Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
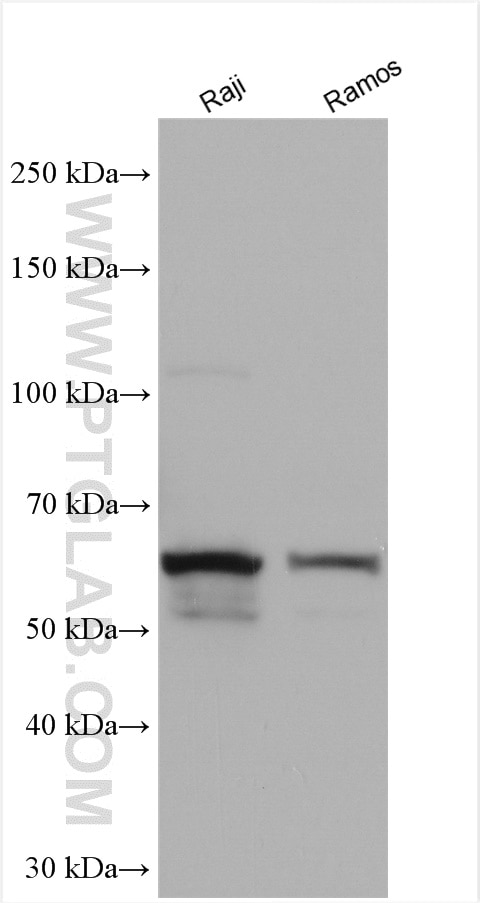
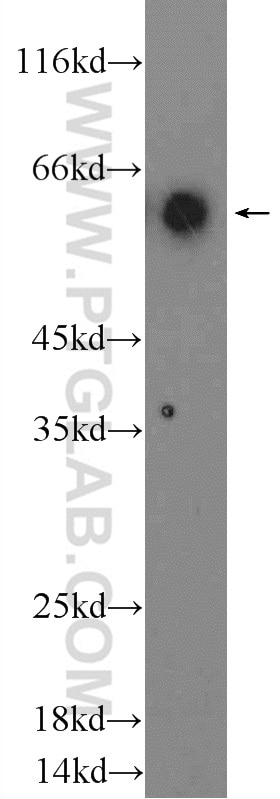
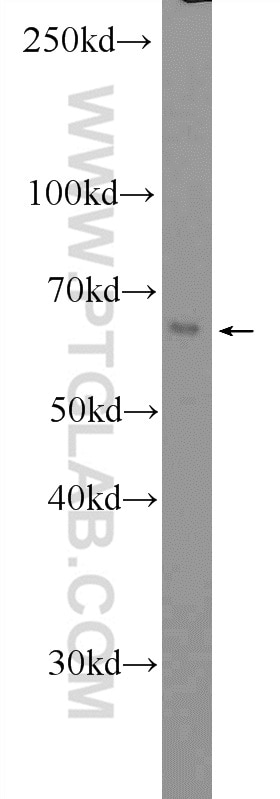
| Positive WB detected in | Raji cells, RAW 264.7 cells, human peripheral blood leukocyte, Ramos cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 12 publications below |
Product Information
14292-1-AP targets CD80 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag5615 Product name: Recombinant human B7-1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 36-228 aa of BC042665 Sequence: IHVTKEVKEVATLSCGHNVSVEELAQTRIYWQKEKKMVLTMMSGDMNIWPEYKNRTIFDITNNLSIVILALRPSDEGTYECVVLKYEKDAFKREHLAEVTLSVKADFPTPSISDFEIPTSNIRRIICSTSGGFPEPHLSWLENGEELNAINTTVSQDPETELYAVSSKLDFNMTTNHSFMCLIKYGHLRVNQT 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | CD80 molecule |
| Calculated molecular weight | 33 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 60 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC042665 |
| Gene Symbol | CD80 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 941 |
| RRID | AB_10640809 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P33681 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
CD80 (also known as B7-1) is a type I membrane protein that is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, with an extracellular immunoglobulin constant-like domain and a variable-like domain required for receptor binding. It is expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs), including B cells, dendritic cells, monocytes, and macrophages. CD80 is the receptor for the proteins CD28 and CTLA-4 found on the surface of T-cells. It is involved in the costimulatory signal essential for T-lymphocyte activation. T-cell proliferation and cytokine production is induced by the binding of CD28, binding to CTLA-4 has opposite effects and inhibits T-cell activation. CD80 also acts as a cellular attachment receptor for adenovirus subgroup B. (PMID: 7545666; 12015893; 16920215)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CD80 antibody 14292-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
ACS Nano Antigen Self-Presented Personalized Nanovaccines Boost the Immunotherapy of Highly Invasive and Metastatic Tumors | ||
ACS Appl Mater Interfaces Fe(III)-Chelated Polydopamine Nanoparticles for Synergistic Tumor Therapies of Enhanced Photothermal Ablation and Antitumor Immune Activation. | ||
Biomaterials Light-controlled oxygen production and collection for sustainable photodynamic therapy in tumor hypoxia. | ||
Bioact Mater Photosynthetic microorganisms coupled photodynamic therapy for enhanced antitumor immune effect. | ||
Int J Nanomedicine Self-Assembly Catalase Nanocomplex Conveyed by Bacterial Vesicles for Oxygenated Photodynamic Therapy and Tumor Immunotherapy. | ||
J Nanobiotechnology Continuous ZnO nanoparticle exposure induces melanoma-like skin lesions in epidermal barrier dysfunction model mice through anti-apoptotic effects mediated by the oxidative stress-activated NF-κB pathway. |