Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
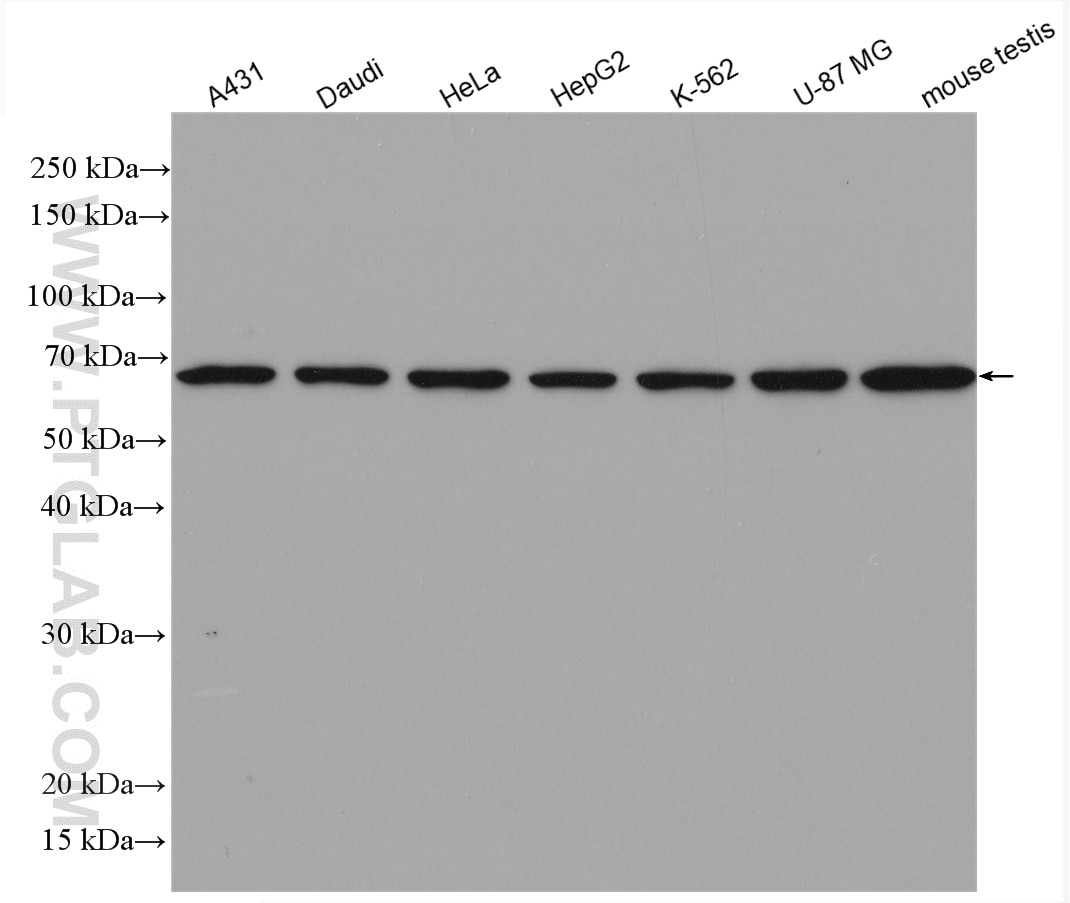
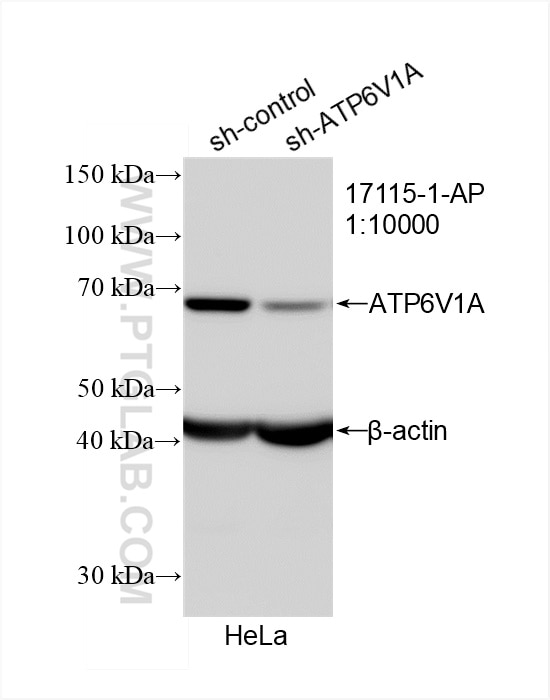
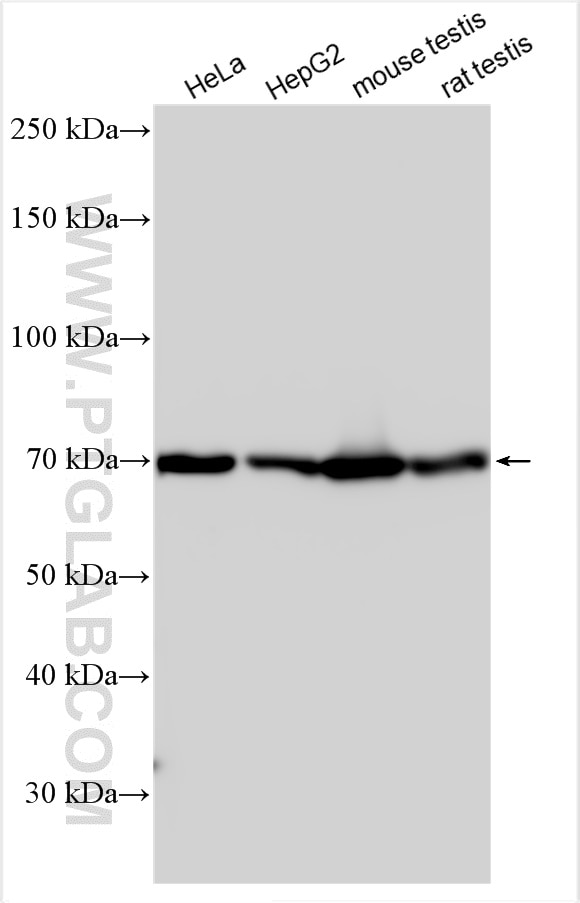
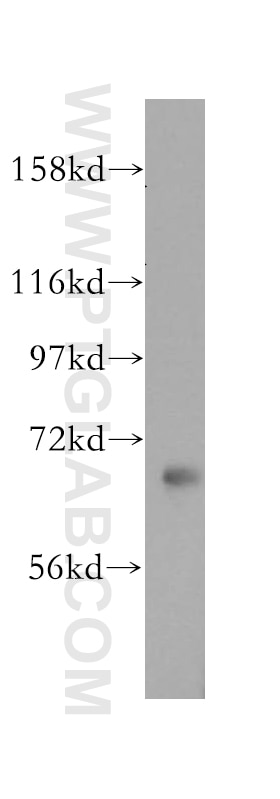
| Positive WB detected in | A431 cells, human placenta tissue, mouse kidney tissue, HeLa cells, Daudi cells, HepG2 cells, K-562 cells, U-87 MG cells, mouse testis tissue, rat testis tissue |
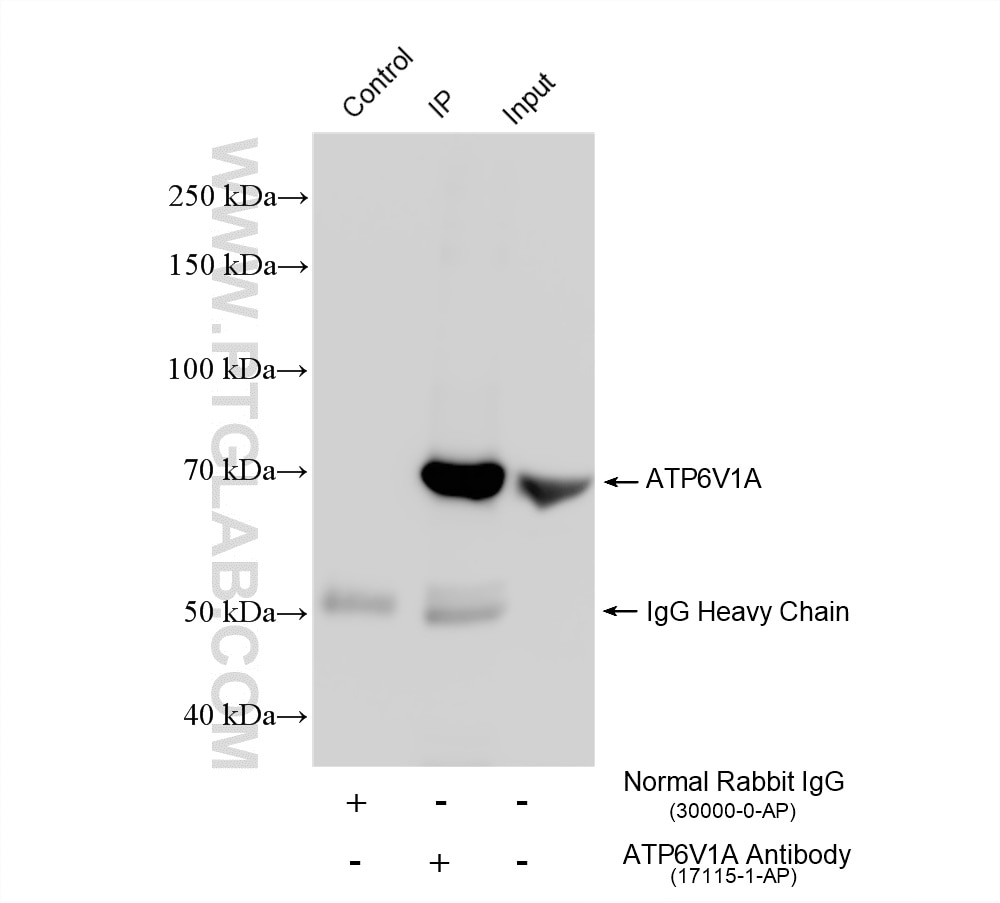
