lethality.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for CUL1 antibody 12895-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for CUL1 antibody 12895-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for CUL1 antibody 12895-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Chem Biol E2-Ub-R74G strategy reveals E2-specific ubiquitin conjugation profiles in live cells | ||
Redox Biol Cardioprotective effect of MLN4924 on ameliorating autophagic flux impairment in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by Sirt1. | ||
Front Bioeng Biotechnol Let-7i-5p Regulation of Cell Morphology and Migration Through Distinct Signaling Pathways in Normal and Pathogenic Urethral Fibroblasts. | ||
Pharmacol Res Cullin-associated and neddylation-dissociated 1 protein (CAND1) governs cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure partially through regulating calcineurin degradation. | ||
J Cell Sci Cullin-3-KCTD10-mediated CEP97 degradation promotes primary cilium formation.
|