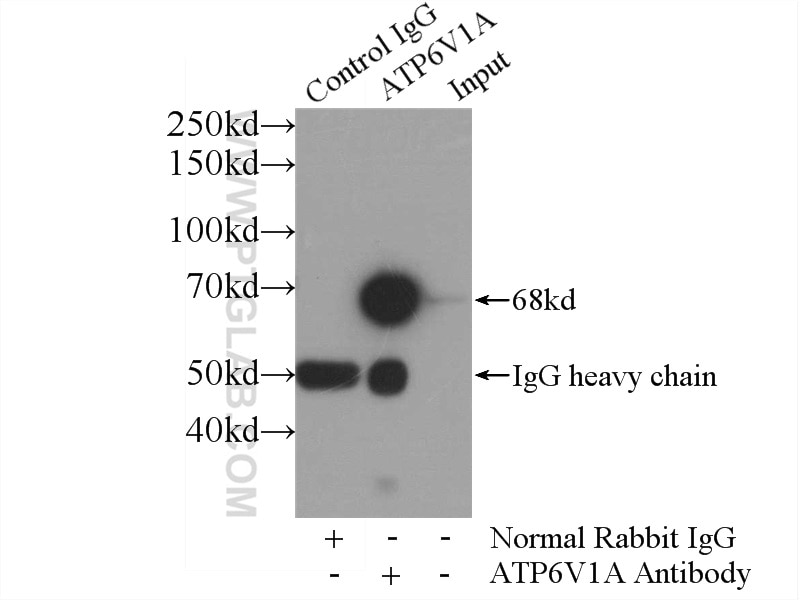
| Positive IP detected in | HeLa cells, RAW 264.7 cells |
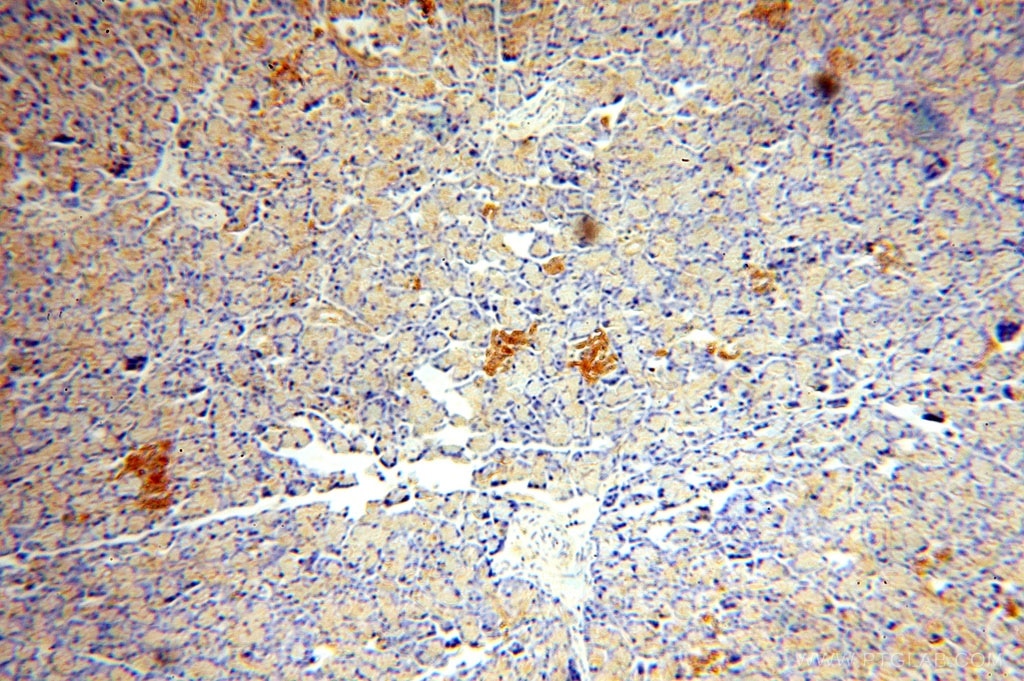
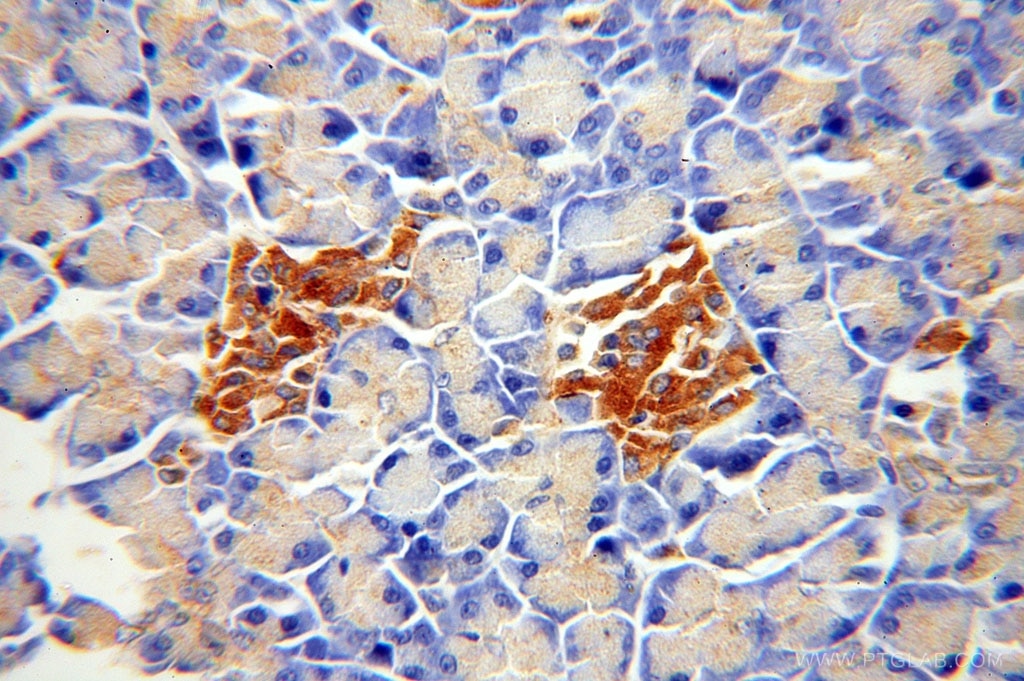
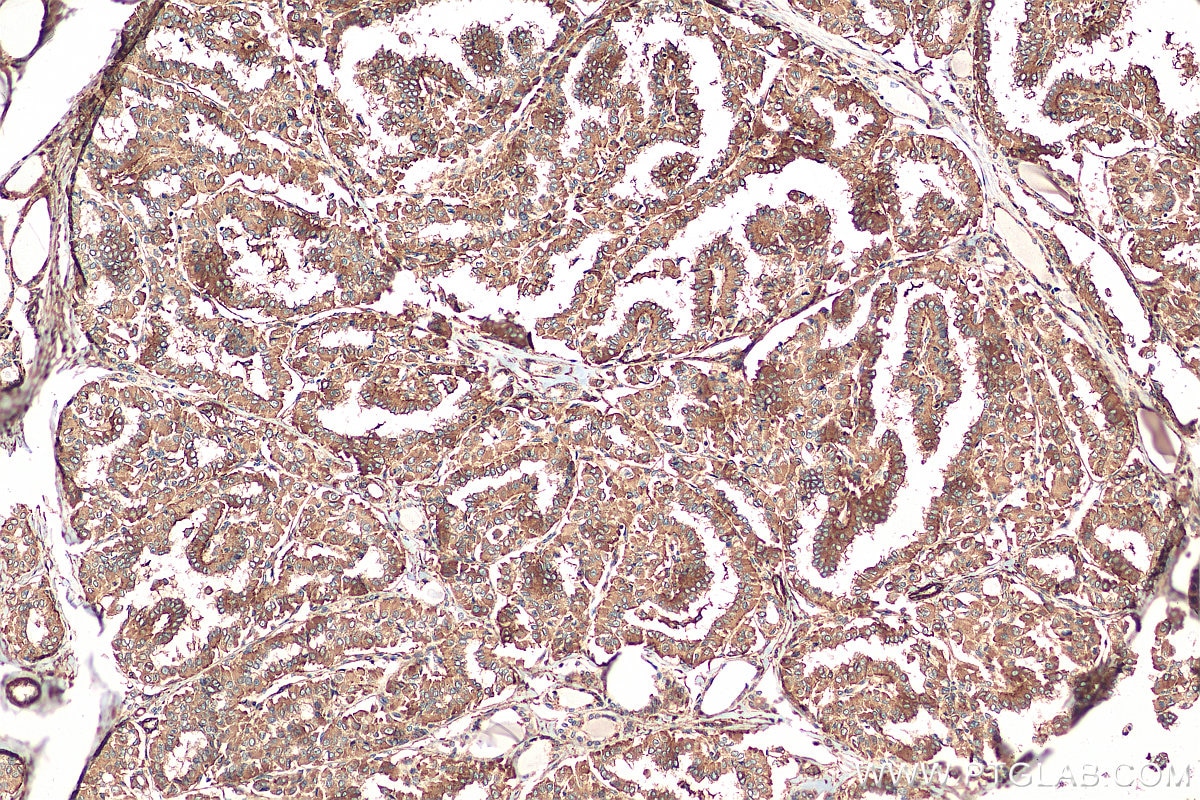
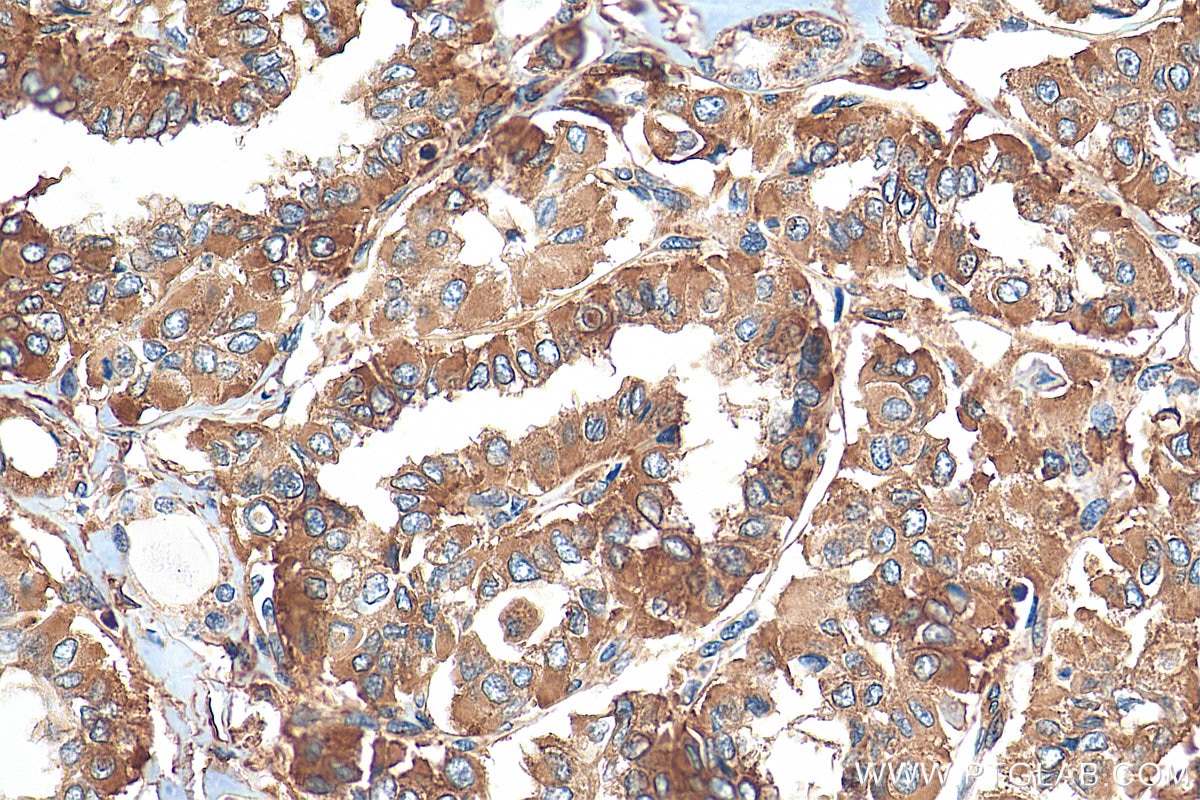
| Positive IHC detected in | human pancreas tissue, human thyroid cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
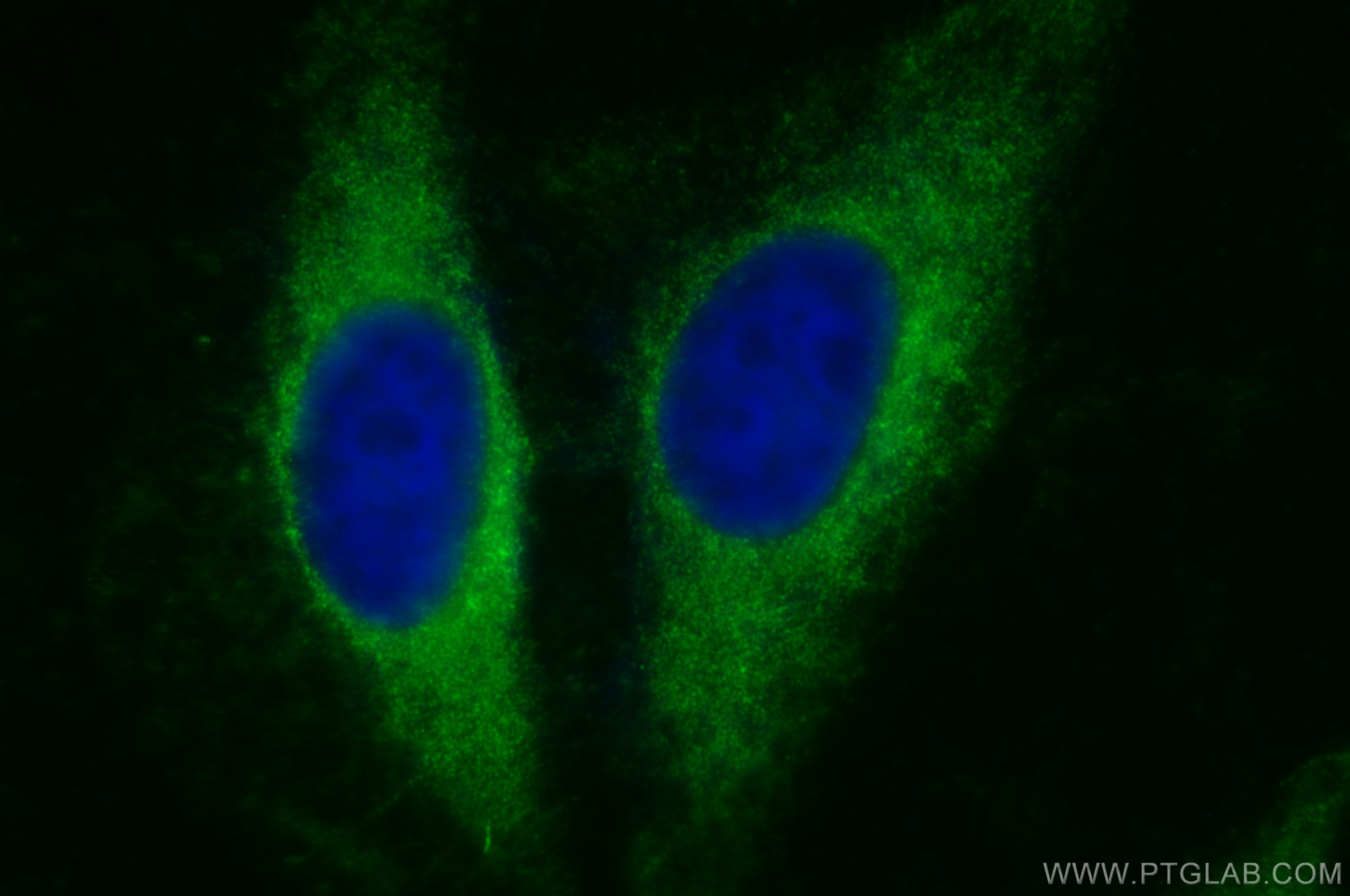
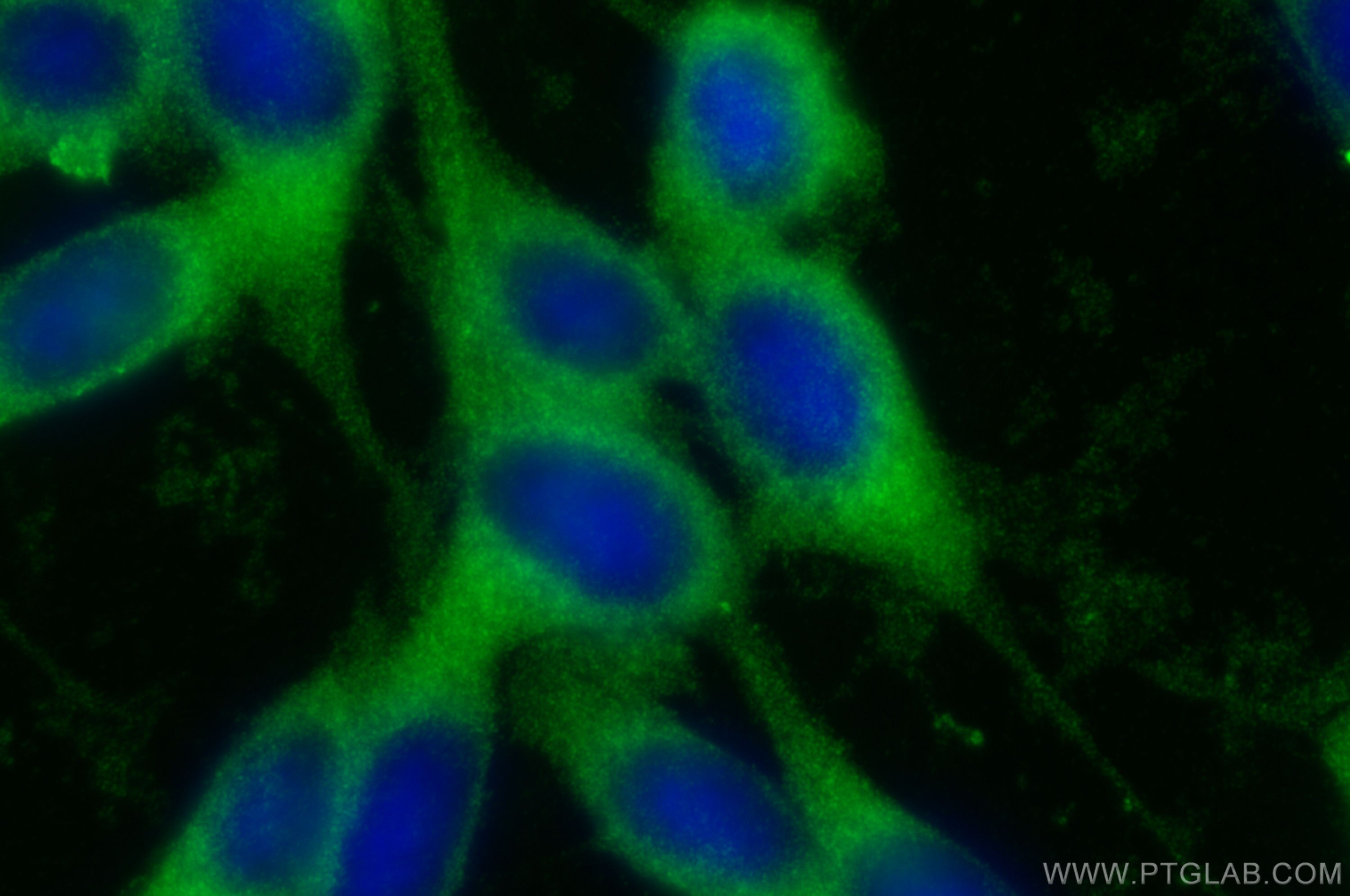
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | NIH/3T3 cells, HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:16000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 33 publications below |
| IHC | See 2 publications below |
| IF | See 14 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
17115-1-AP targets ATP6V1A in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig, monkey, zebrafish |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag10801 Product name: Recombinant human ATP6V1A protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 268-617 aa of BC013138 Sequence: NSDVIIYVGCGERGNEMSEVLRDFPELTMEVDGKVESIMKRTALVANTSNMPVAAREASIYTGITLSEYFRDMGYHVSMMADSTSRWAEALREISGRLAEMPADSGYPAYLGARLASFYERAGRVKCLGNPEREGSVSIVGAVSPPGGDFSDPVTSATLGIVQVFWGLDKKLAQRKHFPSVNWLISYSKYMRALDEYYDKHFTEFVPLRTKAKEILQEEEDLAEIVQLVGKASLAETDKITLEVAKLIKDDFLQQNGYTPYDRFCPFYKTVGMLSNMIAFYDMARRAVETTAQSDNKITWSIIREHMGDILYKLSSMKFKDPLKDGEAKIKSDYAQLLEDMQNAFRSLED 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 70kDa, V1 subunit A |
| Calculated molecular weight | 617 aa, 68 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 68 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC013138 |
| Gene Symbol | ATP6V1A |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 523 |
| RRID | AB_2290195 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P38606 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
The vacuolar-type H(+)-ATPase (V-ATPase) is responsible for the acidification of endosomes, lysosomes, and other intracellular organelles. It is also involved in hydrogen ion transport across the plasma membrane into the extracellular space. The V-ATPase is a multisubunit complex with cytosolic and transmembrane domains. The cytosolic catalytic domain consists of 3 A subunits and 3 B subunits, which bind and hydrolyze ATP, as well as regulatory accessory subunits.ATP6V1A is V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for ATP6V1A antibody 17115-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for ATP6V1A antibody 17115-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for ATP6V1A antibody 17115-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for ATP6V1A antibody 17115-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Immunol Heme drives hemolysis-induced susceptibility to infection via disruption of phagocyte functions. | ||
Nat Microbiol The interferon-inducible isoform of NCOA7 inhibits endosome-mediated viral entry. | ||
Autophagy Follicular lymphoma-associated mutations in the V-ATPase chaperone VMA21 activate autophagy creating a targetable dependency | ||
Mol Psychiatry Sphingomyelin-induced inhibition of the plasma membrane calcium ATPase causes neurodegeneration in type A Niemann-Pick disease. | ||